instability
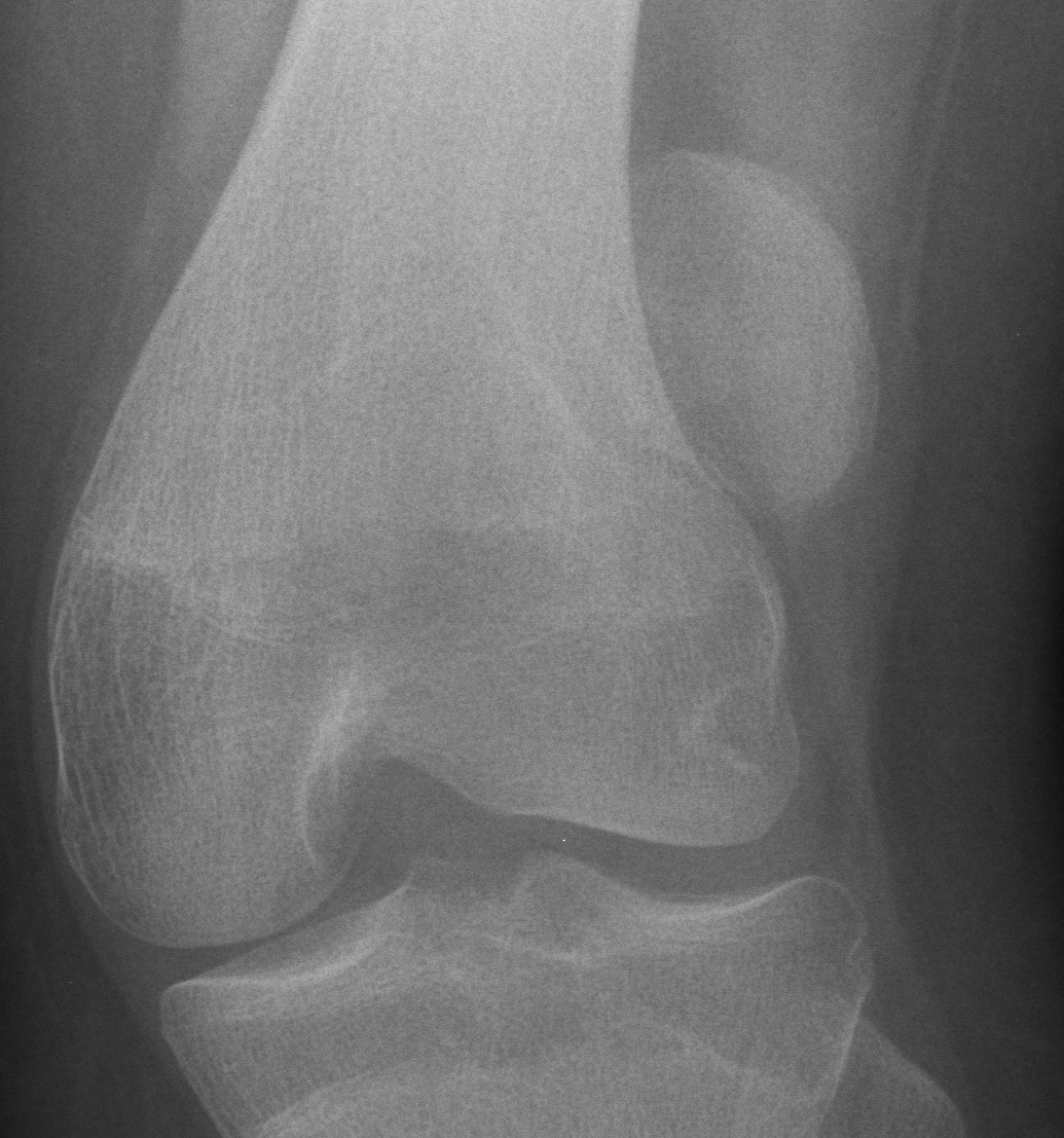
Lateral Compression
LC-1: pubic rami fracture with sacral fracture
Complications
Complications
Subscapularis failure
Rotator cuff failure
Instability
Infection
Periprosthetic fracture
