Epidemiology
10-20% of all talus fractures
Patterns
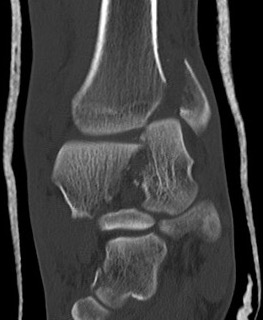
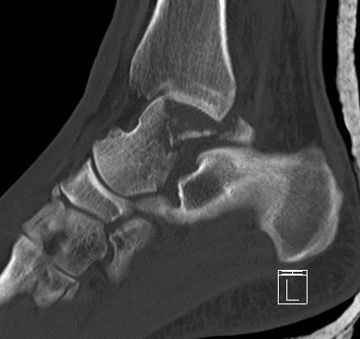
Coronal plane / Sagittal plane
+/- Crush fractures
+/- talar neck
Involve both the tibiotalar and the subtalar joint
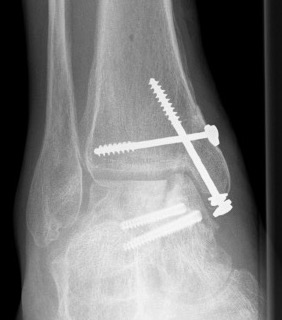
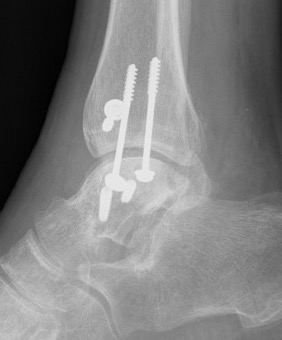
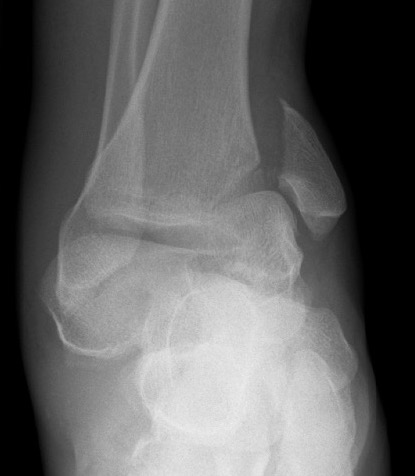
