Complications
Nerve injury 1%
Infection 1%
Instability / dislocation 0.7%
Acromial and scapula spine stress fractures 4%
Peri-prosthetic fracture
Loosening
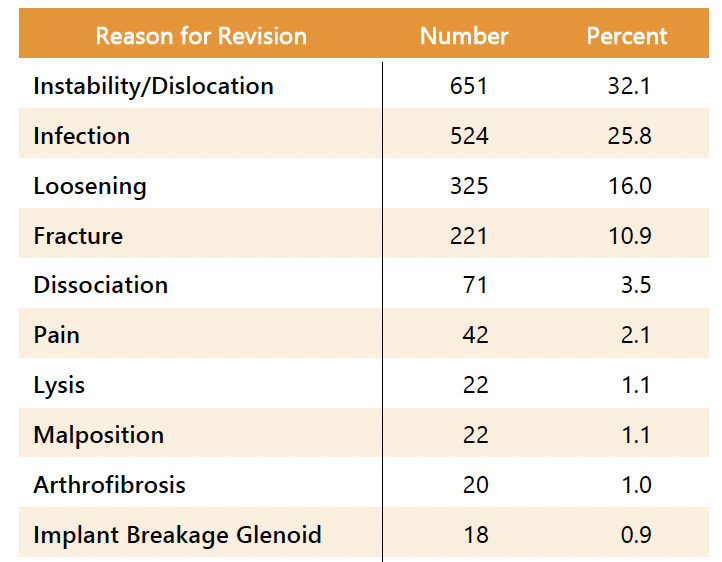
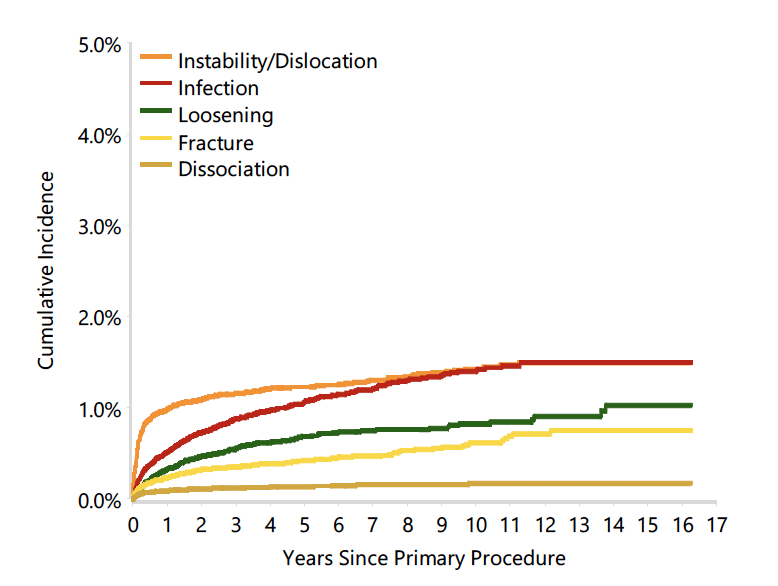
Incidence of complications
Galvin et al J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2022
- systematic review of 52 studies and 5800 rTSA
- complication rate 9%
- infections 1%
- periprosthetic fracture 1%
- dislocation 0.7%
- scapular notching 14%
Australian Joint Registry 2024
Nerve injuries
Incidence
Thought to be more prevalent with rTSA than aTSA due to increase stretch of plexus