Aseptic loosening
Neurological injury
Incidence
Parada et al. J Should Elbow Surg 2021
- 2224 aTSA complication rate 11%, revision rate 5.6%
Atlas / C1 Fractures
3 types
1. Posterior Arch
Mechanism
- axial compression with hyperextension
Associations
- 50% incidence other C1/2 fracture
- i.e. ondontoid fracture
Management
- stable
- soft / philadelphia collar
2. Isolated lateral mass fracture
Mechanism
- asymmetrical axial compression / lateral bend
Complications
General
- haemarthrosis
- DVT
- infection
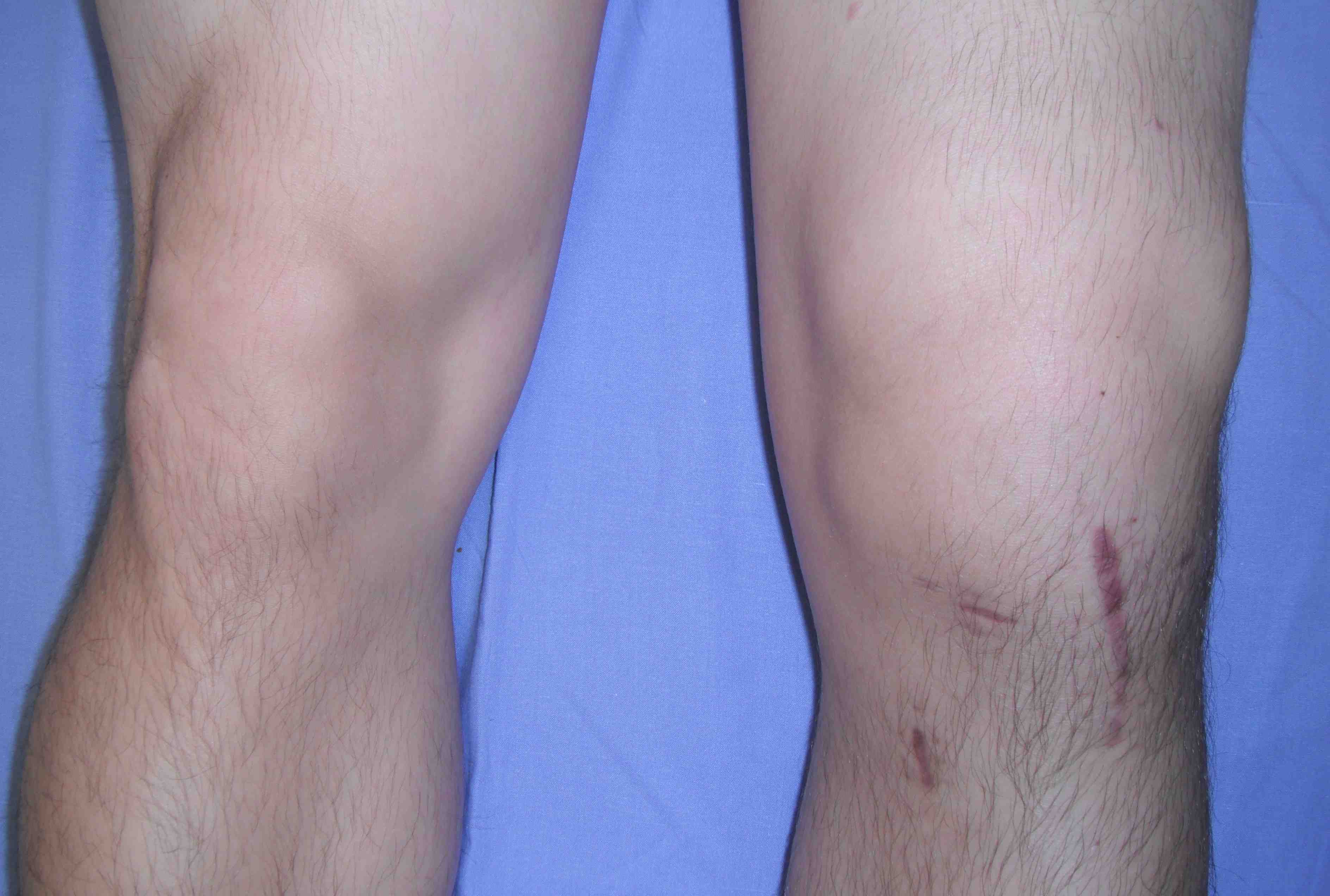
Septic Arthritis
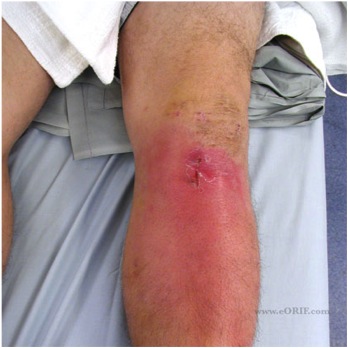
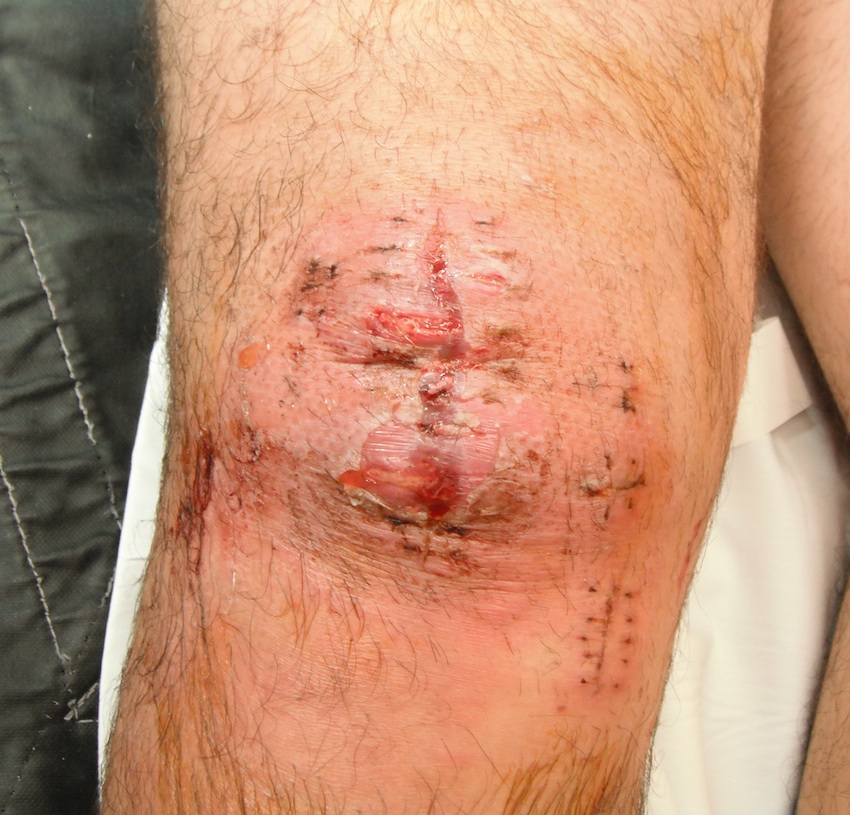
Incidence
Complications
1. Infection
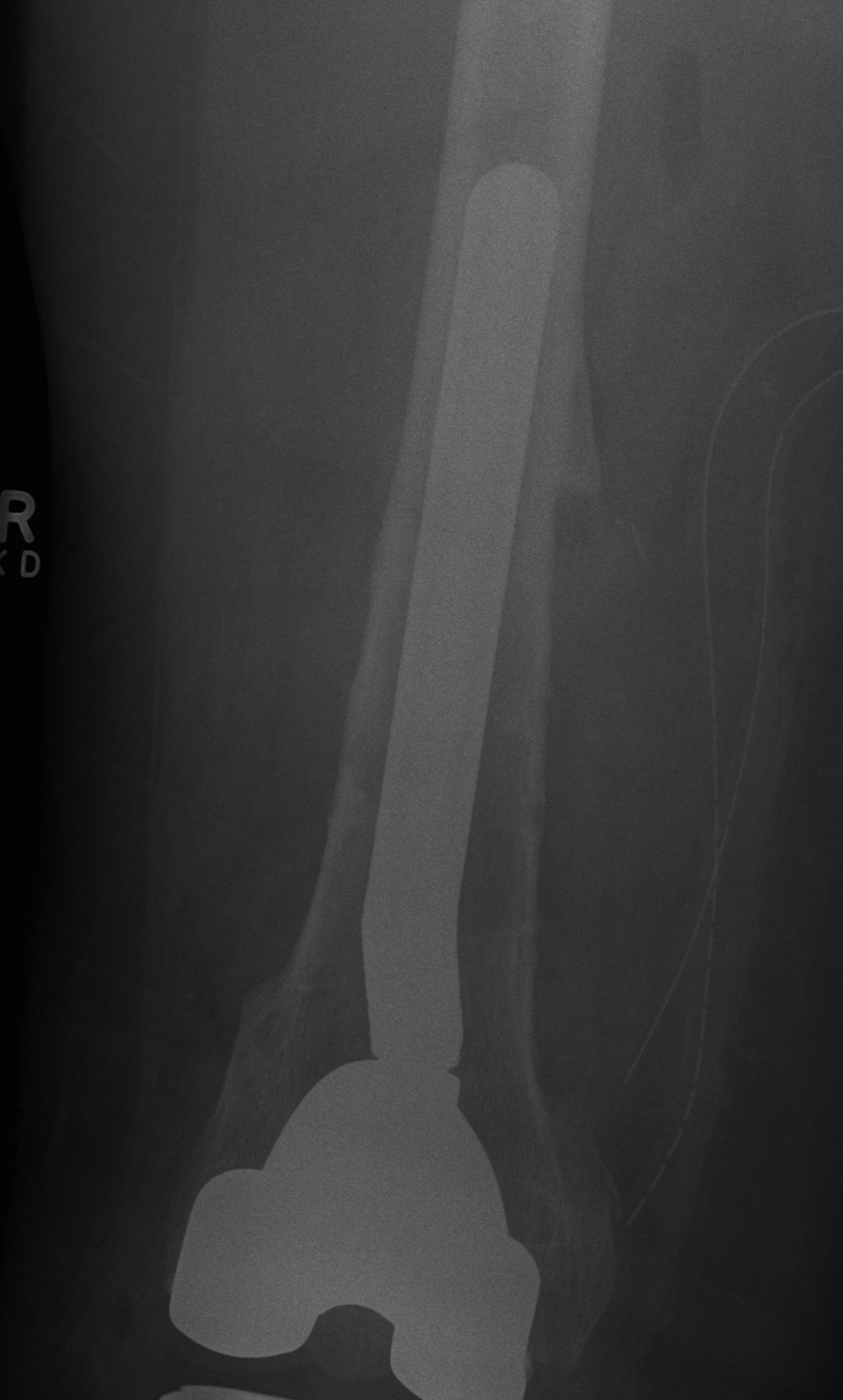
