Definition
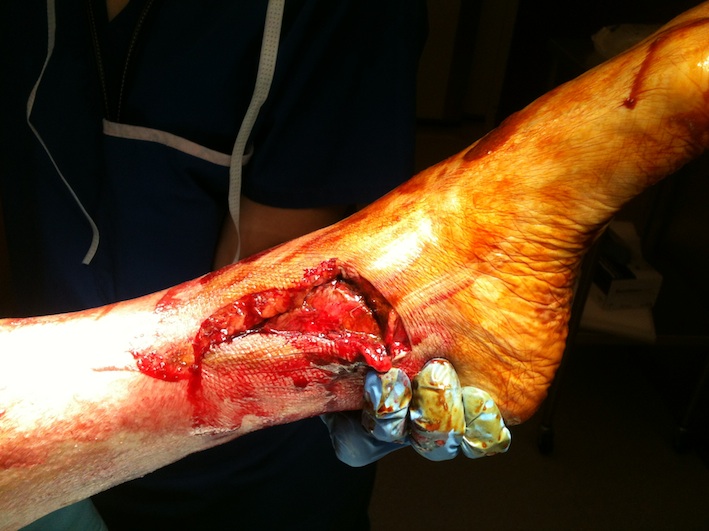
Tibial facture with break in skin
- open wound communicating with fracture or haematoma
Patient is immediately at higher risk of deep infection
Diagnosis
Wound continuously oozes dark red fracture haematoma
Epidemiology
Up to 1/4 of tibia fractures open
Gustilo and Anderson Classification
Type 1
- wound < 1cm
- usually inside out
- minimal muscle contusion
Type 2
- skin laceration 1-10 cm
Type 3a
- > 10 cm wound, able to be closed primarily
Type 3b
- require skin graft procedure for coverage
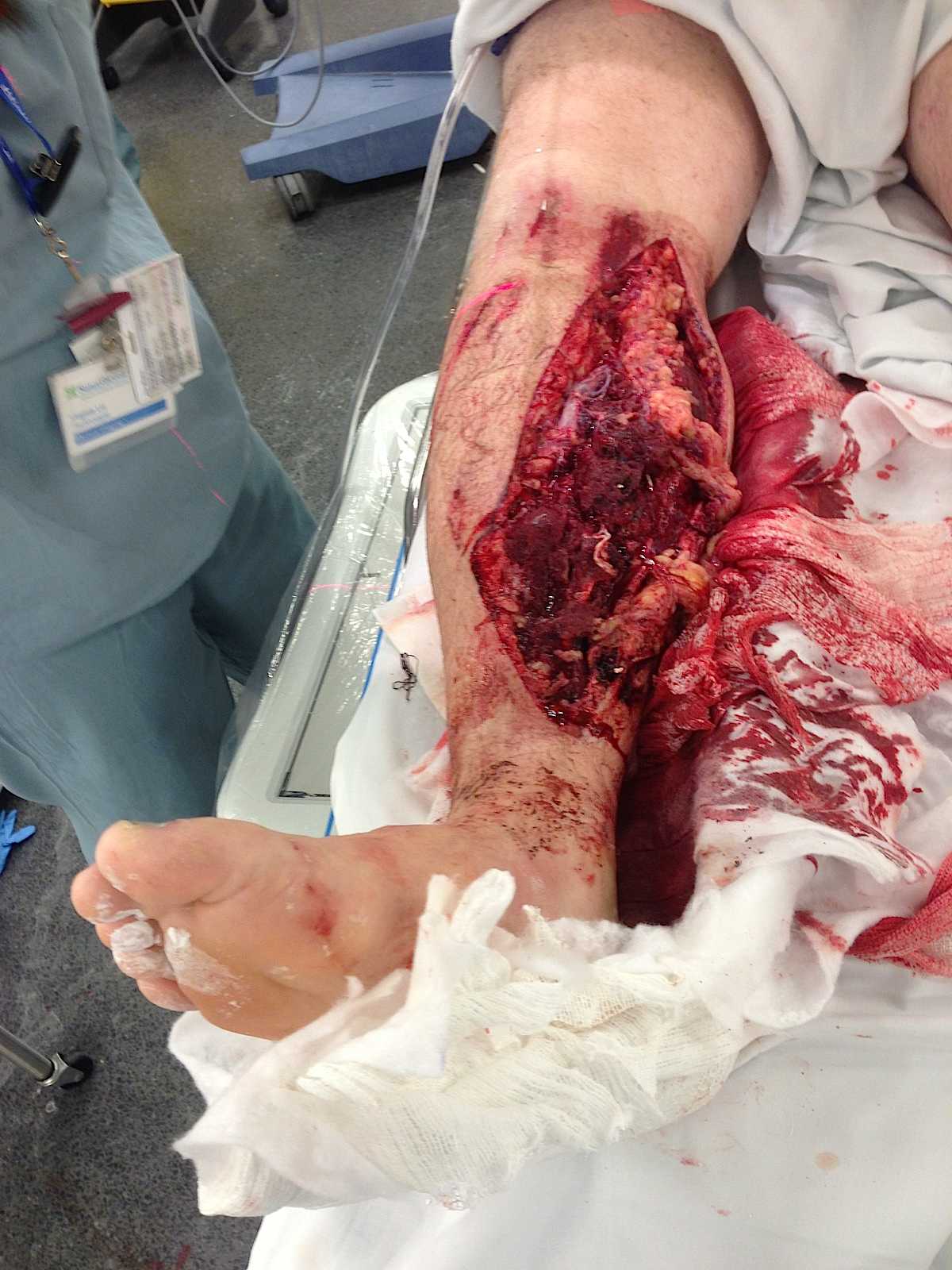
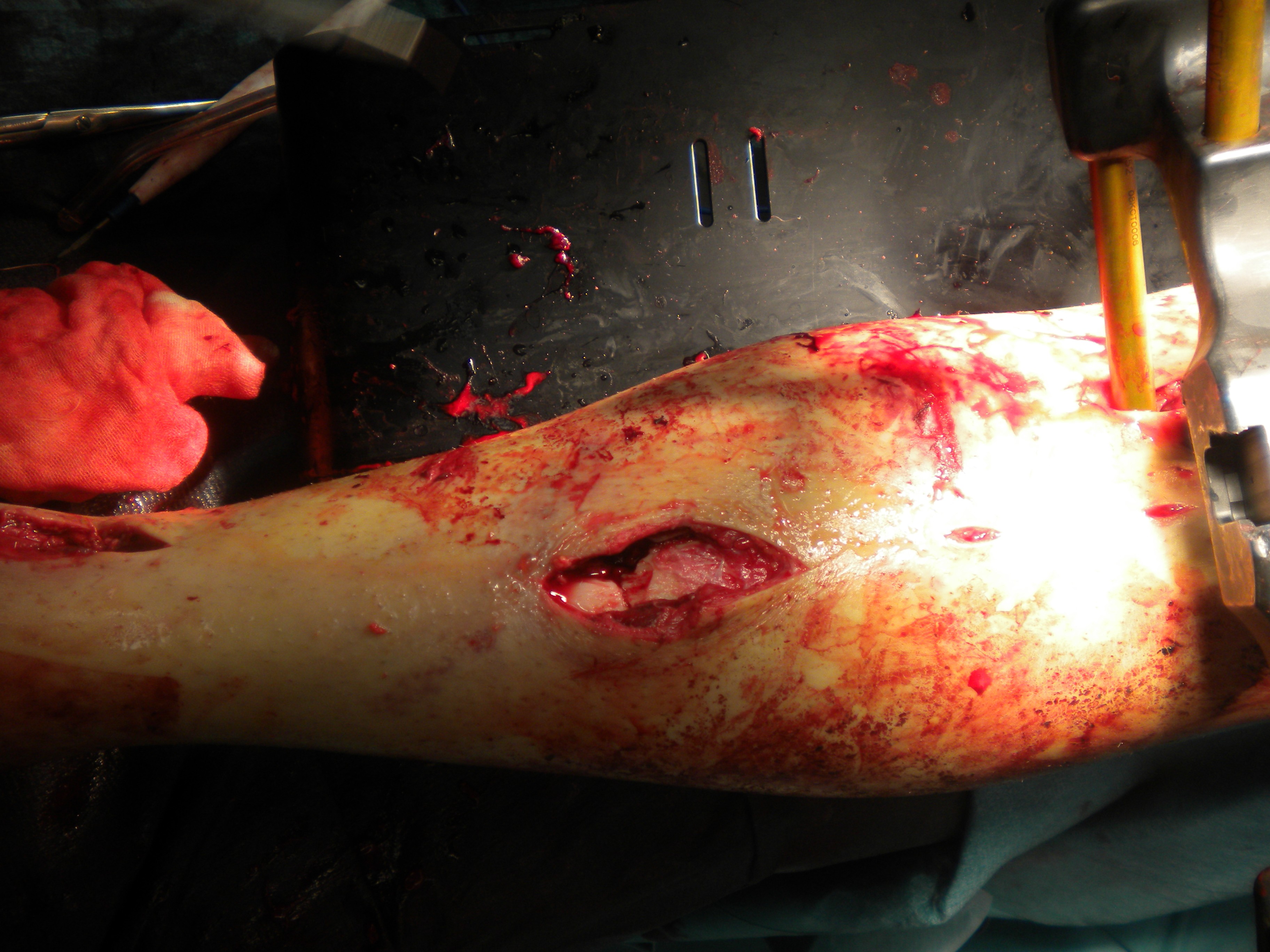
Grade 3c
- vascular injury requiring repair
Management
Immediate / ED Management
EMST / ATLS
- assess and manage entire patient
Assess neurovascular status
Assess wound
- size / site / contamination
- photos very useful to show plastic surgeons
- will it close primarily / will it need plastic surgery
Appropriate Antibiotics
- as per Gustilo Classification
ADT
Wound management
- irrigation
- betadine dressing
Stabilise fracture
- POP
Wound Debridement < 6 hours
Surgical timing
Debridement
Prodromidis et al. J Orthop Trauma 2016
- meta-analysis of 7 studies looking at early (<6 hours) v late (> 6 hours) surgical debridement
- no difference in deep infection or nonunion rates
- suggest that delay when necessary can be appropriate
Skin flap coverage
D'Alleyrand et al J Orthop Trauma 2015
- 69 open tibial fractures requiring flap coverage
- no difference infection flap < 7 days
- 11% increase in complications for every day after 7 days
Surgical Technique
Extend wound
- debride contaminated tisue
- 1 mm skin edge excision
- debride subcutaneous tissue
- deliver and debride bone ends
Assess muscle by 4C's
- Colour
- Consistency
- Contractility
- Capacity to Bleed
Bone
- remove avascular fragments unless very large or critically important
- avascular bone in continuity with vascularized bone can be kept
Washout
- pulse lavage to decrease bacterial contamination
- 9 litres