North et al J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2023
- systematic review of 40,000 rTSA
- overall incidence nerve injury 1.3%
- higher in revision cases and rTSA for fracture patients
- axillary nerve > ulna nerve > median nerve > brachial plexus

Infection
Diagnosis
Elevated ESR > 30 mm/h
Elevated CRP level > 10 mg/L
Aspiration
- positive tissue culture
- synovial neutrophil percentage > 80%
- synovial WBC count > 3000 cells/μL
Bacteria
- systematic review of infection after shoulder arthroplasty
- Cutibacterium acnes 39%
- Staphylococcus aureus at 15%
- Staphylococcus epidermidis at 15%
Management acute infections
Washout and implant retention
- systematic review PJI shoulder arthroplasty
- 38 acute infections managed with washout
- 50% failure rate
Management chronic infections
One versus Two-stage revision
- systematic review PJI shoulder arthroplasty
- 161 cases One-stage revision versus 325 cases with Two-stage revision
- One-stage: reinfection rate 6%, complication rate 13%
- Two stage: reinfection rate 11%, complication rate 22%
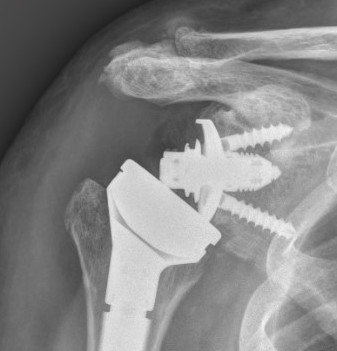
Instability / Dislocation

Early dislocation issues