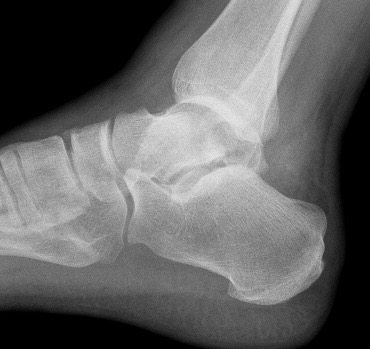
Xray
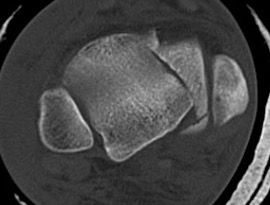
CT


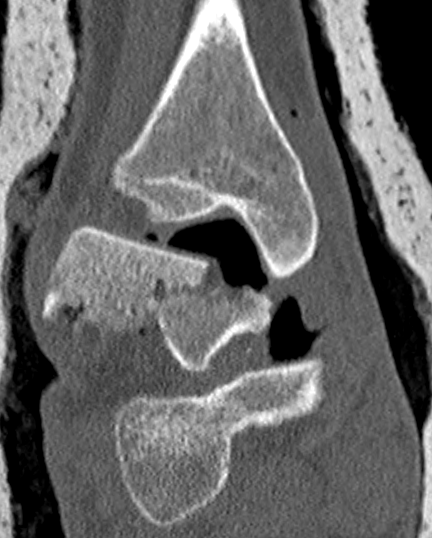
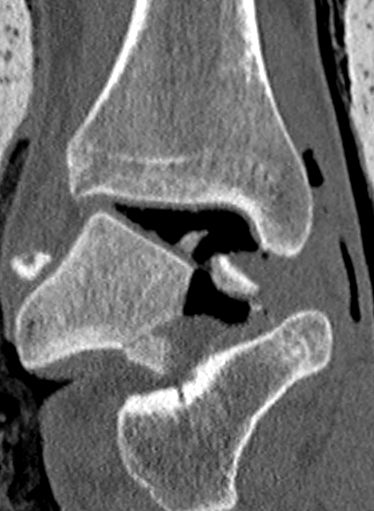
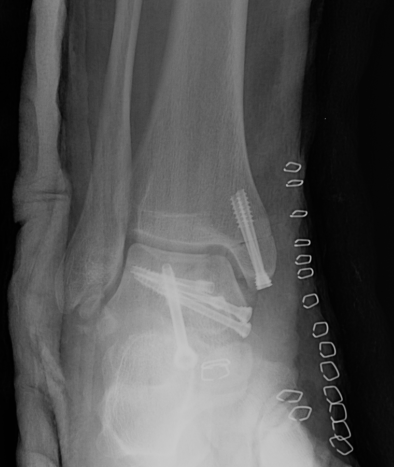
Operative Management
Indications
Displaced / intra-articular fractures
Approach
Anteromedial / anterolateral approach +/- medial or lateral malleolar osteotomy