- photos
Wound management
- close if able without soft tissue tension and clean
- if needs SSG / muscle flap / free flap
- alert plastics immediately
- needs closure within 5 days for good outcome
Skeletal Stabilization
A. Cast
- increased non and mal union in cast groups
B. Temporary unilateral external fixator
Indications
1. Vascular repair
- apply swiftly
- place out of way of vascular repair approach
2. Highly contaminated wound
- inappropriate for metal work
- multiple debridements / skin closure
- eliminate infection
- delayed definitive management
3. Multiple injuries patient / Damage control orthopedics
- temporary external fixator
- convert to nail day 5
A. External fixator for tibial midshaft
Vumedi
https://www.vumedi.com/video/tibial-ao-external-fixeter-application/
C. Tibial nail
Indications
- fracture configuration suitable for nailing
Reaming
- of benefit in closed fractures
- may be no difference in open fractures
- as the ST injury worsens the benefits of reaming decreases
Swiontkowski JBJS Am 2008
- SPRINT trial
- no difference in outcome in compound fractures between reamed and unreamed nails
Bhandari et al JBJS Br 2001
- systemic review of treatment for open tibial fractures
- compared unreamed nails and external fixators
- unreamed nails decreased reoperations / superficial infections / malunions
D. Ilizarov frame
Indication
- bone defects which will need addressing
Soft Tissue Envelope
Godina Yugoslavia 1986
- 532 patients free flaps
Gp 1 - within 72hrs
Gp 2 - 72hrs - 3/12
Gp 3 - 3/12 - 12.6yrs (average 3.4 years)
| Flap Failure | Infection | Union | |
| Group 1 | 0.75% | 1.5% | 7 months |
| Group 2 | 12% | 17.5% | 12 months |
| Group 3 | 9.5% | 6% | 29 months |
Management of Soft Tissue
Definitive coverage within 7 days
Type 1, 2, 3a close with DPC
Type 3b
- 94% will require plastics
- 71% require flap cover
Skin Cover Options (see separate article)
- SSG if muscle present over wound
- proximal third gastrocneumius local muscle flap
- middle third soleus muscle local flap
