arthroscopic
TFCC tears
Definition
Present with pain but not instability
Types
Traumatic
Degenerative
Different treatment algorithms for each
History
Ulna side wrist pain
- may be worse with rotation
- opening doors and jars
History of trauma
Examination
Local tenderness DRUJ
Arthroscopic Reconstruction PCL Technique Single Bundle
Aim
Reconstruct anterolateral bundle
Graft Options
A. 4 strand hamstring autograft
B. Achilles Allograft
- bony block for femur (9 x 20 mm)
- tubularise tendon to fit through 9 or 10 mm tunnel
- don't cut tendon short
Vumedi Dr Bruce Levy Cadaveric video
PVNS
Definition
Pigmented Villo-Nodular Synovitis
- benign inflammatory process that arises in synovial tissues
- contains significant amounts of hemosiderin
Epidemiology
Age: 20 - 50
Sex: M > F
Types
A. Diffuse
- throughout joint synovium
- more difficult to treat / excise fully
Latarjet / Bristow
Bristow
Concept
Non-anatomical bony block
- transfer of coracoid process through subscapularis
- dynamic anteroinferior musculotendinous sling
- provides subscapularis tenodesis
- preventing lower portion from displacing proximally as arm abducted
- when shoulder in vulnerable position abduction and ER
Subtalar and Triple Arthodesis
Biomechanics
Able to achieve relatively high level of function after STJ fusion
- previously believed that isolated STJ fusion should not be performed
- believed that triple arthrodesis was operation of choice for hindfoot
- STJ fusion has superior result with less stress on AJ
Average loss of DF 30% / PF 10%
Position of hindfoot determines flexibility of transverse tarsal (CCJ & TNJ) joints
- imperative that fusion be positioned in ~ 5o valgus
Full thickness tears
Surgical Options
1. Open antero-lateral approach
Large / Massive Cuff Tear
2. Deltopectoral approach
Large Subscapularis tear
3. Arthroscopic Assisted Mini-open
Indication
- Small / Moderate Cuff Tear < 3cm
- no retraction
Technique
- arthroscopic SAD
Ganglions
Epidemiology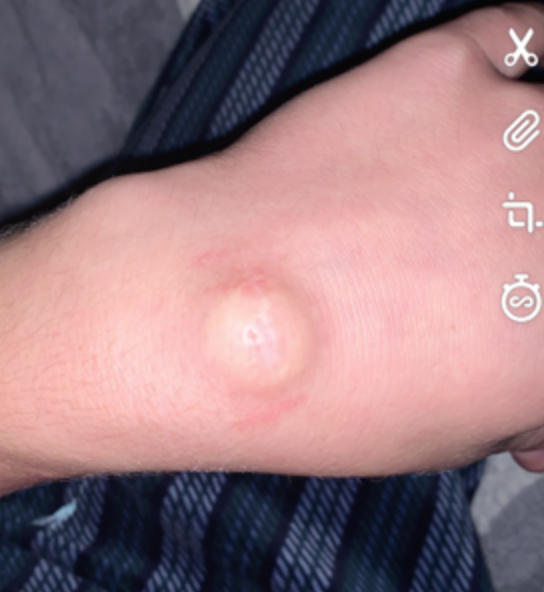
Most common tumour of hand
F > M
2nd - 4th decade
Aetiology
Unknown
Trauma
Mucoid degeneration of collagen tissue
Synovial herniation
Location
Recurrent Posterior Instability
Definition
Patients usually complain of subluxation rather than dislocation
- rarely requires reduction
Different entity to acute posterior dislocation usually
Epidemiology
Rare
Aetiology
1. Ligamentous laxity > 50%
- commonly associated with MDI
- posterior only 20%
- posterior & inferior 20%
Multidirectional Instability
Definition
Instability in at least 2 planes
- postero-inferior
- antero-inferior
- antero-postero-inferior
Epidemiology
Recognised as a common problem
- often misdiagnosed
Most patients athletic