AO surgery reference anteromedial approach talus
AO surgery reference anterolateral approach talus
AO surgery reference medial malleolar osteotomy

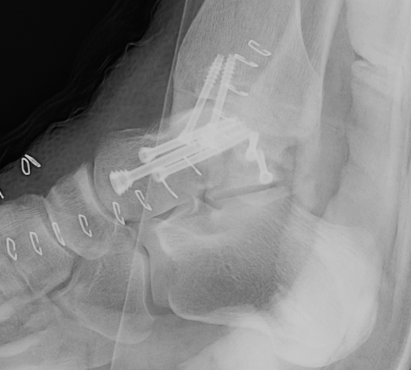
ORIF talar body utilizing medial malleolar osteotomy
Posterior fractures
- posteromedial approach +/- distraction with external fixation
- posterolateral approach +/- distraction with external fixation
- posterior ankle arthroscopy
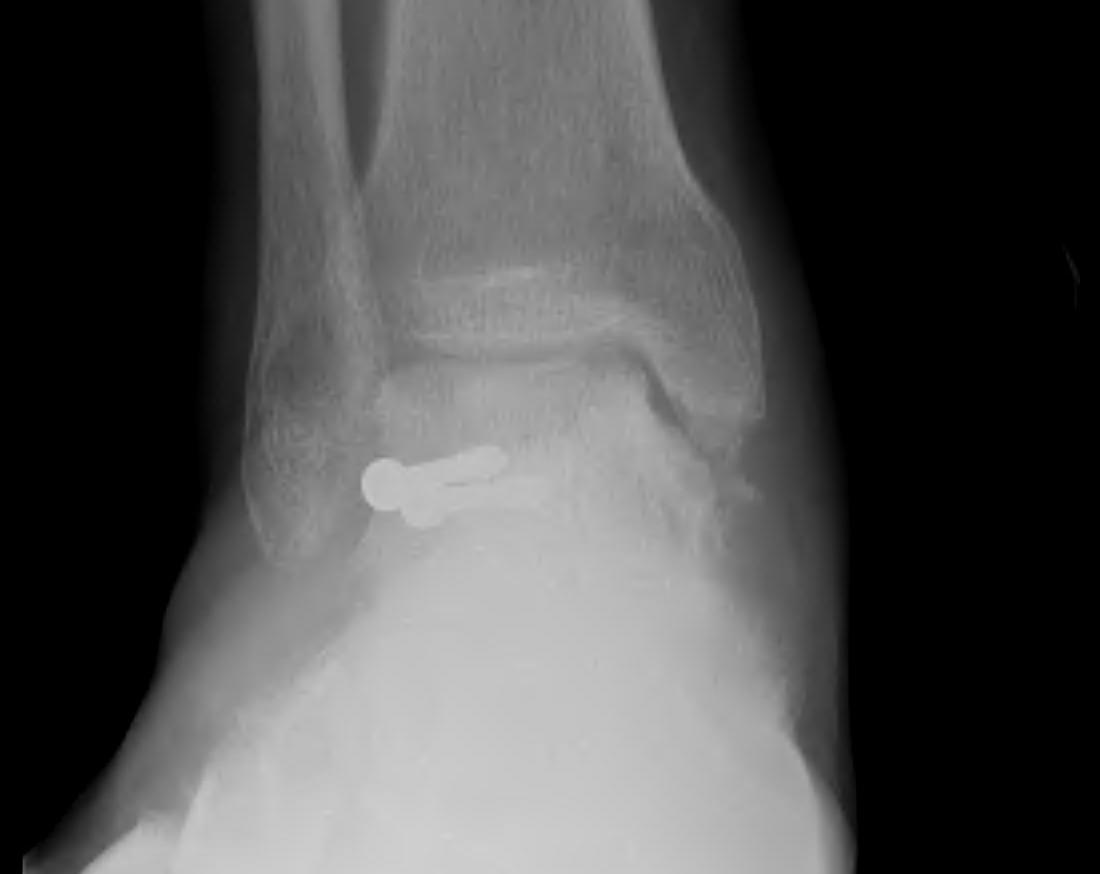
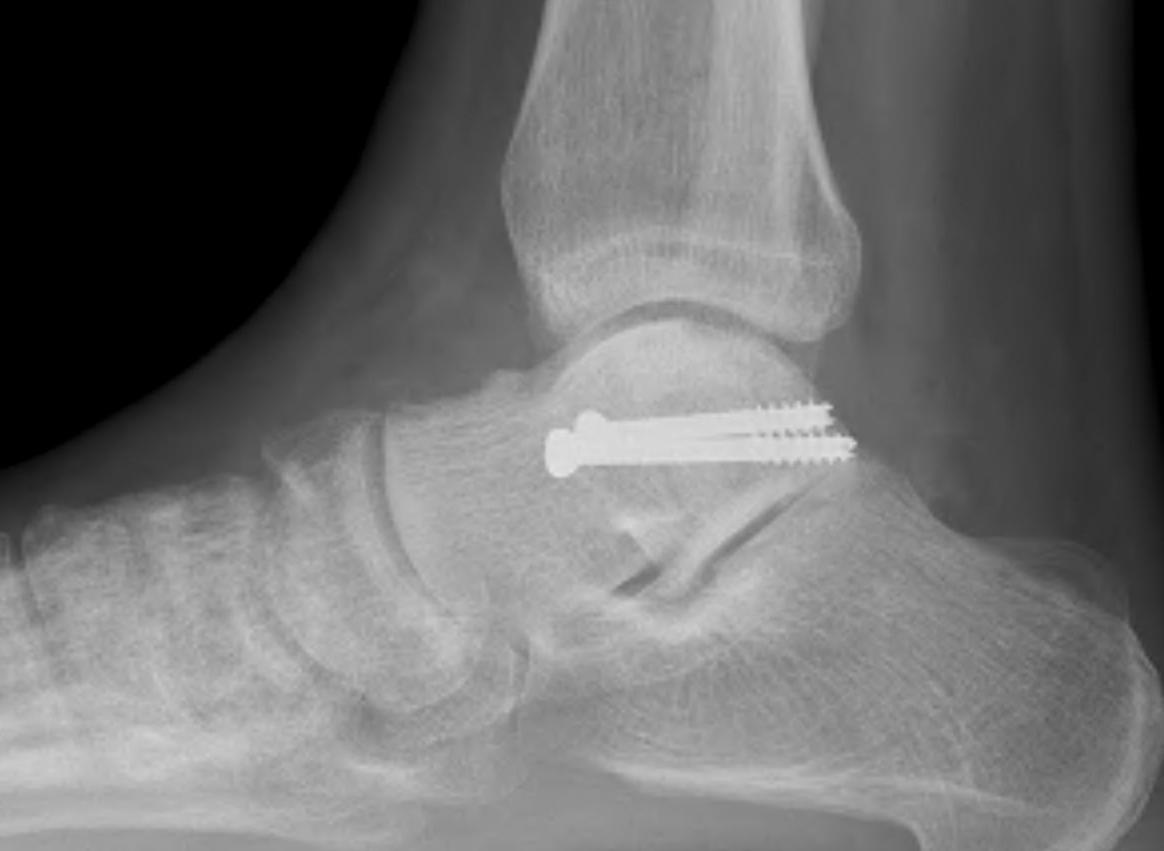
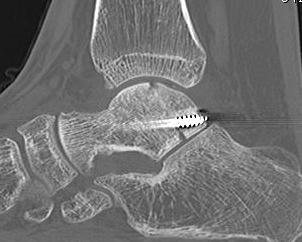
Results
Ebraheim et al Int Orthop 2008
- 19 talar body fractures treated with ORIF
- 52% (10/19) good outcomes
- 26 talar body fractures treated with ORIF
- 65% (17/26) ankle OA
- 35% (9/26) subtalar OA