| Soft tissue tension | Axillary nerve palsy | Component position | Component size |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Humeral distalization - increased liners - longer humeral body |
Inferior base plate / inferior impingement
|
Increased glenosphere size increases jump distance | |
|
Glenoid lateralization - lateralized glenosphere |
|||
| Subscapularis |
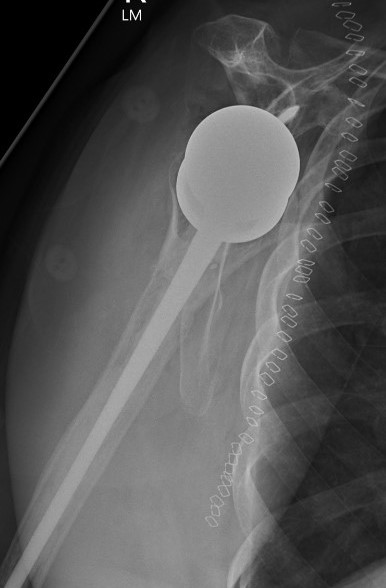
Late dislocation
Liner wear
Heterotopic ossification
Revision
- revision for instability in 36 rTSA
- glenoid sided revision: 66% successful
- humeral sided revision: 66% successful
- bipolar revision: 90% successful
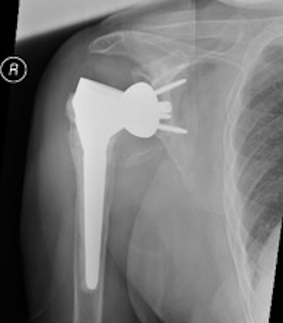
Inferior scapula notching

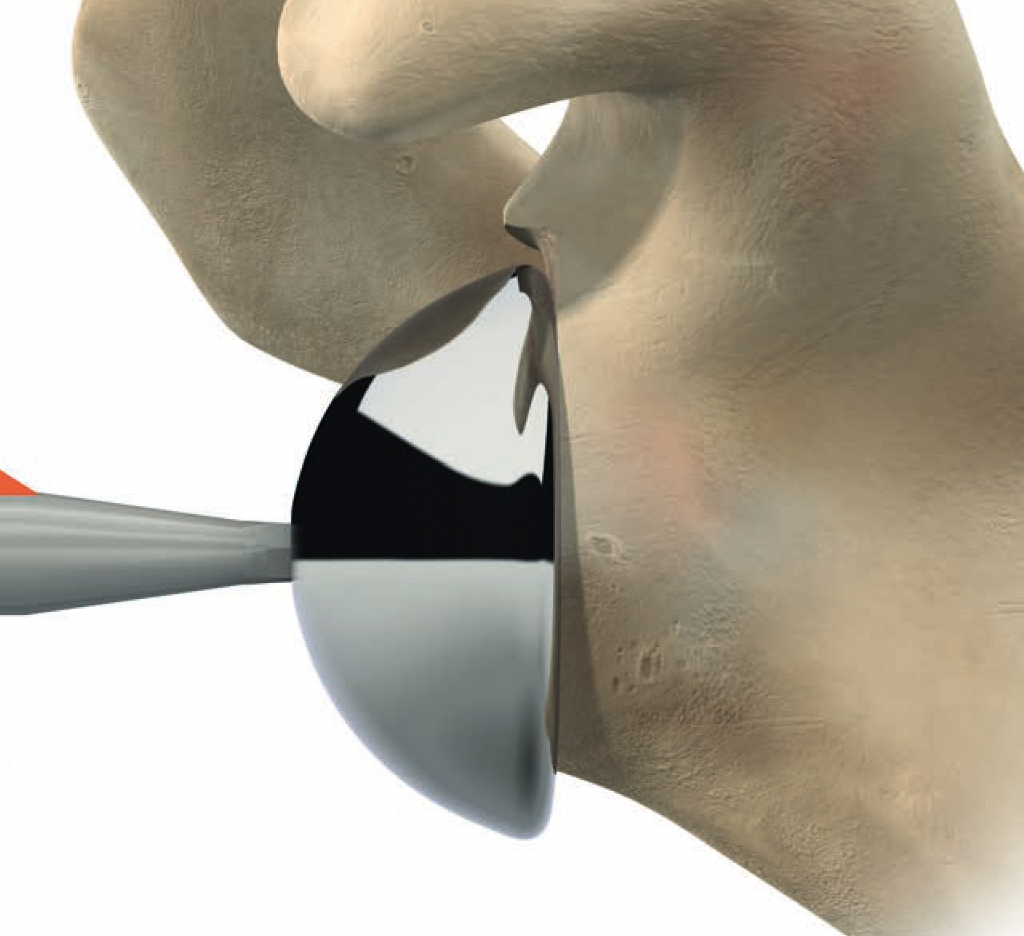
Scapula notching. Prevented by inferior glenosphere overhand (Depuy Synthes Delta Xtend)
Mechanism
Impingement of humerus component on scapular neck
With arm in extension / adduction / external rotation
Prevention
Glenosphere position
- inferior hang - eccentric glenosphere design
- inferior tilt
- lateralization
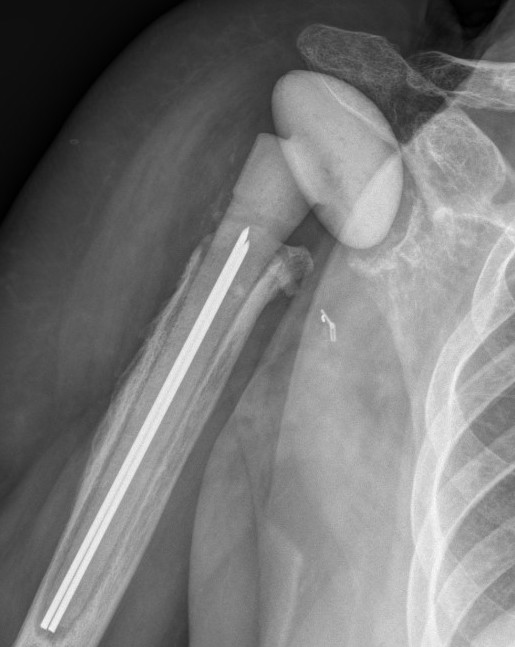
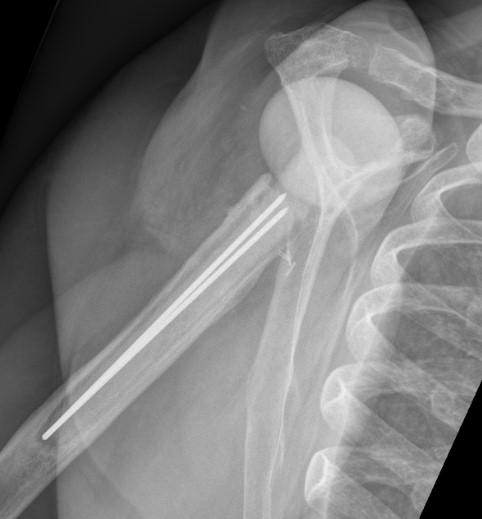
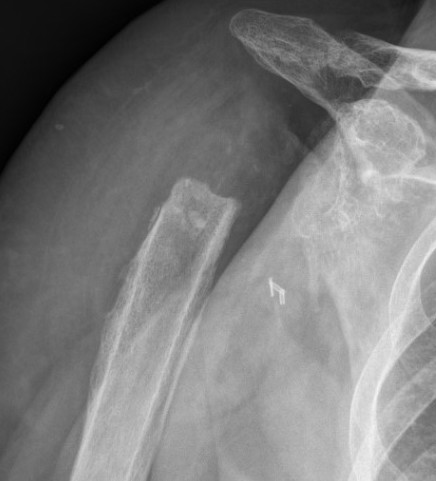
Acromial / scapular spine stress fractures
Incidence
- systematic review of rTSA
