Definition
Congenital fibrous, cartilaginous or bony connection of 2 or more tarsal bones
Secondary to failure of segmentation of mesenchyme / failed joint cleft formation
Epidemiology
Incidence
- present in 10% of population
- symptomatic in 1% of population
- bilateral in 50%
- 20% multiple coalitions
AD with variable penetrance
Associations
Multiple synostosis syndrome - hand / wrist / elbow / neck
PFFD / Congenital short femur / Fibula hemimelia
Classification
1. Location
- calcaneonavicular most common (2/3)
- talo-calcaneal second most common (1/3)
- remainder uncommon (talonavicular / calcaneocuboid)
2. Ossification
- synostosis - completely or partially ossified
- synchondrosis - cartilaginous
- syndesmosis - fibrous
Natural history
Majority are asymptomatic & remain so in adulthood
Symptoms usually develop in adolescence when bar ossifies
Calcaneonavicular coalition - 8 - 12 years of age
Talocalcaneal coalition - 12 - 16 years of age
Symptoms
Recurrent ankle sprains
Mechanical pain with activity
Vague aching pain aggravated by activity
Signs
Stiff subtalar joint
- especially talocalcaneal bar
- may still have movement if not ossified
Rigid Pes Planus / Flatfoot
- doesn't correct on heel raise or Jack's Test
- heel doesn't swing into varus
