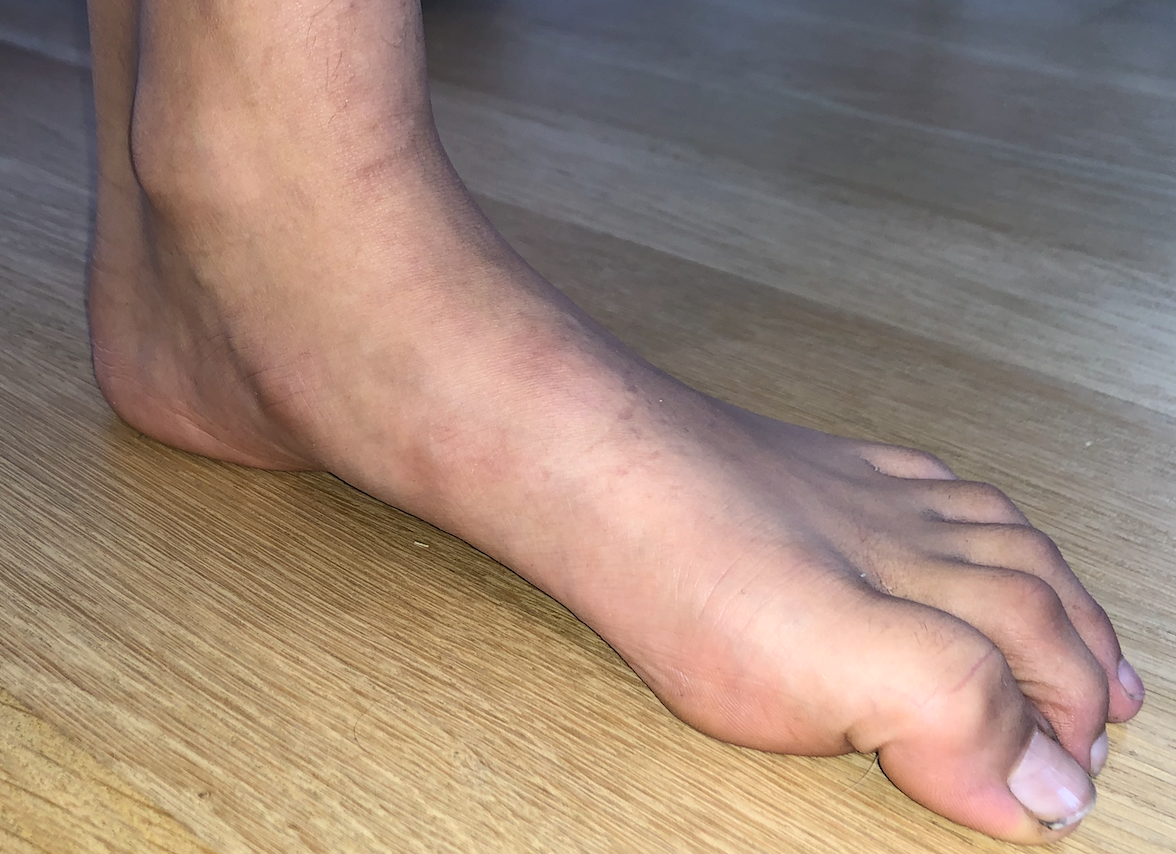


Definition
Pes planus - loss of medial longitudinal arch
Flexbile / correctable
Epidemiology
Usually bilateral with strong family history
More common in Black than White populations
Natural History
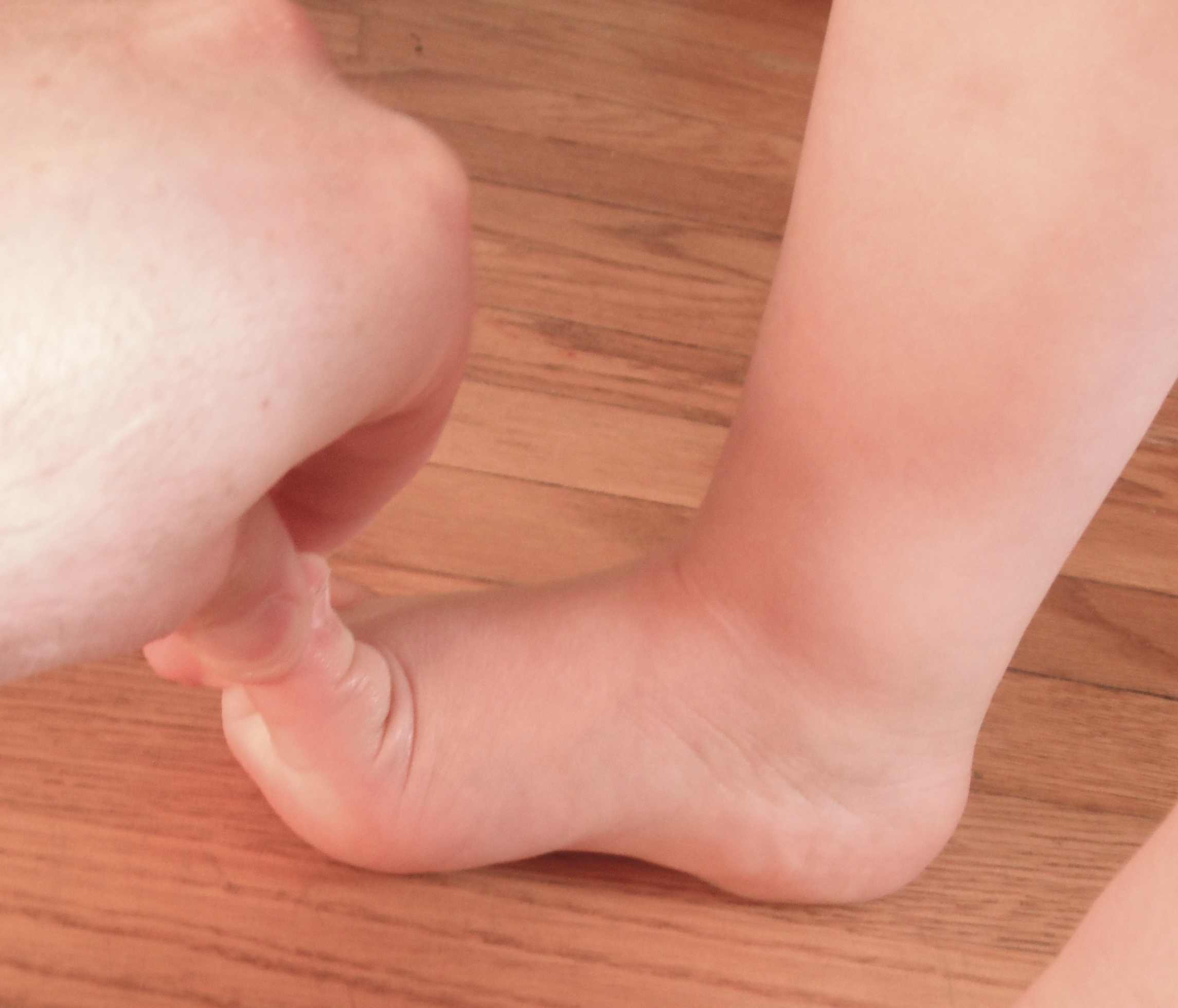
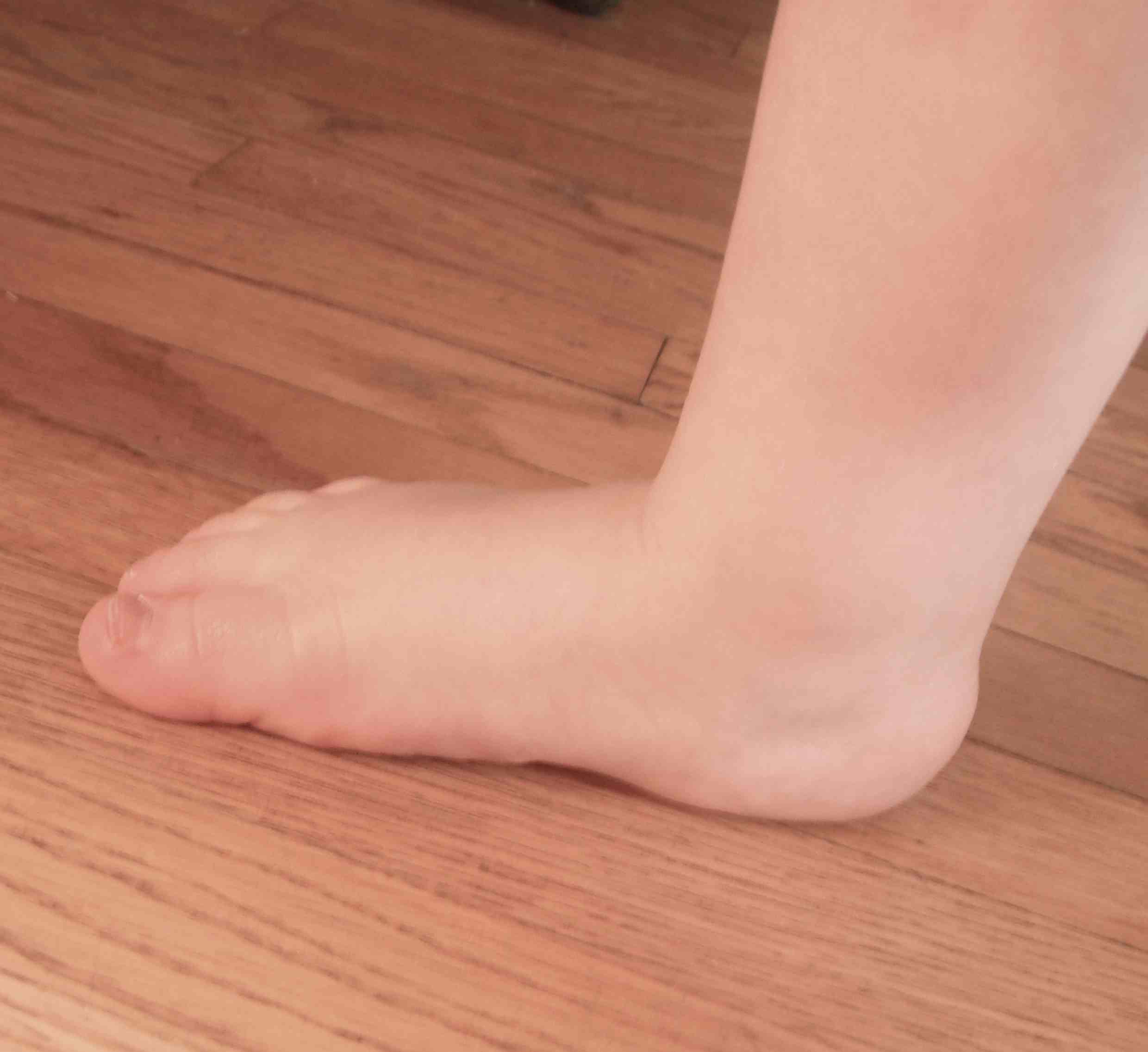

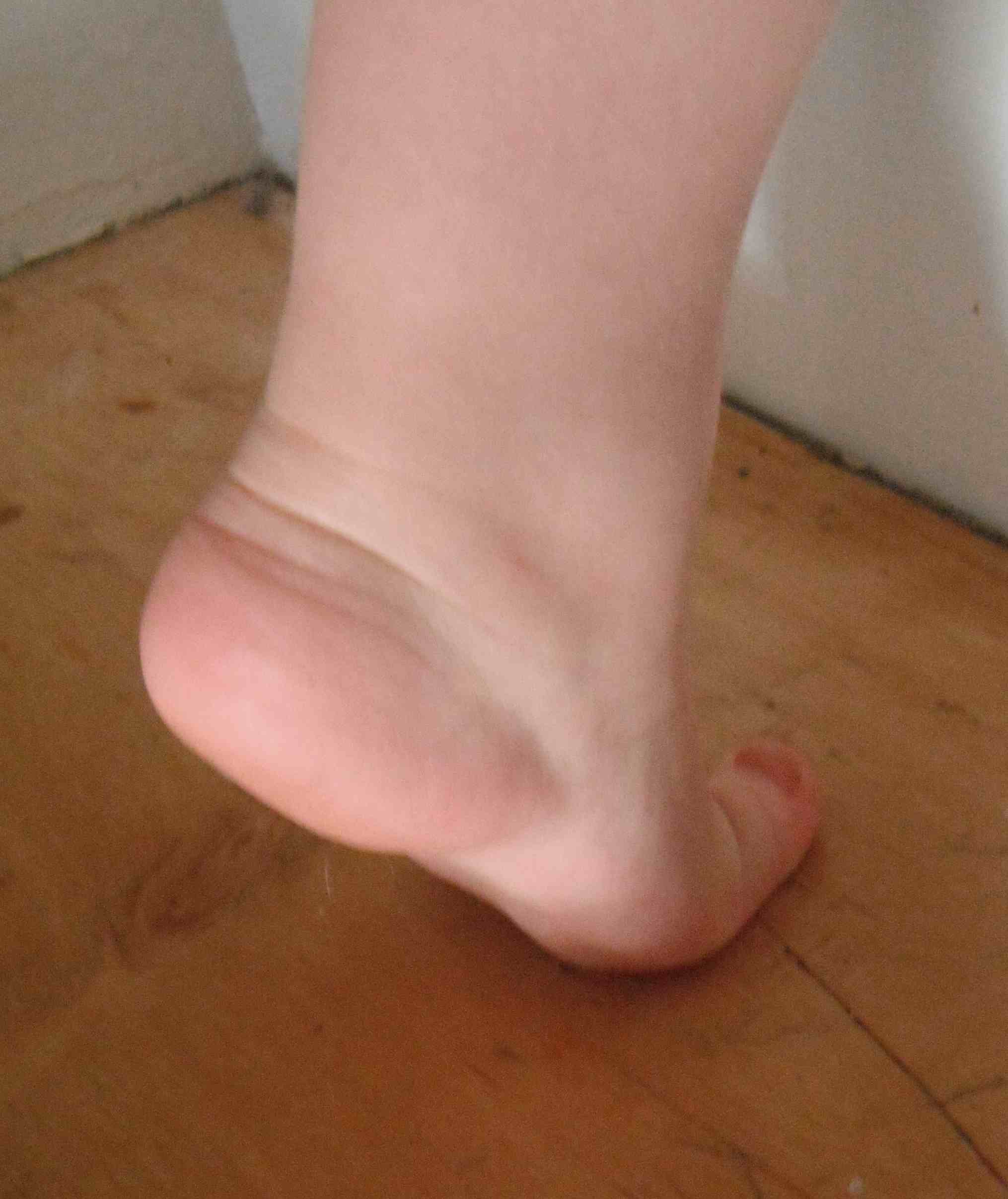
All infants have flat feet
- at birth foot is in calaneovalgus & there is no medial arch
- foot has large medial fat pat
- arch begins to develop in 2nd & 3rd year with walking
Thus flatfeet are
- usual in infants
- common in children
- in normal range for adults
Etiology
Physiological
Compensatory
1. Genu Valgum - physiological knock-knees (age 3-4) leads to apparent flatfoot, corrects by ~ age 6