- incidence 2.8%
- more common with lateralized glenosphere
Usually within first year
Associated with worse clinical outcomes
Cause
- over tensioning deltoid from over lengthening arm / distalizing humerus
- increased risk in women / osteoporosis
- increased risk with superior screw towards scapular spine instead of coracoid
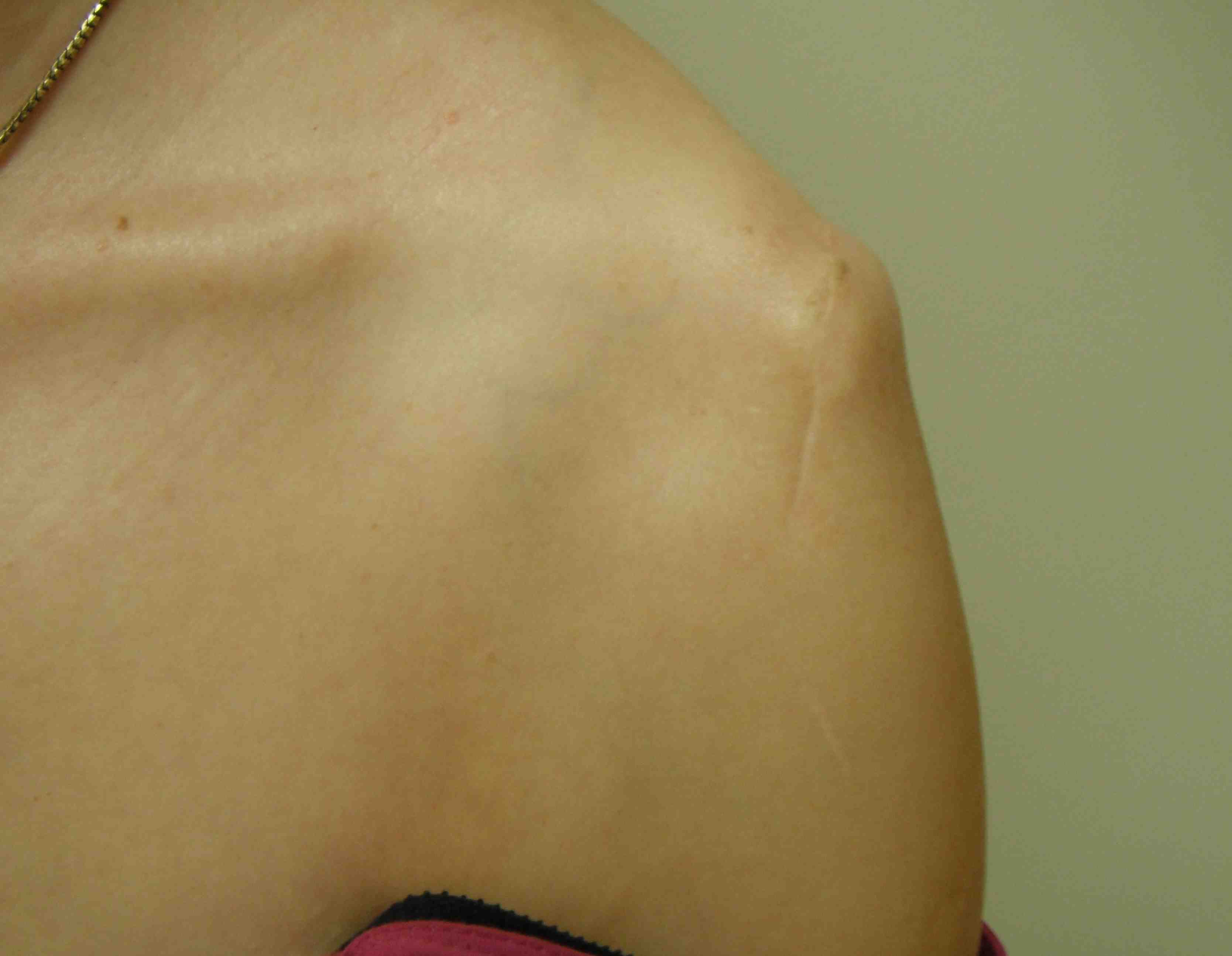
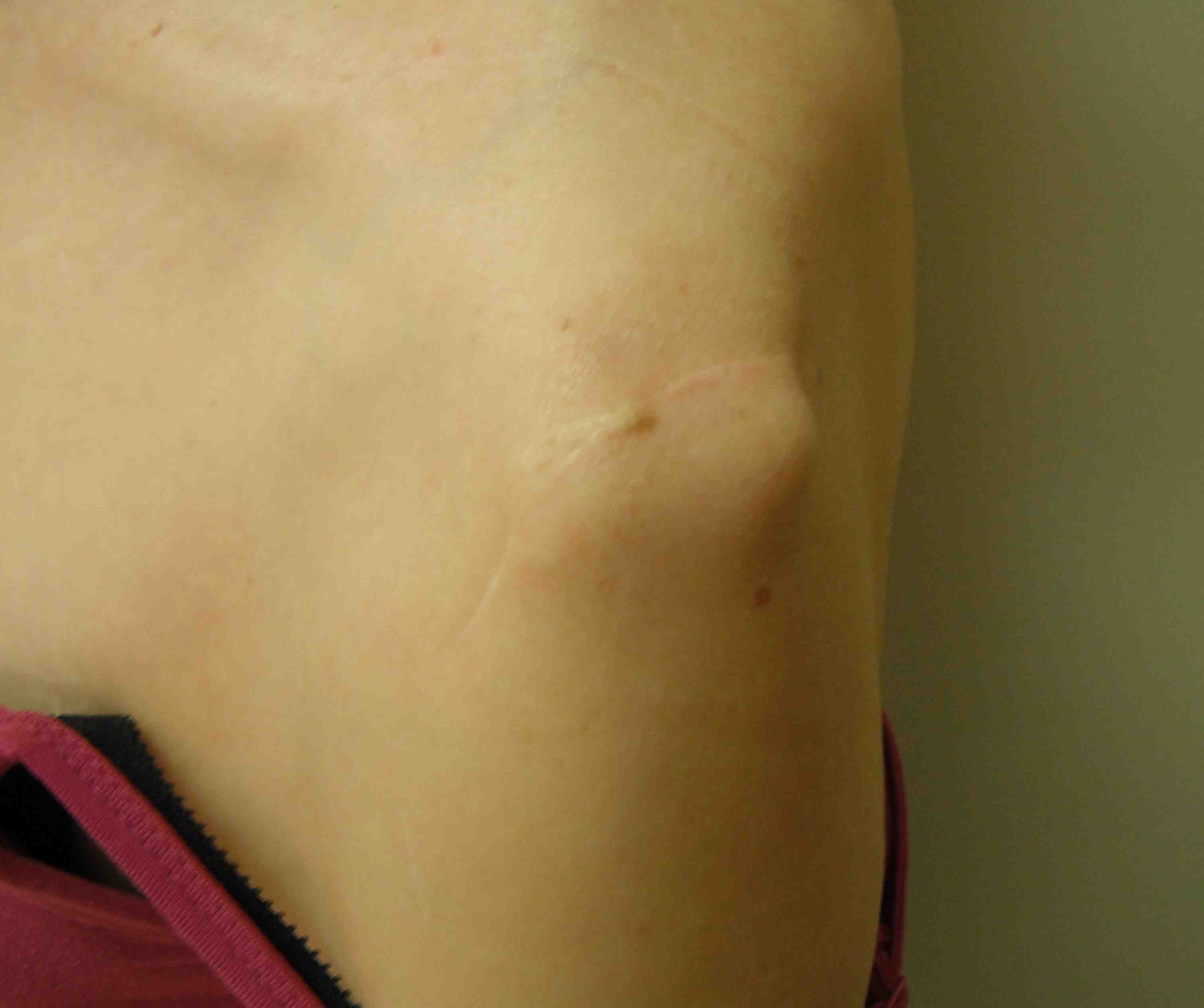
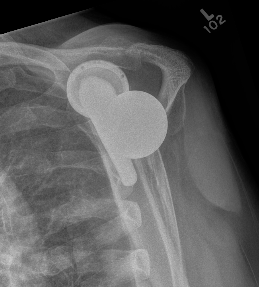
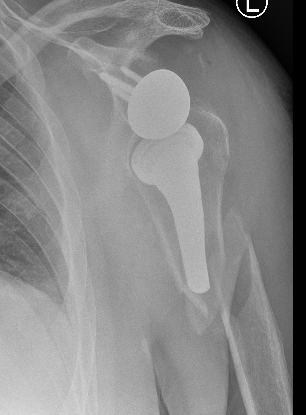
Overlengthened arm post rTSA
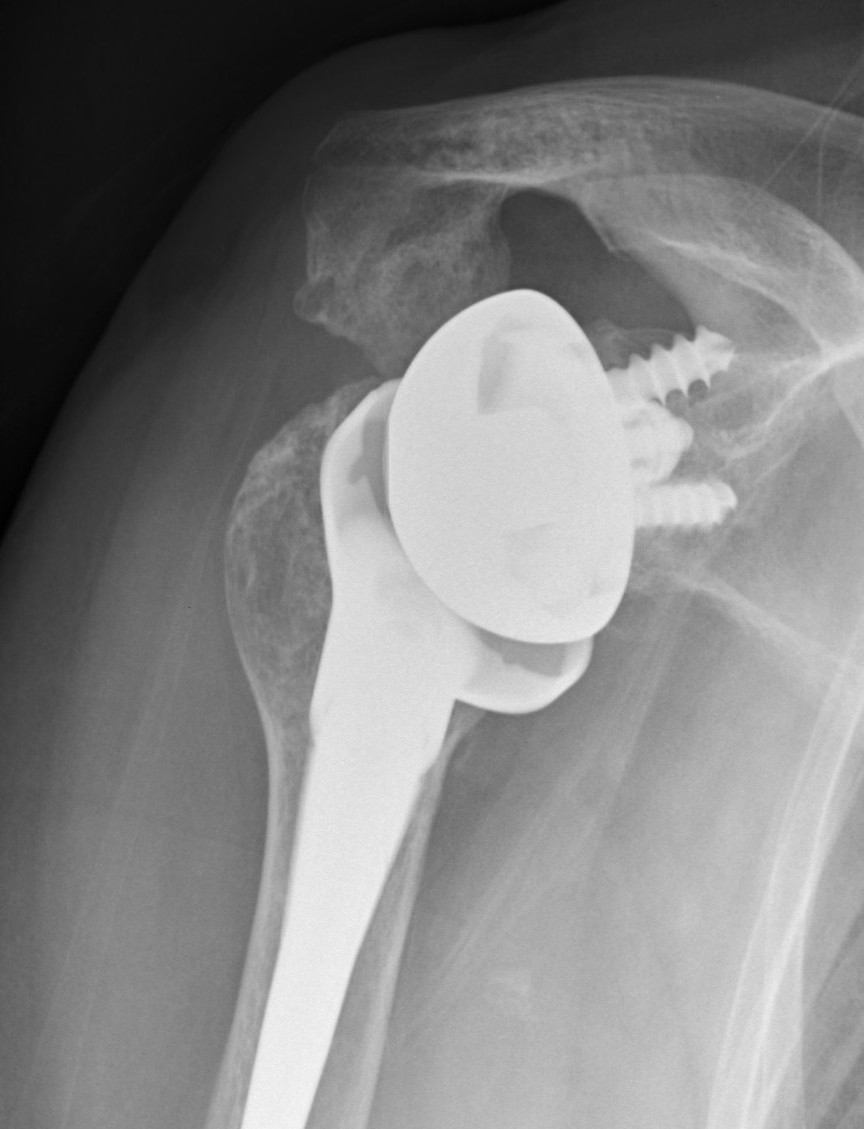
Acromial stress fracture on xray