- distal third / gastrocneumius or soleus damaged - free gracilis muscle flap
Management Bone defects
Priniciple is to decrease dead space
ABx beads
- may decrease infection from 16% to 4% (OTA)
- prevent haematoma and scar
- can place flap over top
Can place segmental Abx cement
- new French technique
- at 6/52 there is a periosteal sleeve about the cement
- aids in bone grafting techniques
Delayed bone reconstruction options
- see Complications / Segmental Bone Loss
Union Rates
Court-Brown JBJS 1991
Type 1
- good union rates
Type 2, 3a
- high union rates but slower
- 6 - 7 months to unite
- deep infection 3.5%
Type 3b
- union time 1 year
- infection rates 17-23%
- not affected by reaming
- not affected by nail v external fixator
- very dependent on ST coverage
Court-Brown
- a lot of effort has gone into assessing the mechanics of fracture management
- it is the treatment of ST that governs prognosis
Indications for Amputation
Absolute indications (Lange) with arterial injury
1. Crush injury with warm ischaemia > 6 hours
2. Anatomic division of the tibial nerve
Scoring Systems
- MESS
- NISSA (nerve, ischaemia, shock, soft tissue, age)
- shown not to be predictive
Leap Study
- plantar parasthesia non predictive of outcome
- doesn't predict function of tibial nerve
- many will recover over time
See Principles of Trauma / Amputation
Ng et al, Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2023
- Meta-analysis of 645 patients with Gustilo IIIB/C tibia fractures
- Primary amputation had fewer complications (RR = 0.21), infections (RR = 0.46) and total number of operations (-4.17), and ambulated earlier
- Functional outcomes similar
Complications
Non-union
No progression of union over 3/12
Rule out infection
Options
1. Dynamise
2. Exchange nail
3. Bone Graft
4. Fib Osteotomy
5. Ring fixator
Deep Infection
Options
1. Reamed exchange nail
2. Excision dead bone and necrotic tissue / Ilizarov frame
- elimination dead space
- ST coverage
- appropriate Abx
- delayed bone grafting