- 38% (10/26) AVN
Complications
Nonunion
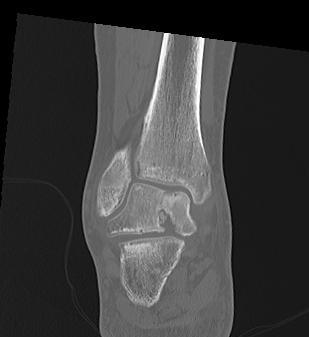
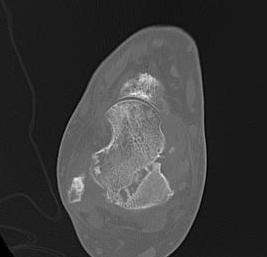
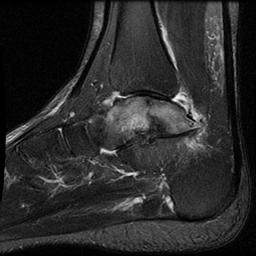
Non / malunion of nonoperatively treated talar fracture
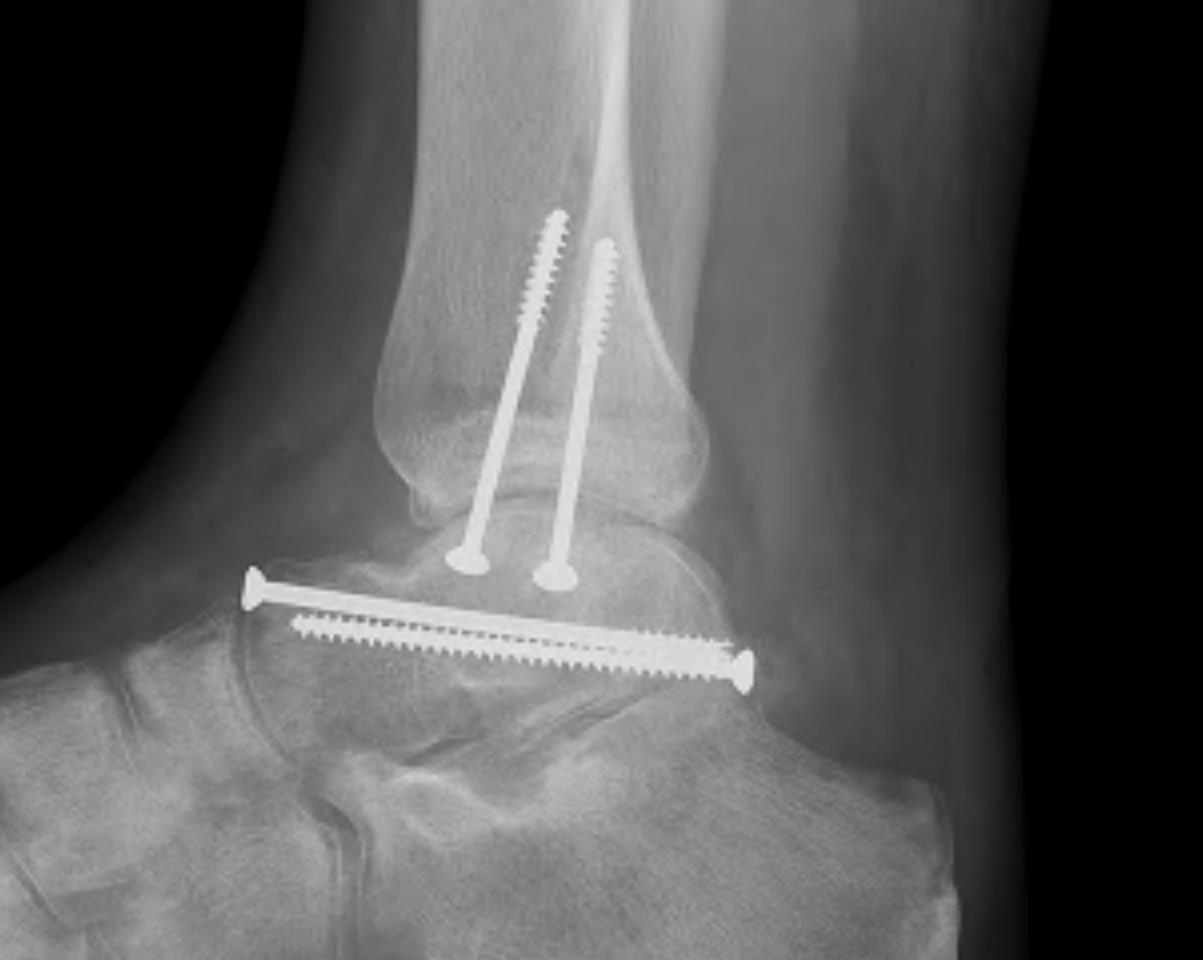
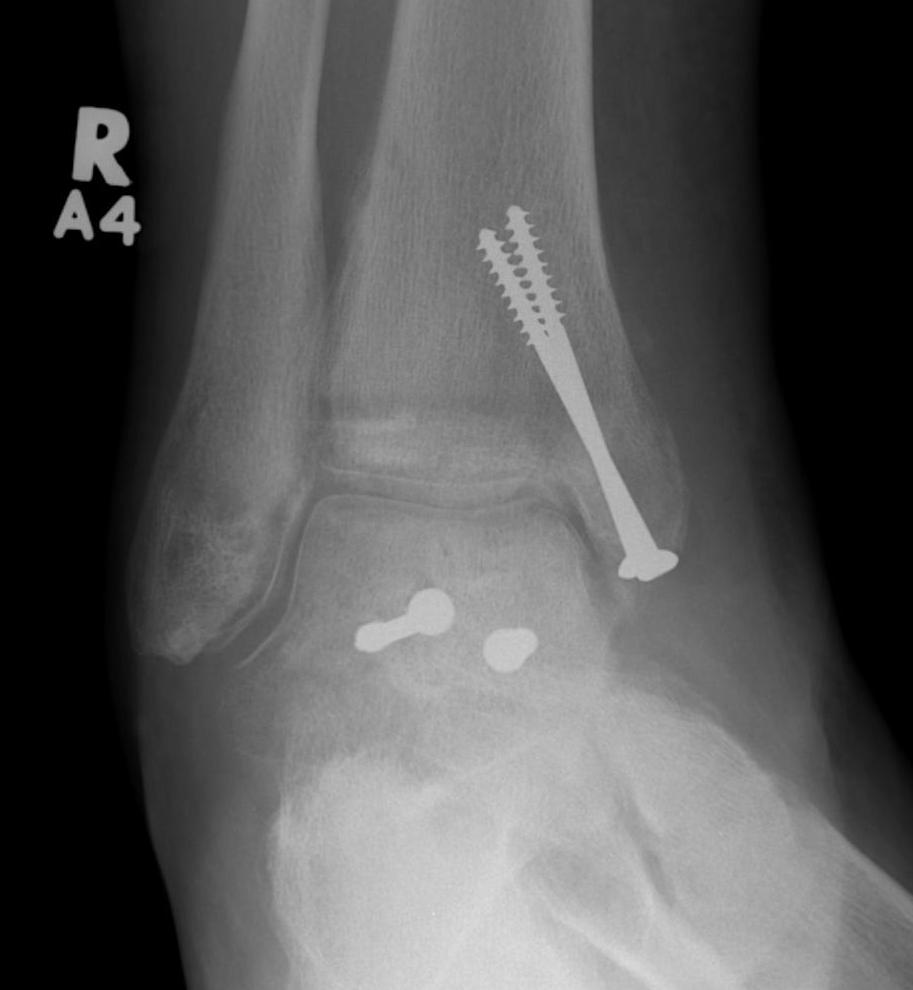
Post ORIF of the nonunion utilizing a medial malleolar osteotomy
Malunion / AVN