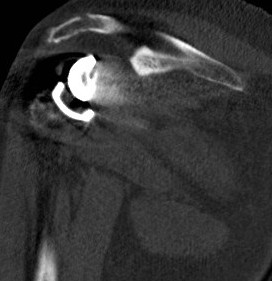
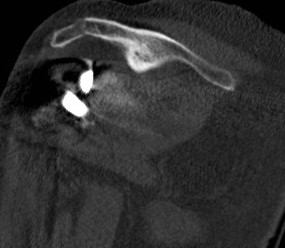
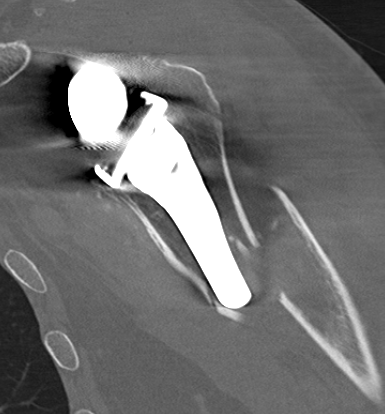
CT demonstrating acromial stress fracture
Levy Classification
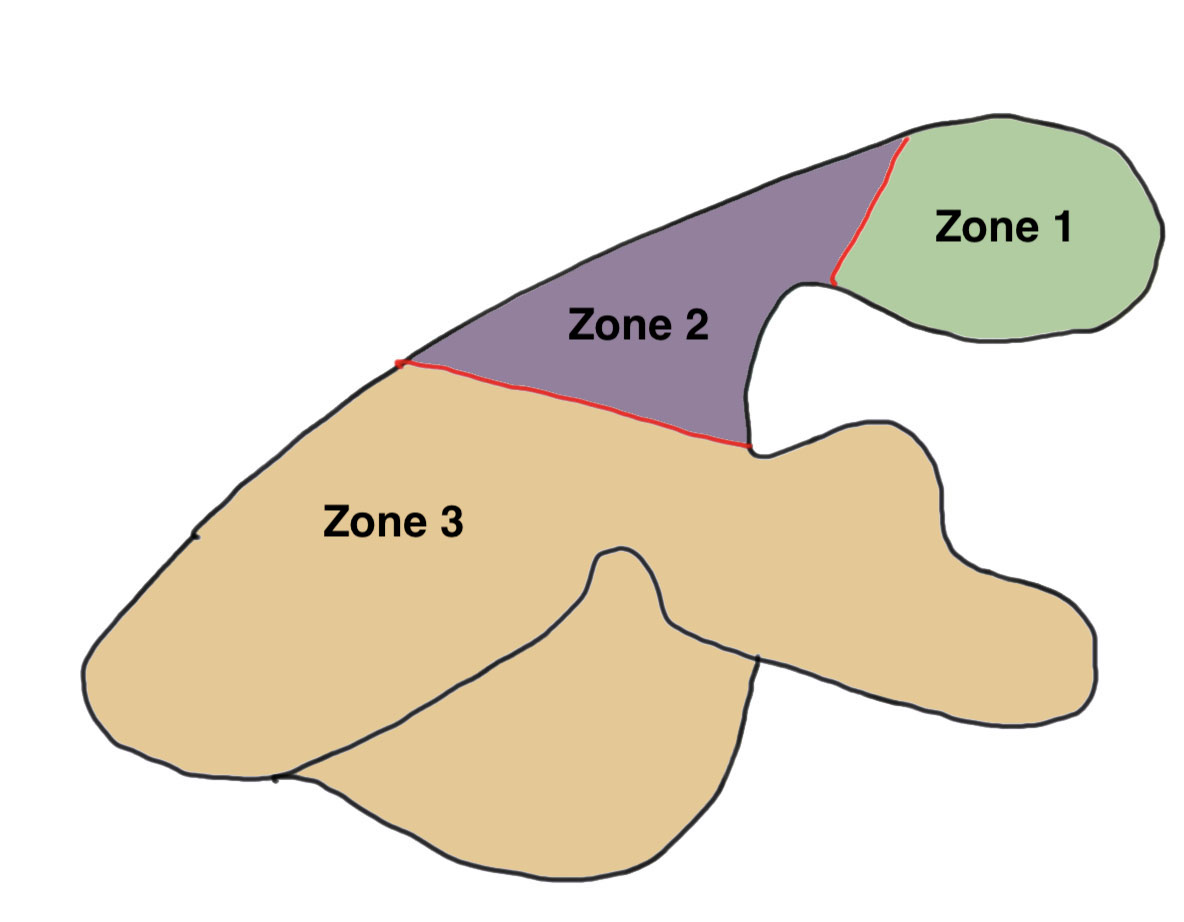
Nonoperative management
Cui et al J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2023
- systematic review of nonoperative management of acromial and scapular spine stress fractures
- worse outcomes than controls / non stress fracture rTSA patients
- worst outcomes with scapula spine fracture / Levy III
Operative management
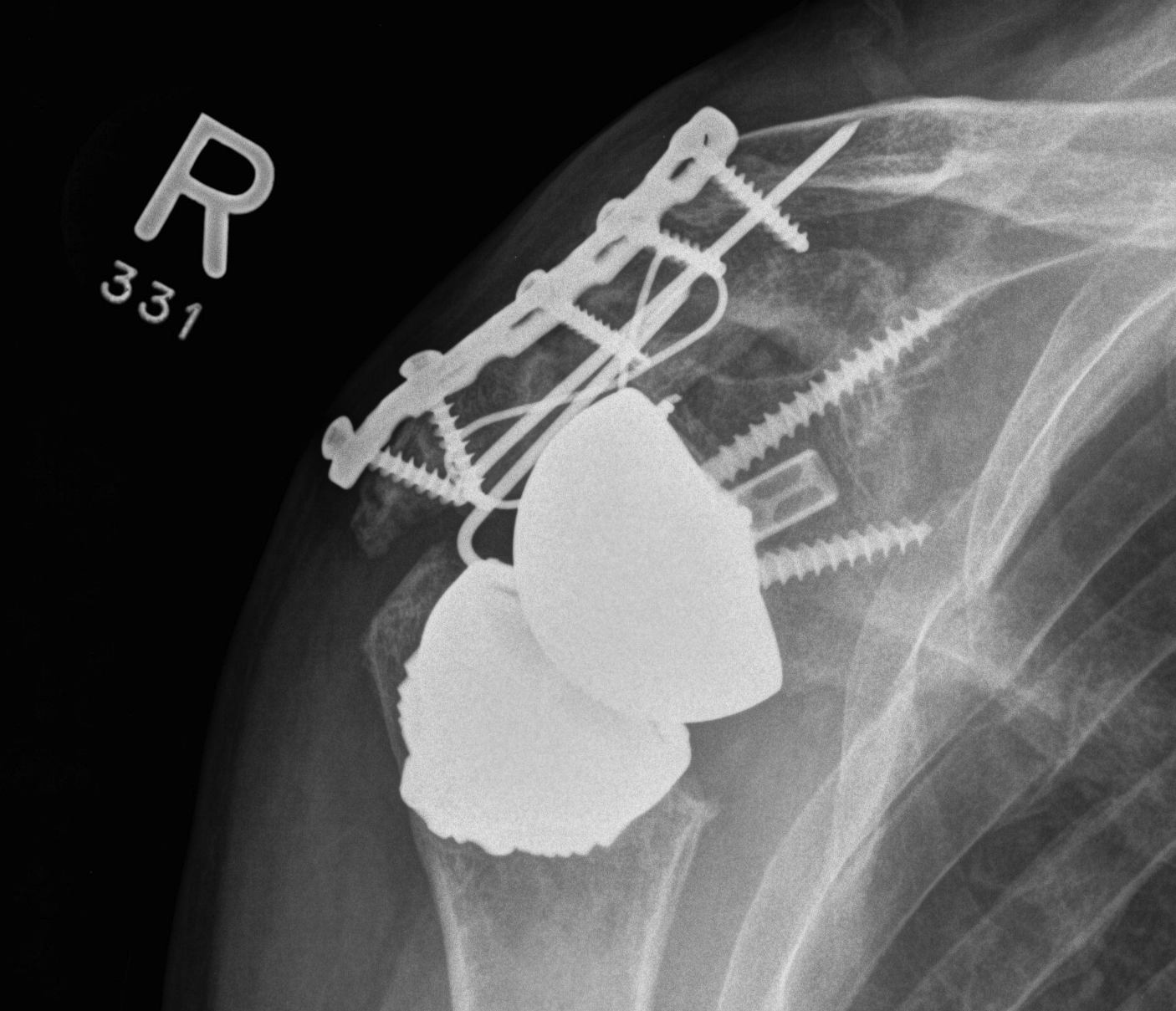
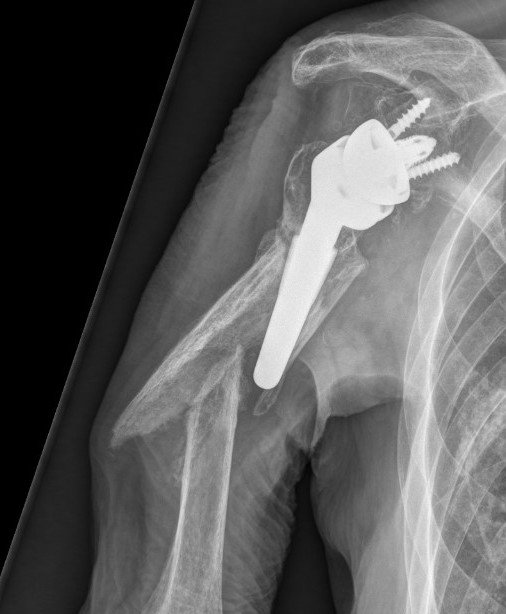