Valgus heel with talocalcaneal bar
Nonoperative management
Orthotics with arch support
Walking boots
Cast immobilization
Steroid injections
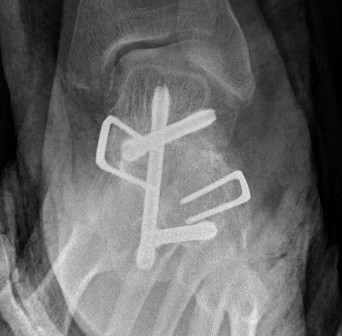
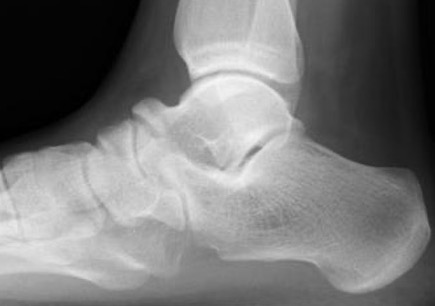
Calcaneonavicular bar
Pathology
Abnormal connection between
- anterior process calcaneum
- lateral edge navicular
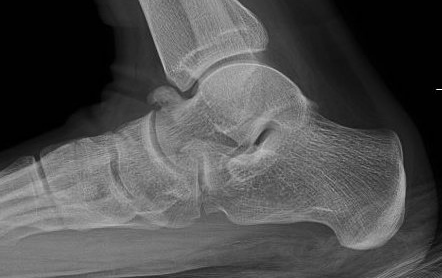
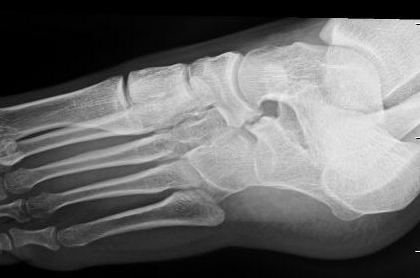
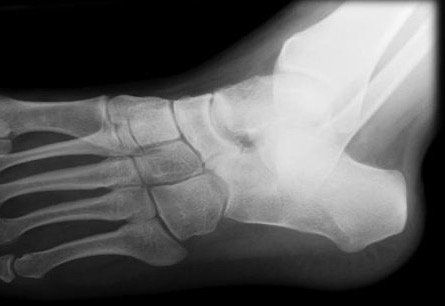
X-ray
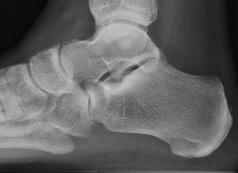
Anteater sign
- oblique xray
- elongated process on calcaneum or prolongation of navicular
CT
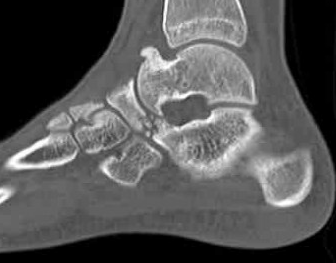
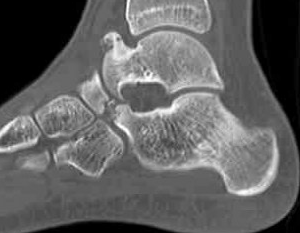
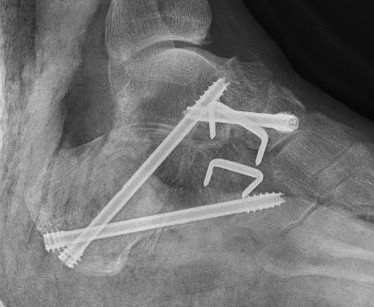
Open Calcaneo-navicular bar resection
Technique
Anterolateral / Ollier approach
- 1cm distal to fibular tip obliquely across sinus tarsi to superolateral margin TNJ
- protect superficial CPN
- EDL & P tertius anteriorly
- peroneals plantarward
- elevate EDB proximal to distal
- beware of its motor branch from DPN
- expose sinus tarsi / anterior process calcaneum and bar
Resection
- resect 1cm of bone with osteotomes
- check with on table oblique intra-operative image
- interpose fat / EDB / bone wax into defect
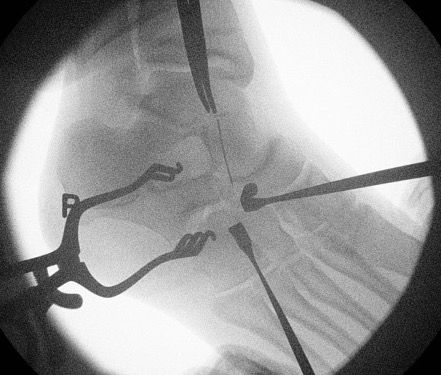
