Definition
Formation of lamellar bone / osteoid matrix in soft tissue
Types
Acquired / traumatic - fractures, total joint arthroplasty
Neurogenic - head injury, spinal injury
Genetic - fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva
Incidence
Zhu et al Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2015
- systematic review of 6500 cases THA
- incidence of HO 30%
- increased with male / cemented implants / ankylosing spondylitis
Risk factors
Male
Ankylosing spondylitis
Cemented femoral stems
History of HO
Surgical approach
Herzberg et al Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 2024
- systematic review of 26 studies and 6500 THA
- increased risk of HO with lateral approach
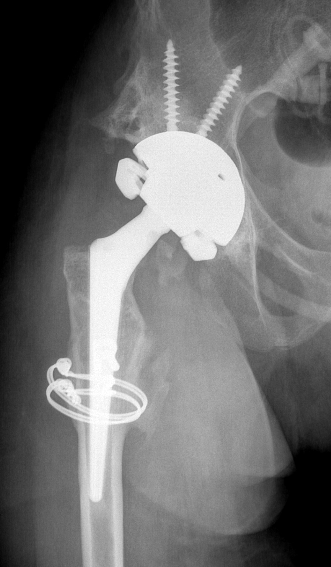
Brooker Classification: Type III and Type IV clinically relevant
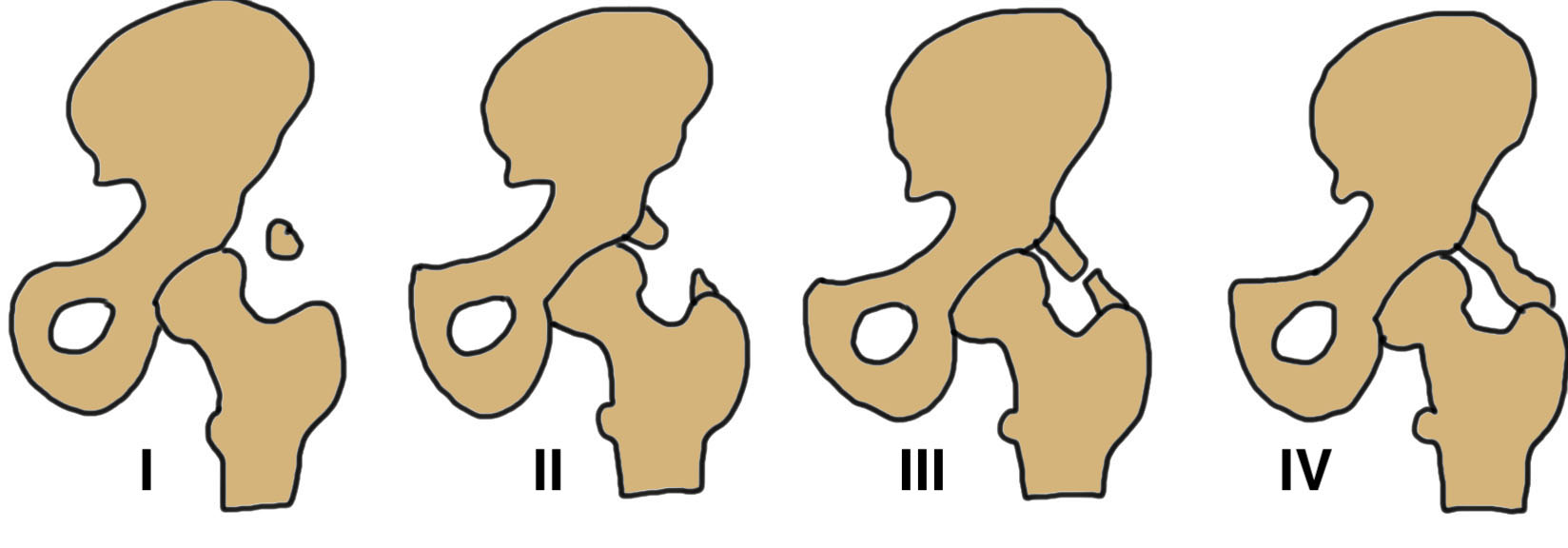
Type I: Isolated islands of bone
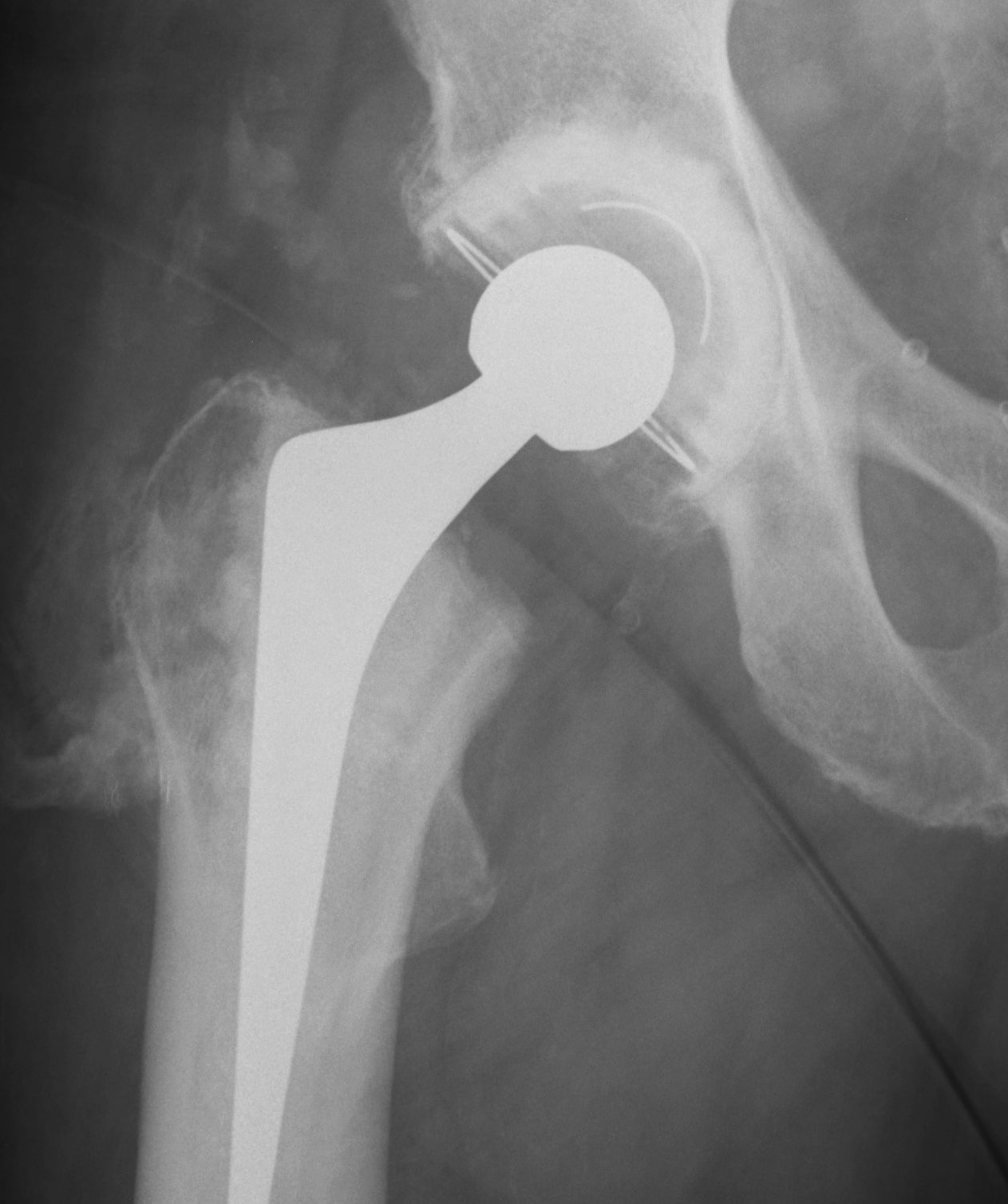
Type II: Bony spurs from pelvis and proximal femur, gap > 1 cm
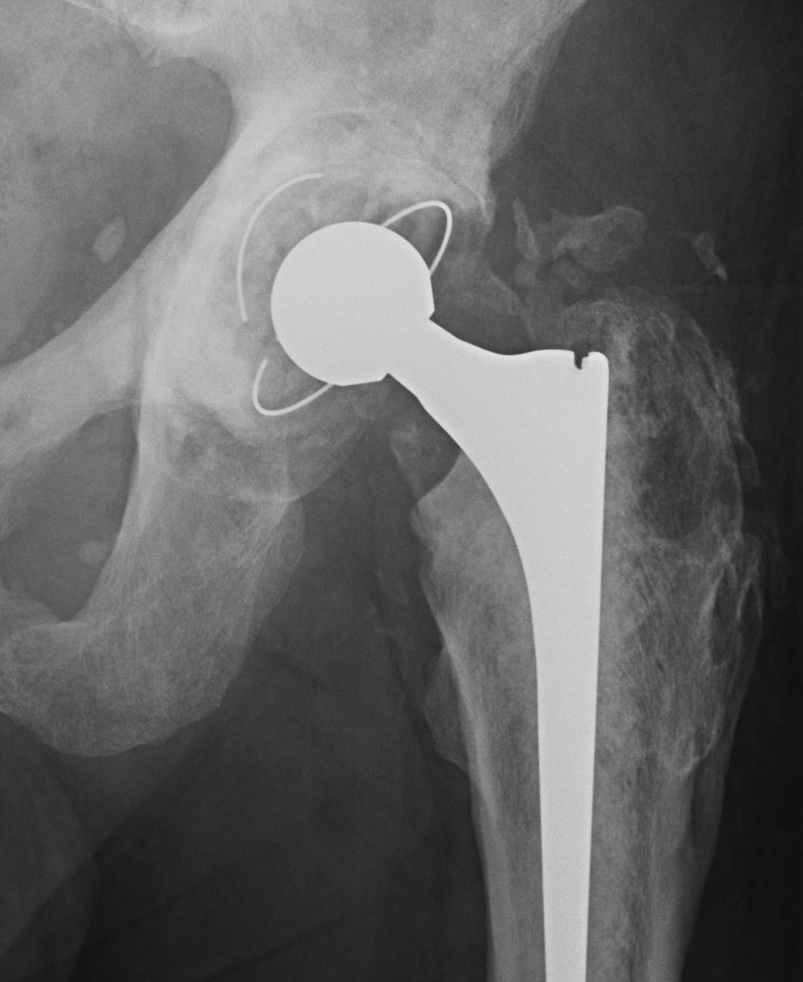
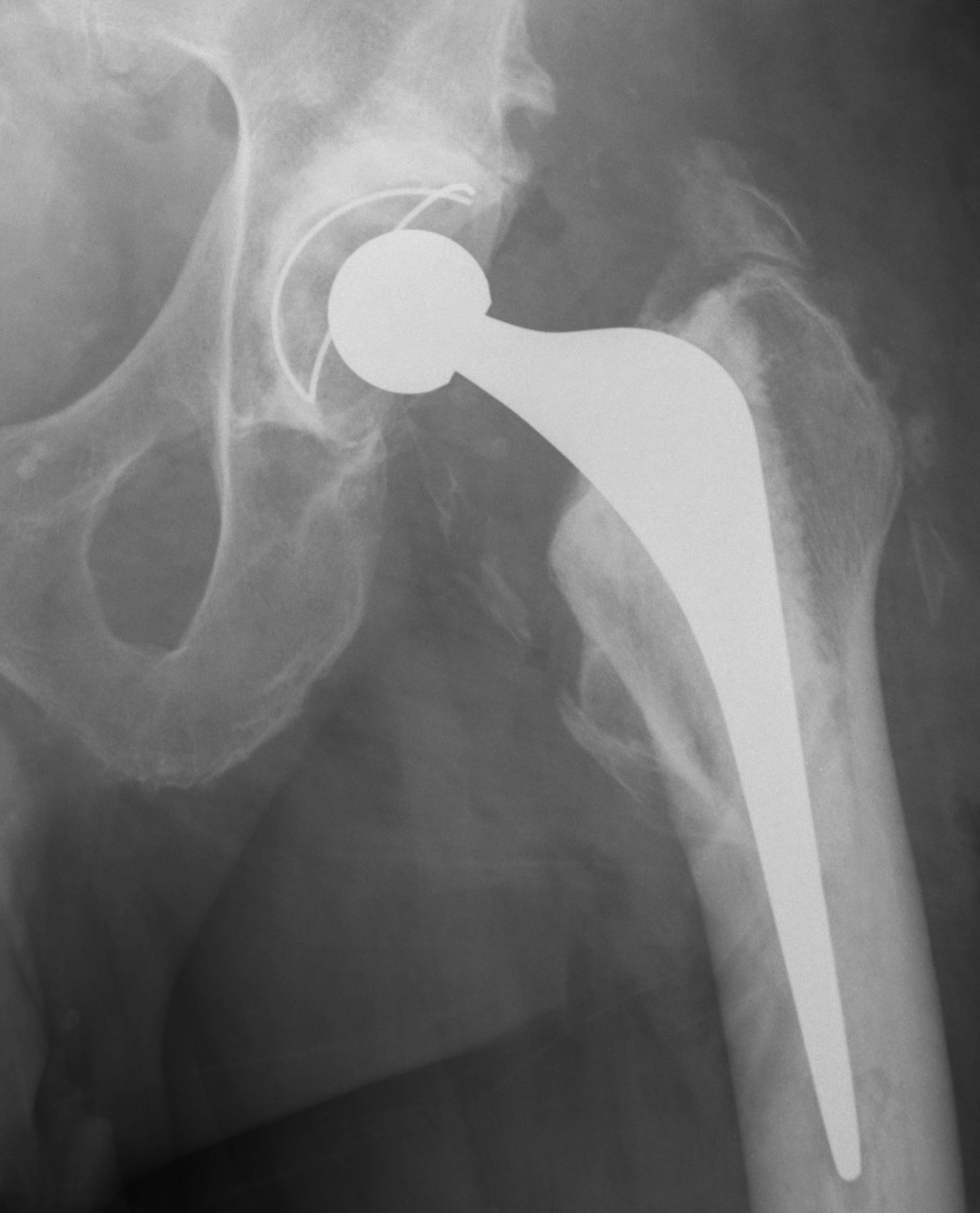
Type III: Gap < 1 cm
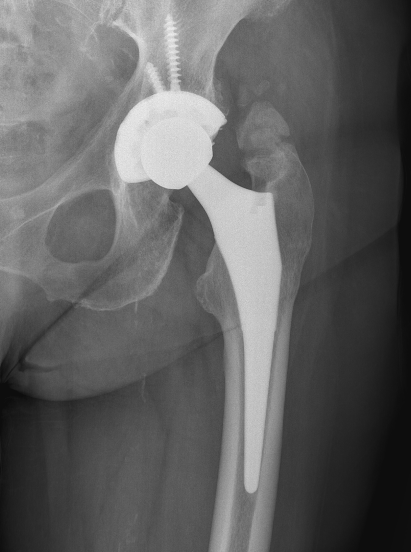
Type IV: Apparent ankylosis
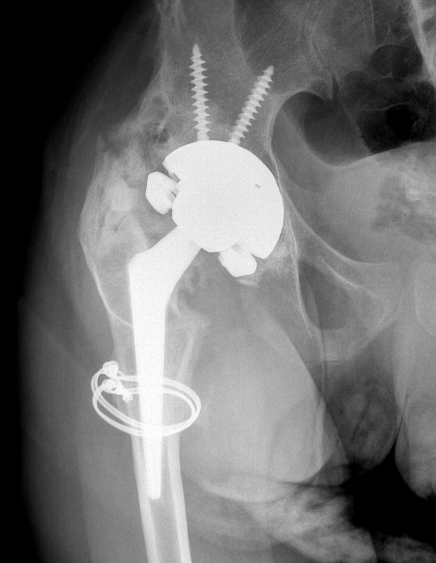
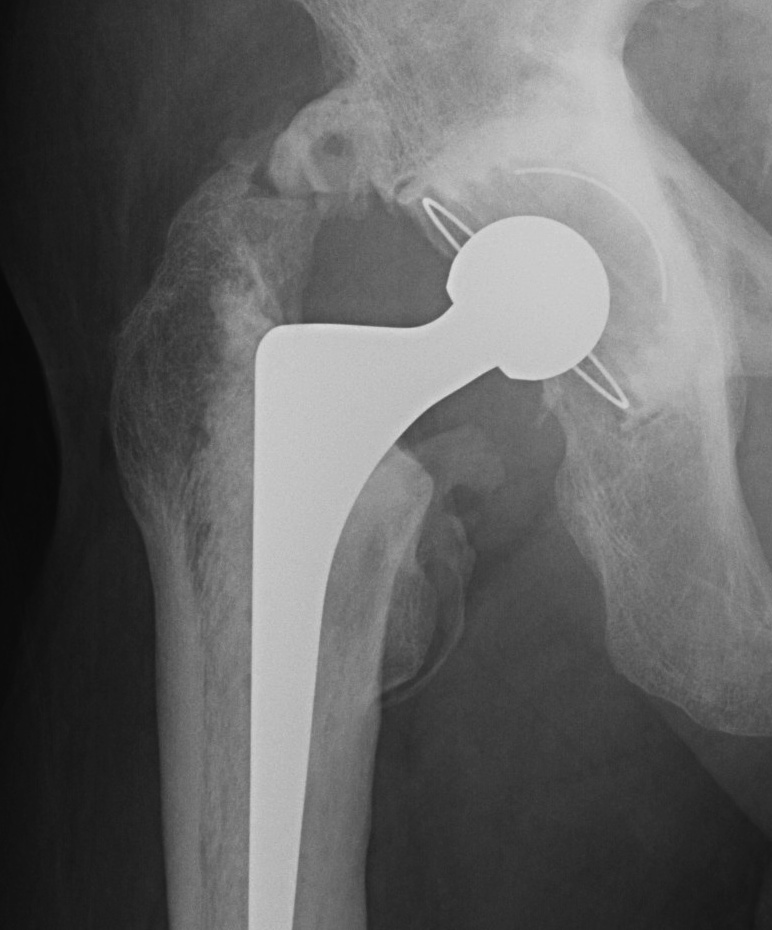
Clinical
Usually asymptomatic
Brooker III / IV - stiffness
Other
- pain
- sciatic nerve irritation
- dislocation secondary to impingement
Natural history
Willburger et al J Orthop Surg Res 2022