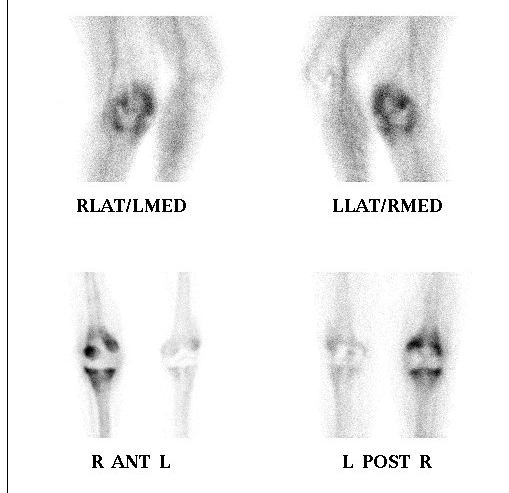
Peters et al J Arthroplasty 2009
Instability
Types of Instability
1. AP Instability
2. Varus Valgus Instability
3. Global Instability
4. Frank Dislocation
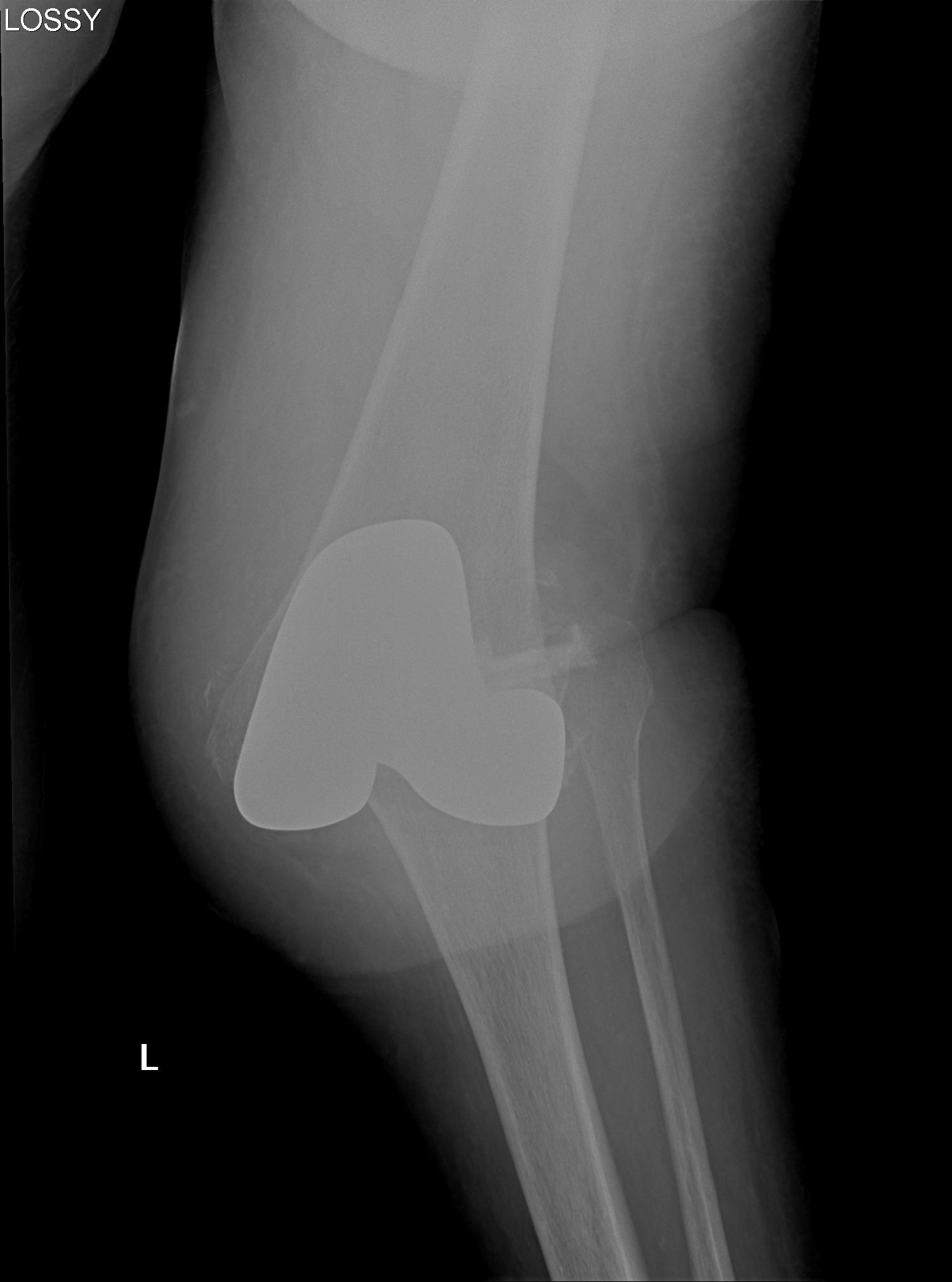
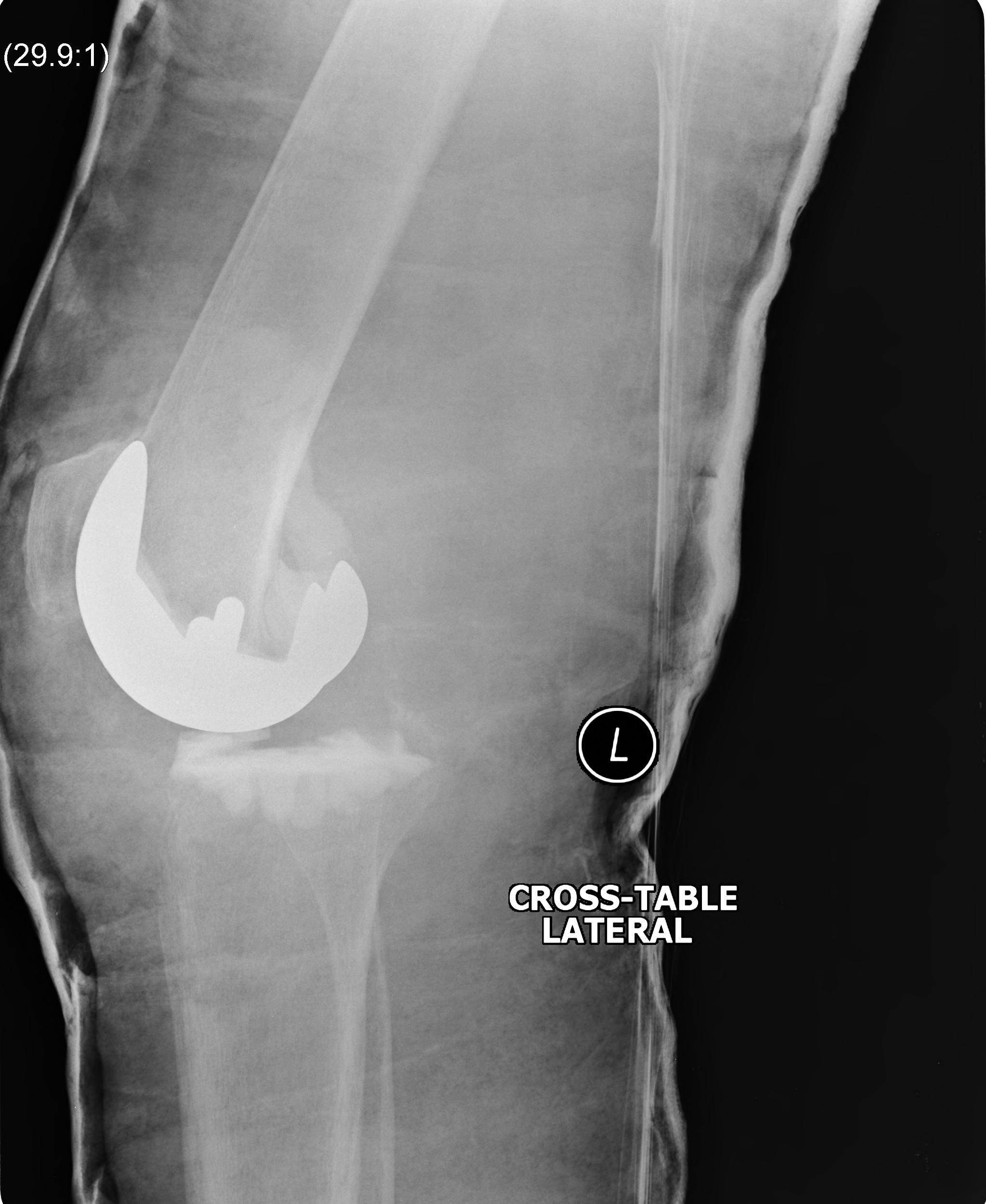