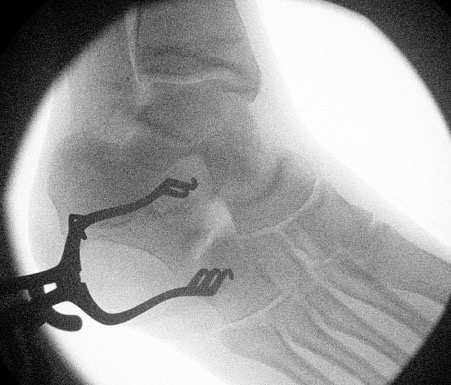
Results
- systematic review of CN bar resection in 380 feet
- average age 12 years
- 83% successful outcomes
- 14% recurrence
- progressive ankle and subtalar arthritis in 7%
Masquijo et al J Paediatr Orthop 2017
- 48 patients undergoing CN bar resection
- compared bone wax / fat graft / EDB interposition
- significantly higher regrowth with EDB (40%)
Arthroscopic resection
Corin et al J Child Orthop 2022
- 127 resection CN bar
- revision rate: 15% arthroscopic, 2% open
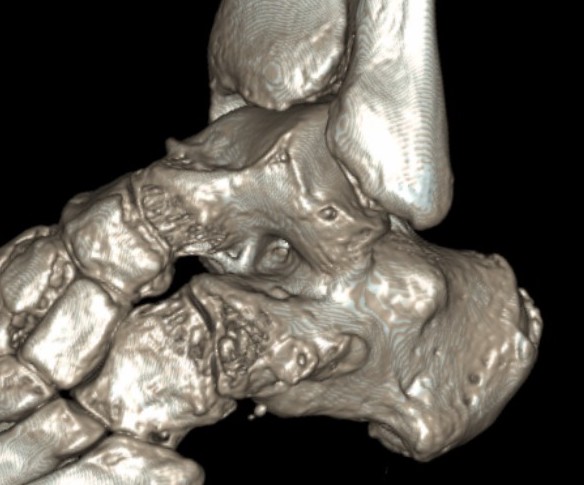
Talocalcaneal Bar
Pathology
Central
- affects articular facets (anterior / middle / posterior)
- middle most common
Peripheral
- extra-articular
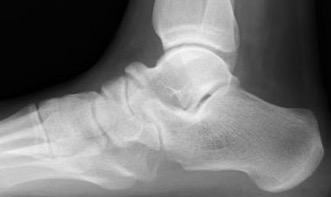
Xray
| Talar beaking | C Sign | Harris axial view | Ball and socket ankle joint |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traction spur due to increased stress | Medial outline talar dome and posterior sustenaculum tali |
40 degree axial view Ski jump view Visualize middle facet |
Secondary to rigid subtalar joint Develops to allow inversion / eversion |
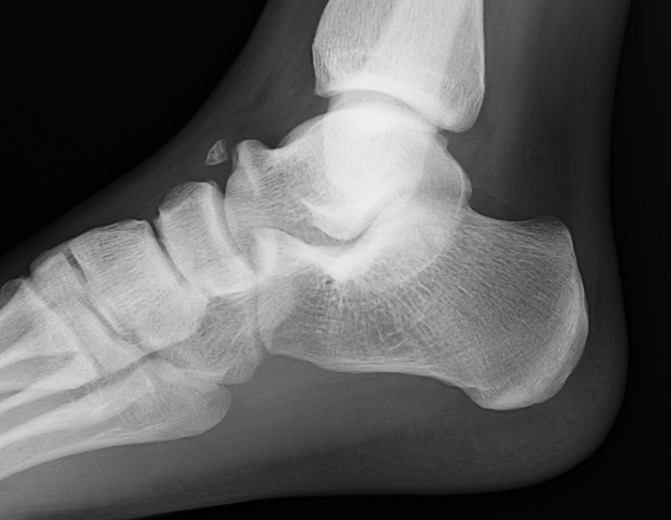
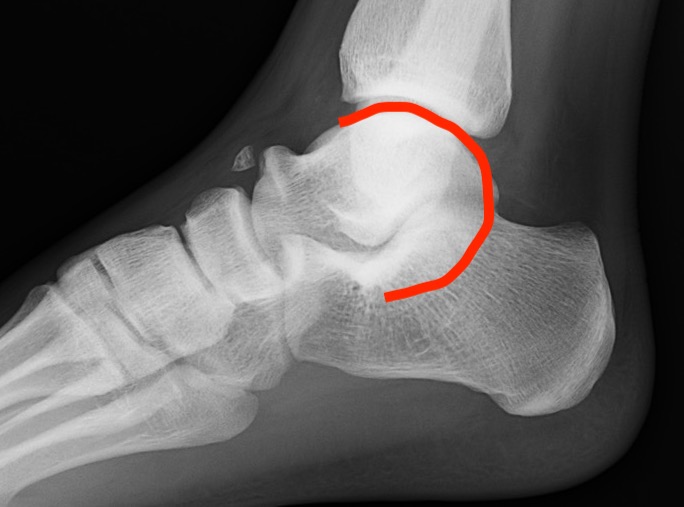
Talar beaking with C sign
CT
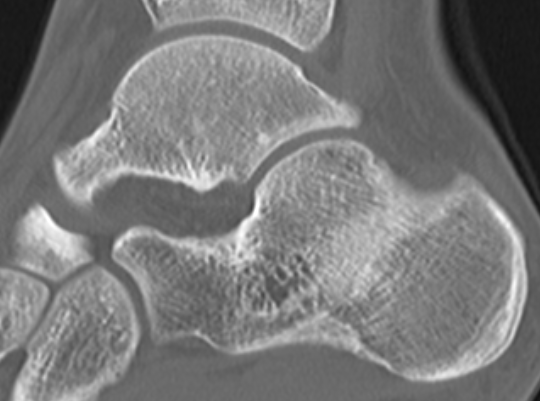
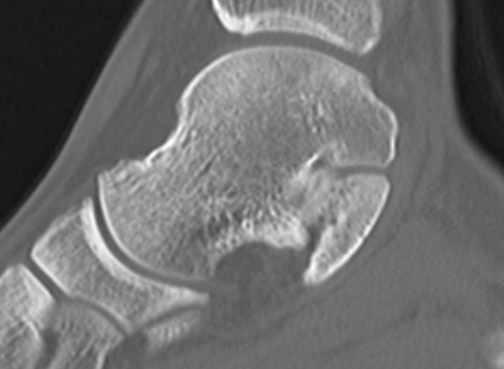