2. Out-toeing - external rotation of foot causes body weight to fall anteromedial to ankle
3. Tight Tendoachilles - lack of dorsiflexion compensated by heel eversion & forefoot pronation
4. Joint laxity - i.e. Marfan's, Ehlers-Danlos
Symptoms
Medial arch pain with prolonged standing
Examination


Loss of medial arch on weight bearing
Valgus hindfoot
Flexible flatfoot
Recreation of longitudinal arch & heel varus
- suspended / non weightbearing
- toe raise / windlass mechanism
- passive dorsiflexion of great toe with weight bearing (Jack's test)
Mobile or hypermobile subtalar joint

Differential diagnosis of fixed flatfoot
Congenital - congenital vertical talus / tarsal coalition / skewfoot
Trauma - tibialis posterior rupture / midfoot fracture / Lisfranc / rupture spring ligament / rupture plantar fascia
Neuromuscular - CP, spina bifida, polio
X-ray

Meary's angle
- Talus - first metatarsal angle
- lateral weight bearing view

Cobey's
- hindfoot alignment view
- foot plantarflexed over a block
- see that calcaneum is under the fibula not tibia
Nonoperative
Options
Medial arch support / medial heel raise / UCBL
Results
Molina-Garcia et al Children 2023
- systematic review of orthoses for flexible flat feet in 680 children
- RCTs and comparative trials
- evidence for improved symptoms with orthoses
Operative
Indications
Failure non operative measures to relieve pain
Options



Subtalar arthroeresis
Lateral column lengthening
- Evan's calcaneal lengthening osteotomy