Background
Definition
Repeated dislocation of patella with minimal trauma
- 15-20% of paediatric acute patella dislocations
- more common girls
- often bilateral
Dislocation occurs unexpectedly when quadriceps contracted with knee in flexion
Direction
Management
Non-operative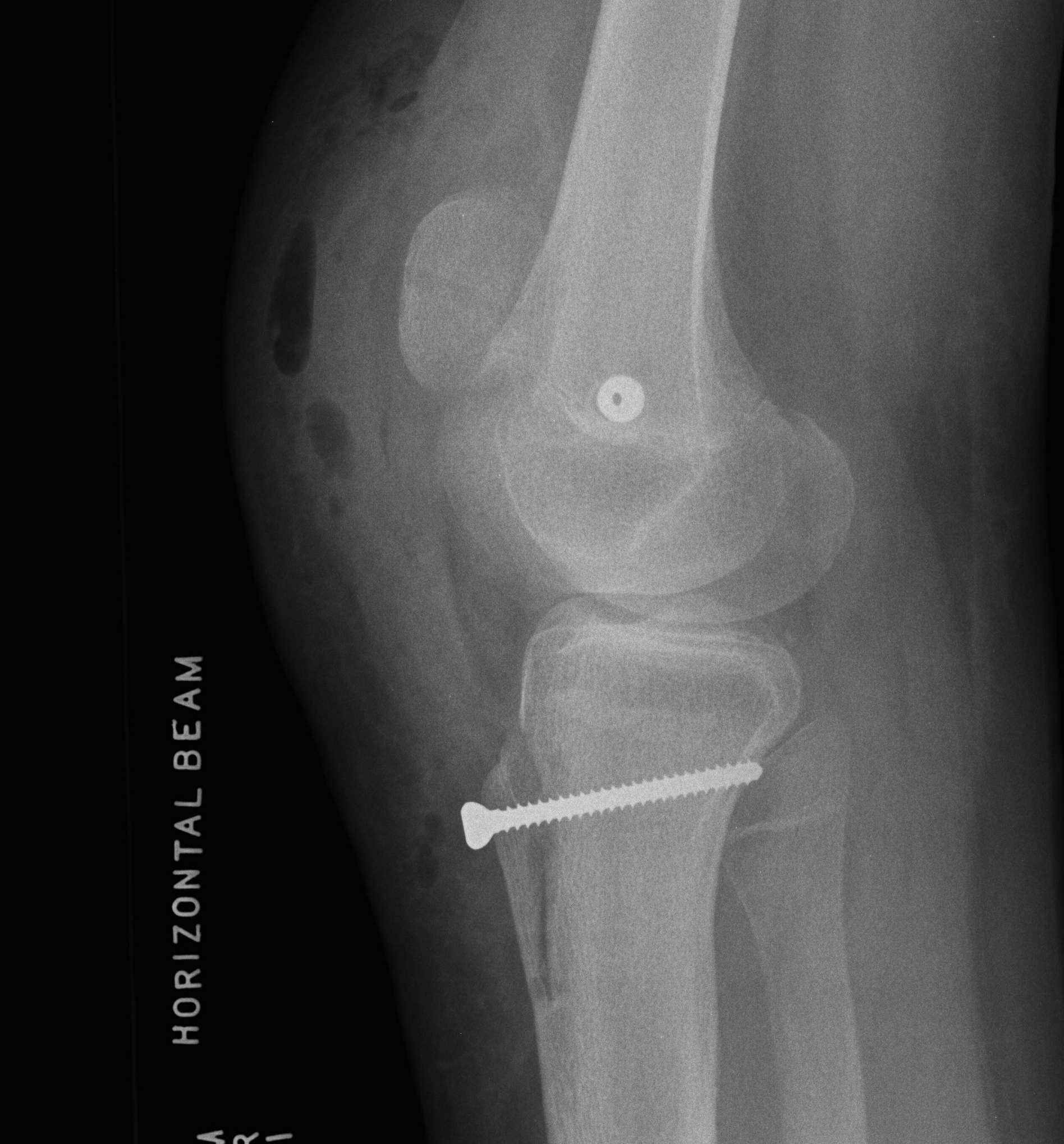
Results
90% respond
- very important
- 6 - 12 months minimum before offering surgery
Physiotherapy
1. Stretches
- quads stretches
- ITB
- lateral retinaculum