nerve injury
Background
Anatomy
Pelvis is a true ring
- any anterior fracture must have a posterior injury as well
- integrity of the posterior sacroiliac complex is key
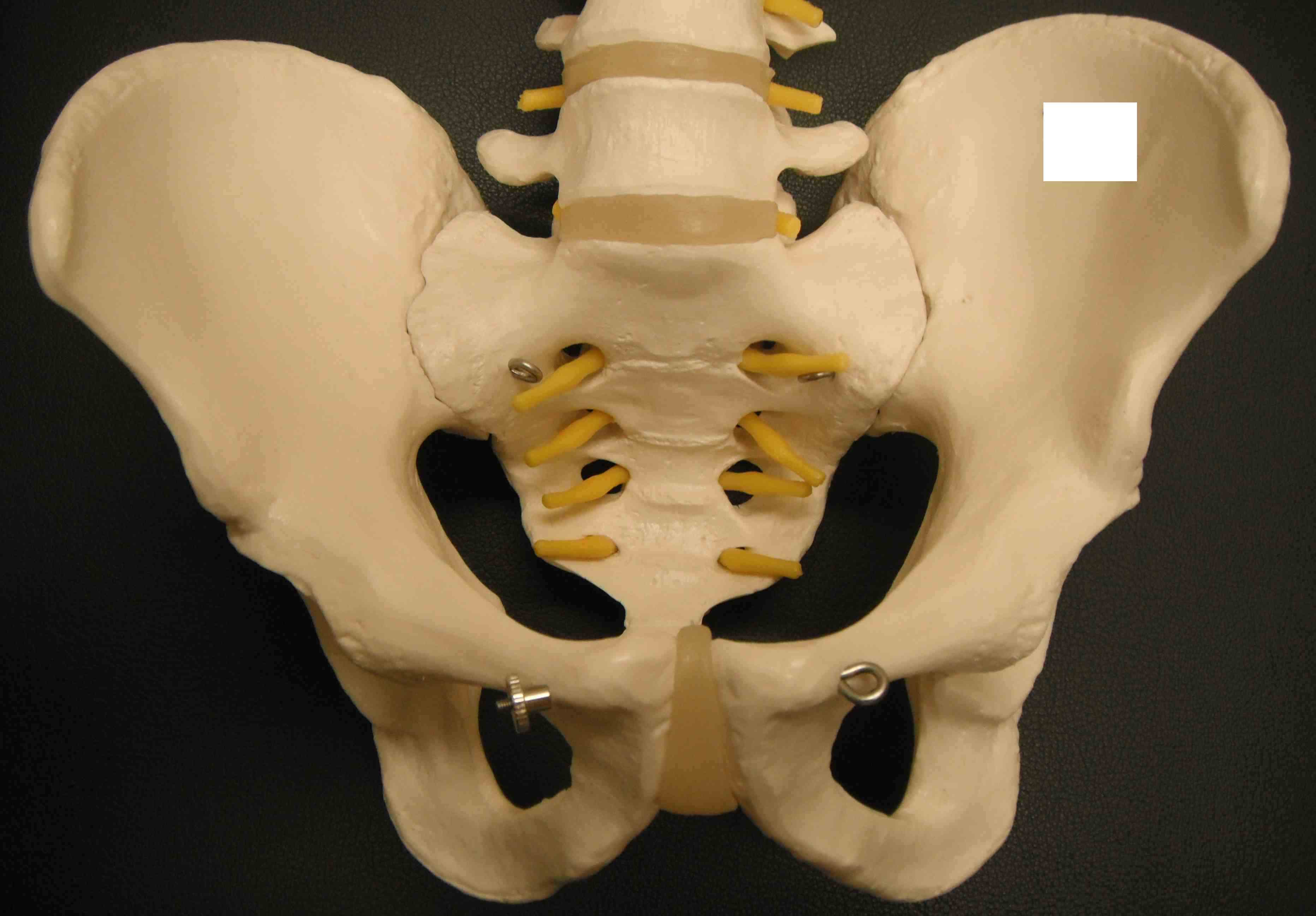
Bony Anatomy
2 innominate bones + sacrum
Symphysis pubis < 5mm
SI joint 2-4 mm
Latarjet / Bristow
Bristow
Concept
Non-anatomical bony block
- transfer of coracoid process through subscapularis
- dynamic anteroinferior musculotendinous sling
- provides subscapularis tenodesis
- preventing lower portion from displacing proximally as arm abducted
- when shoulder in vulnerable position abduction and ER
Nerve Injury
Epidemiology
Primary THR 1%
Revision THR 3%
DDH 5%
Sciatic nerve 90% of nerve palsy
Other
- femoral nerve
- CPN
- ulna / radial nerve from positioning
Aetiology
Direct
Laceration
- exposure / sciatic and superior gluteal nerve
- drill reamer / obturator nerve
- spike of cement / obturator nerve
Arthroscopy
Indication
Diagnostic
Pain / Stiffness / Locking
Instability
- exclude OCD
Assess syndesmosis
Therapeutic
Synovitis
Osseous lesions / Tibiotalar impingement spurs
Osteochondral defects