- 75 THA followed for 10 years
- took up to 3 years for all HO to mature
Prevention
Indications
High risk patients
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
- previous HO
- Pagets / DISH
Options
NSAIDS
Radiotherapy
Results
- systematic review of NSAIDS versus radiotherapy in high risk THA
- severe HO with radiotherapy: 0 - 12%
- severe HO with NSAIDS: 0 - 2%
Anti-inflammatories / NSAIDS
Indomethacin / Ibuprofen
- 1200 patients post THA
- no patient with indomethacin or ibuprofen developed Brooker III or IV
Diclofenac
- meta-analysis of diclofenac in 6 RCTs and 1000 THA
- diclofenac effective
- no clinically significant HO (Brooker III and IV)
COX-2 inhibitors
- meta-analysis of 8 RCTs and 1600 THA
- selective COX2 inhibitors as effective as non selective NSAIDS
- reduced gastrointestinal effects with selective COX2 inhibitors
Radiotherapy
Indication
Very high risk patients
- previous HO
- NSAIDS contraindicated
- post surgical excision of HO
Dosing
Milakovic et al Radiother Oncol 2015
- systematic review
- no difference low dose (<25Gray) versus high dose (>25Gray)
- typically single dose of 7Gy
Timing
- within 3 hours before or 3 days after
Results
- meta-analysis of 10 RCTs and 1200 patients
- efficacy of both pre- and postoperative radiotherapy at prevention
- multiple fractions more effective than single fractions
Sheybani et al Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2014
- case control of 3500 patients
- no evidence of increase malignancy with radiotherapy for HO prevention
Biphosphonates
Doesn't prevent osteoid formation
- delays calcification and xray appearance of bone
- calcification occurs once drug stopped
- no longer used
Surgical Excision

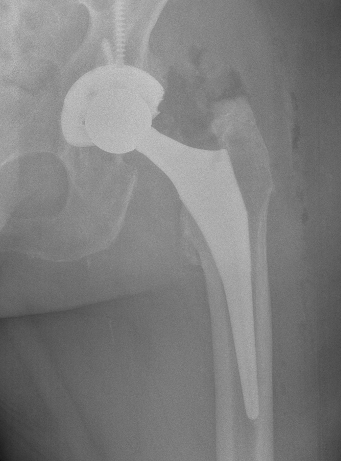
Indications
Significant symptoms / reduced ROM
Brooker III / IV
Timing
Mature HO
- cold bone scan
- serum ALP normal
Prophylaxis
Radiotherapy postoperatively as high risk
Technique
Results
Lachiewicz et al J Arthroplasty 2022
- systematic review of 7 studies and 4 patients with grade III/IV HO
- good improvement in ROM
- inconsistent improvement in pain
- irradiation prevented recurrence