- distraction calcaneocuboid arthrodesis
- calcaneo/cuboid/cuneiform (triple C) osteotomy
1st metatarsal plantarflexing osteotomy / Cotton dorsal opening wedge osteotomy of the medial cuneiform
Results
Arthroeresis v Lateral column lengthening
- systematic review of lateral column lengthening v arthroeresis
- similar satisfaction rates
- greater functional improvement with lateral column lengthening
- similar reoperative rate
- greater complication rate with lateral column lengthening (CCJ subluxation)
- persistent pain most common complication arthroeresis
Calcaneal lengthening osteotomy v CCJ distraction arthrodesis
Modha et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2021
- systematic review
- increased graft failure with allograft v autograft
- reduced lateral foot pain with CCJ arthrodesis v calcaneal osteotomy
Calcaneal osteotomy v Triple C osteotomy
Moraleda et al J Pediatr Orthop 2012
- 30 triple C osteotomy v 30 calcaneal osteotomy
- no difference in clinical outcome
- 10% complication triple C osteotomy
- 18% complication calcaneal osteotomy
- 52% CCJ subluxation calcaneal osteotomy
Subtalar arthroeresis



Concept

Arthrex ProStop
Sinus tarsi implants limit excessive pronation
Types


Endosinotarsal - implant in the sinus tarsi


Exosinotarsal - screw external to the sinus tarsi
Technique
Arthrex ProStop Technique guide
Vumedi surgical technique video
Oblique incision inferior to fibula
- identify sinus tarsi
- remove fat pad
- insert guide wire
