plate
Proximal Tibial Fractures
Definition
Metaphysical
Extra-articular
Treatment options
IMN
Plate
Results
Jindal et al. Indian J Orthop 2020
- systematic review
- no different in malunion
- infection more common in plate
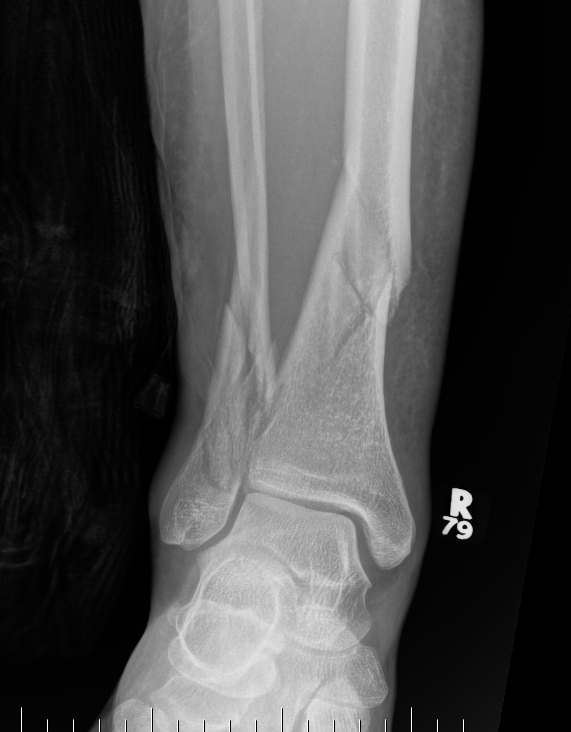
Distal Tibial Fractures
Distal Tibial Fractures
Definition
Metaphyseal
Extra-articular
Intra-articular Extension
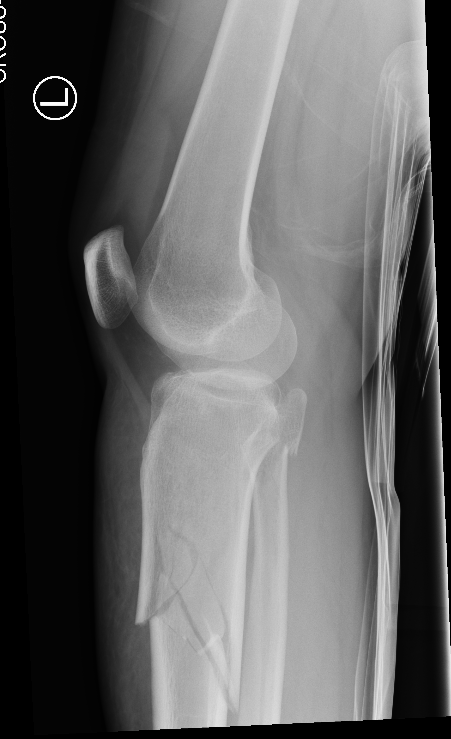
Distal Femur Fractures
AO Classification
Types
1. Supracondylar
2. Unicondylar
3. Intracondylar
Xrays
Supracondylar / Extra-condylar
Midshaft Tibial Fracture
Epidemiology
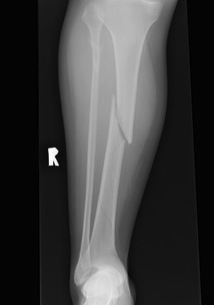
Most common long bone fracture
Aetiology
Young patients / sports
Elderly / simple falls
MVA - often compound
Tscherne Soft Tissue Classification
Grade 0
- nil ST injury
Grade 1