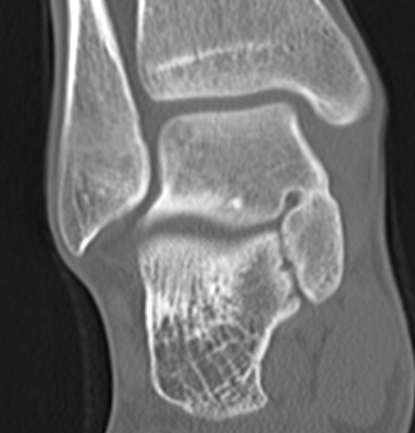
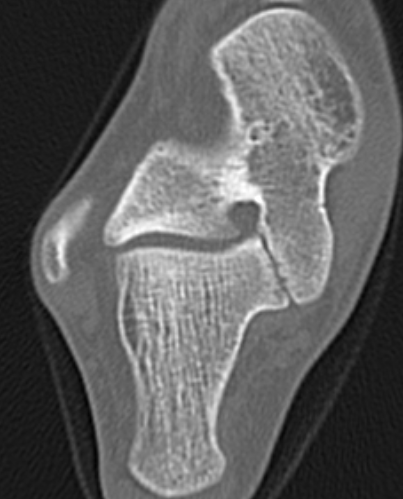
TC coalition middle facet
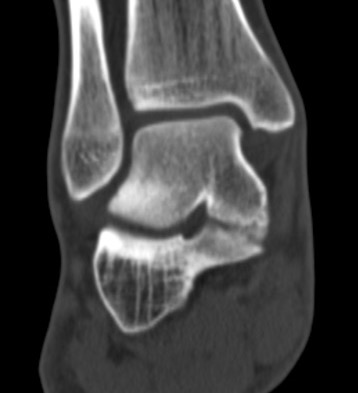
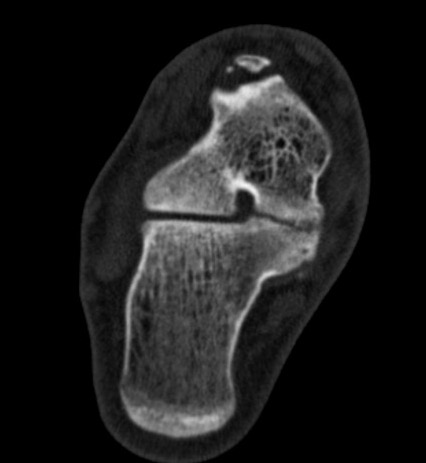
TC coalition middle facet
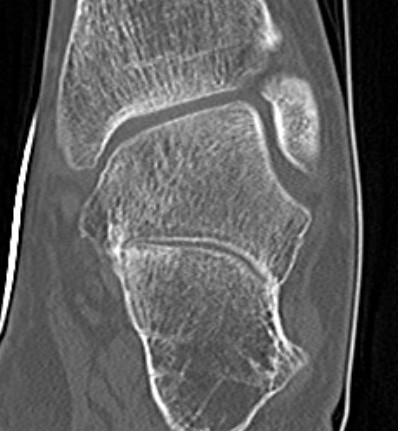
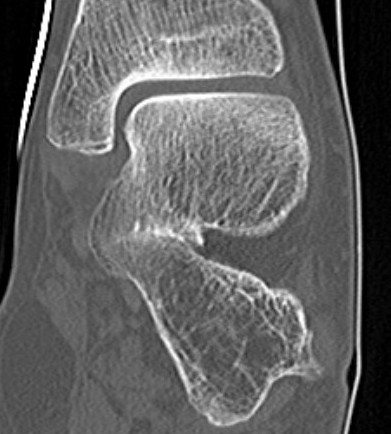
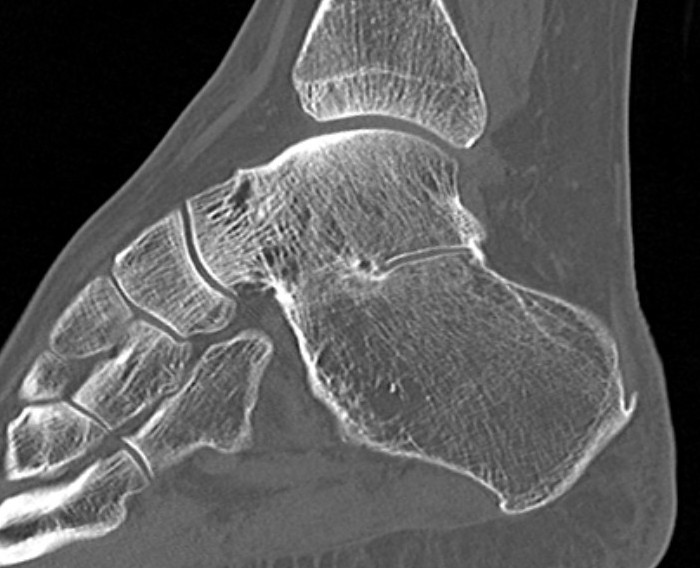
Complete synostosis of the medial TC joint with OA of the posterior subtalar joint
MRI
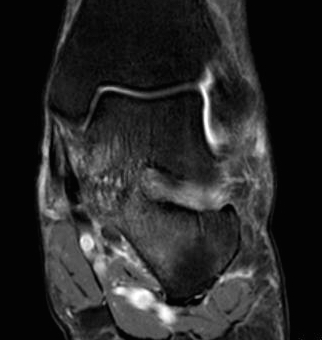
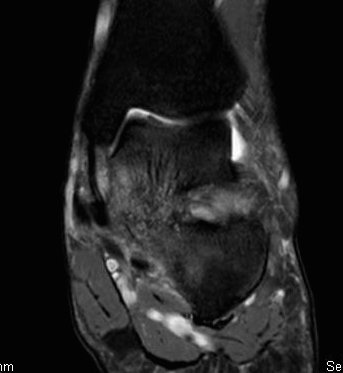
TC coalition middle facet
Management options
Resection of bar
Isolated STJ fusion - degeneration of STJ only
Triple Arthrodesis - rigid planovalgus foot
Indications for bar resection
No degeneration of subtalar joint
Single coalition
? coalition < 50% and hindfoot valgus < 16 degrees
Wang et al J Orthop Surg Res 2024
- comparison resection posterior coalition v posterior + middle coalition
- worse outcomes with combines posterior + middle coalition
- 20 patients
- worse outcomes when coalition > 50% posterior facet and hindfoot valgus > 16 degrees
Koshbin et al Foot Ankle Int 2013
- 14 year follow up
- good results with coalition > 50% joint and hindfoot valgus > 16 degrees
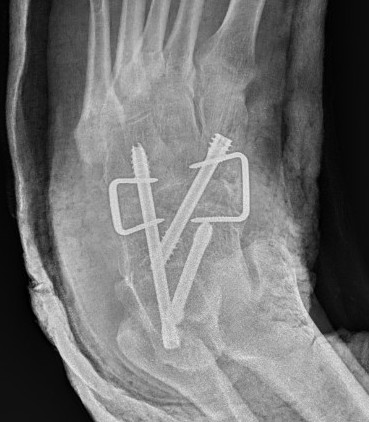
Open Middle Talocalcaneal bar resection +/- calcaneal lengthening osteotomy
Technique
JBJS Essential techniques middle TC coalition resection
JBJS Essential techniques middle TC coalition resection and flatfoot reconstruction
POSN Academy surgical technique video with navigation
Medial approach
- navicular tuberosity to medial border T Achilles
- 2cm superior to superior calcaneal tuberosity
- release flexor retinacular sheath
- elevate T Post and FDL tendon anteriorly
- neurovascular bundle and FHL retracted plantarward
- identify posterior facet
Resection
- can be difficult to identify normal identity
- protect subtalar joint
- remove more bone from talus than sustentaculum talus to preserve hindfoot stability
- insert fat graft / ITB allograft / half FHL
+/- calcaneal lenthening osteotomy
- use bone resected from coalition
- K wire to stabilize calcaneocuboid joint
Arthroscopic Talocalcaneal resection
Indications
Posterior facet coalition
< 50%
Results
Wang et al Foot Ankle Int 2022
- 32 patients with both posterior and posterior + middle facet coalition
- arthroscopic resection
- 81% good / excellent outcomes
- no difference in outcomes between two groups
Triple arthrodesis
Indication
Subtalar arthritis



Technique
Lateral arthroscopic arthrodesis for talocalcaneal coalition surgical technique PDF