- trial sizes and insert implant
Results




Smith et al EFORT Open Rev 2021
- 24 articles and 2500 flexible flat feet treated with arthroeresis
- excellent results 80%, poor results 5%
- complications 7%, reoperation rate 3%
- systematic review of endo- v exosinotarsal implants for flexible flatfoot
- 6 studies and 800 feet
- increased pain and screw breakage in exosinotarsal
- increased implant dislocation in endosinotarsal
Evans Calcaneal Lengthening Osteotomy
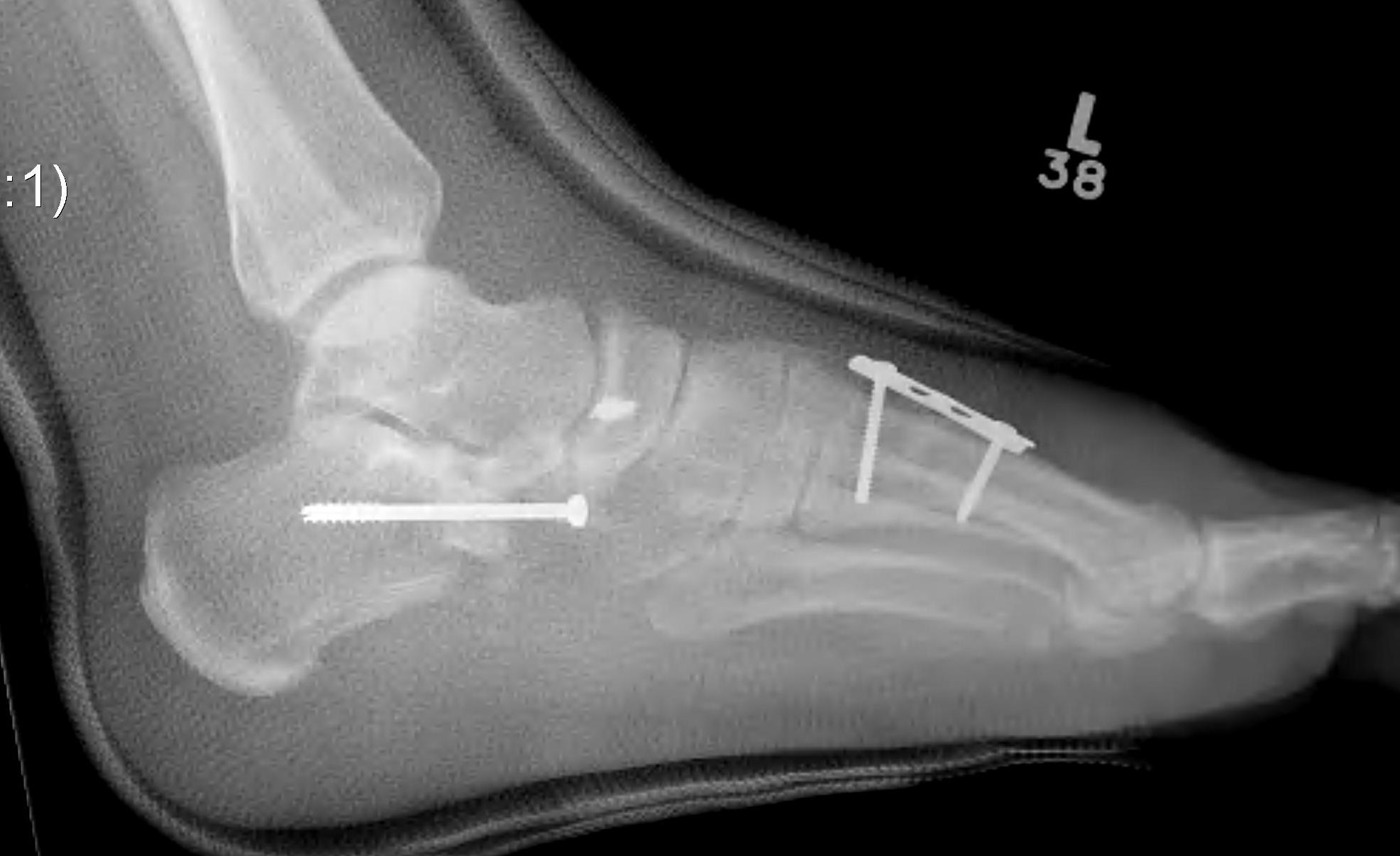
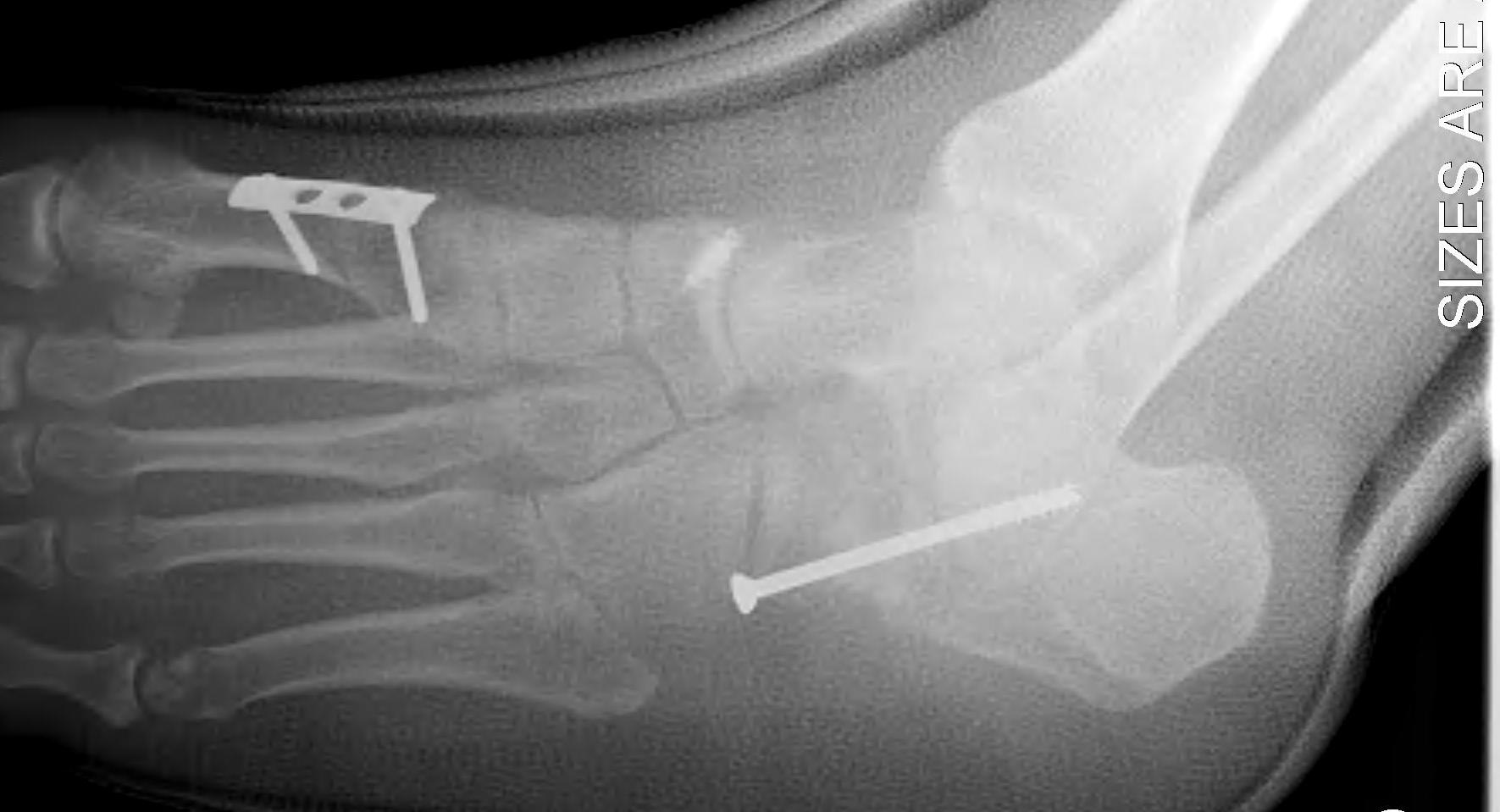
Technique
Vumedi calcaneal lateral lengthening osteotomy video
Incision over anterolateral distal calcaneum
- sural nerve retracted plantar
- P longus retracted plantar
- identify CCJ
- Z lengthen P brevis
- homan retractor in sinus tarsi (between middle and anterior facets)
- homan retractor inferior calcaneum
- K wire into CCJ to prevent subluxation
Opening wedge osteotomy
- 1.5cm proximal to CCJ
- between middle and anterior facets medially
- begin with saw, complete with osteotome
- open 1 cm
- triangular / trapezoidal bone graft (allograft, iliac crest / mid fibular autograft)
- fixation with plate / staple / screw
+/- tendoachilles lengthening
+/- modified Kidner procedure (imbricate spring ligament, Tibialis posterior advancement)
Results
- systematic review Evans osteotomy
- 7 studies and 150 feet
- good / excellent 72%, fair / poor 18%
- complications 18% (nerve, nonunion, undercorrection, overcorrection, implant related)