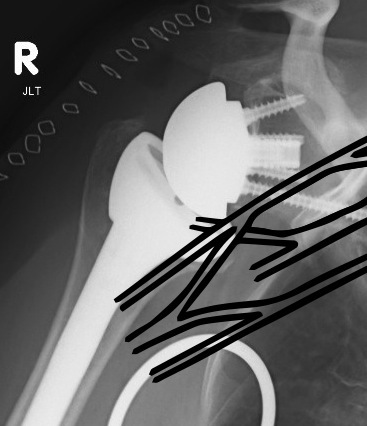
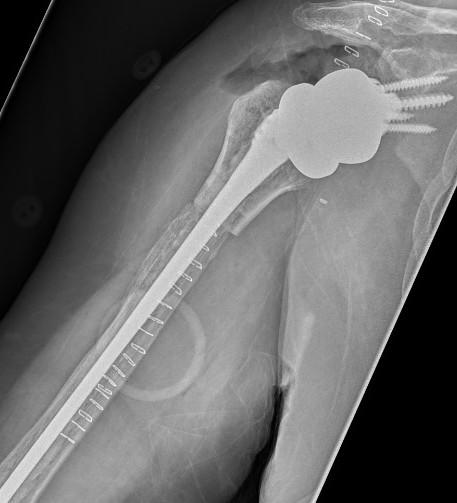
Periprosthetic fracture
Intra-operative glenoid fracture 0.4%

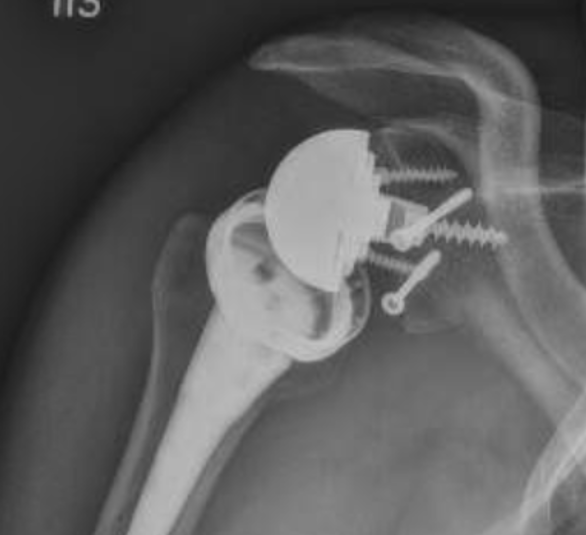
Humeral shaft fractures
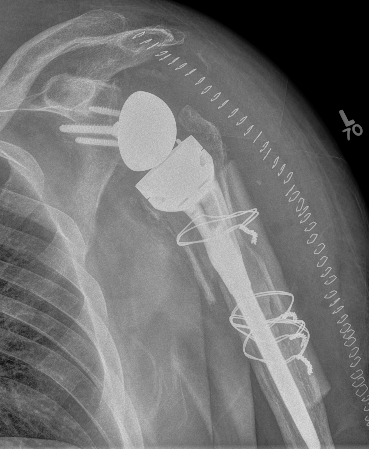
Stable humeral component treated with ORIF
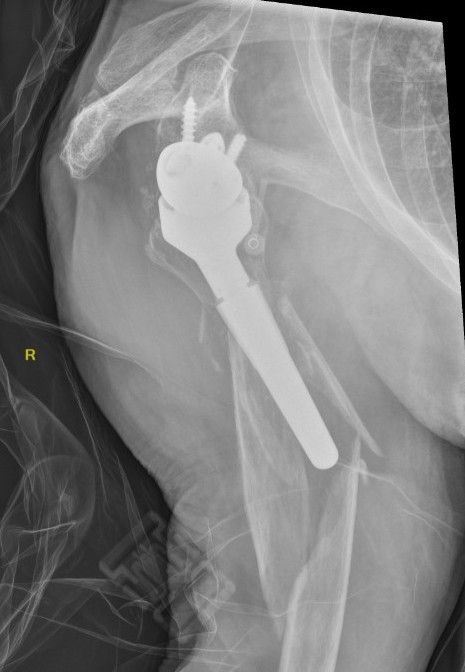
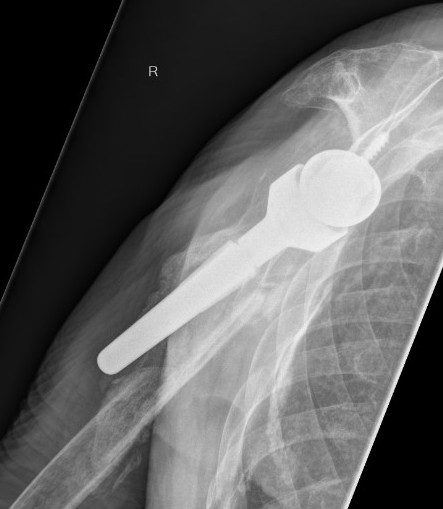
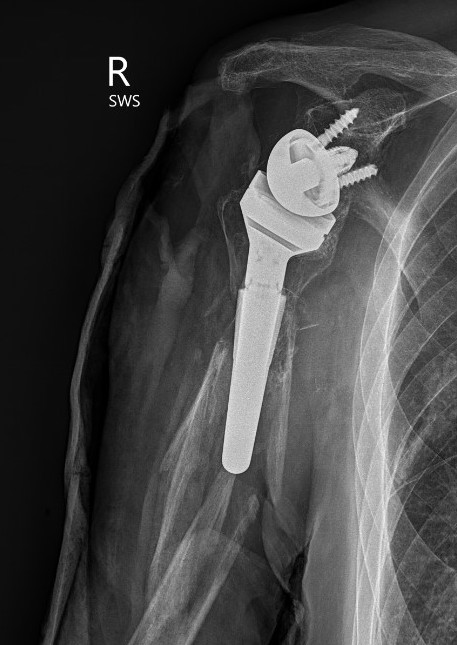
Unstable humeral component
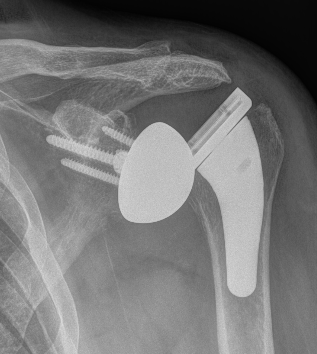
Loosening
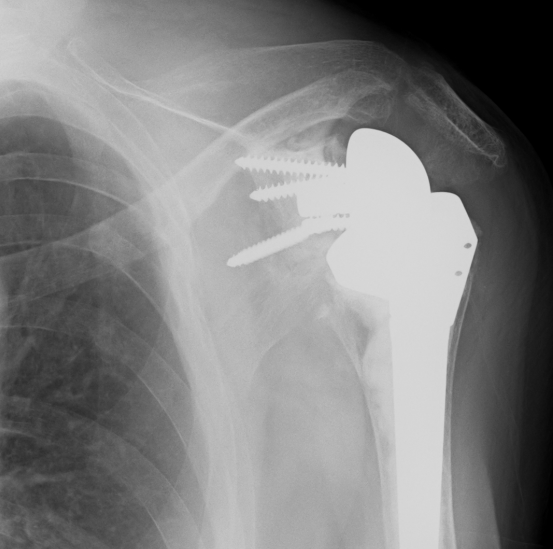
Loose metaglene
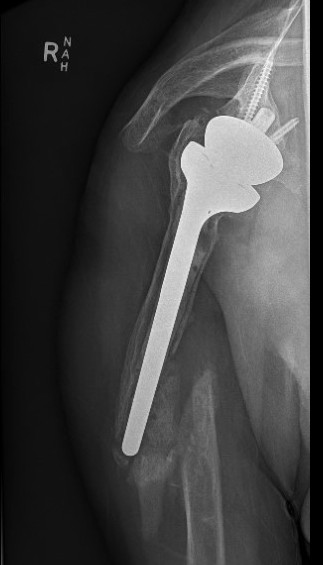
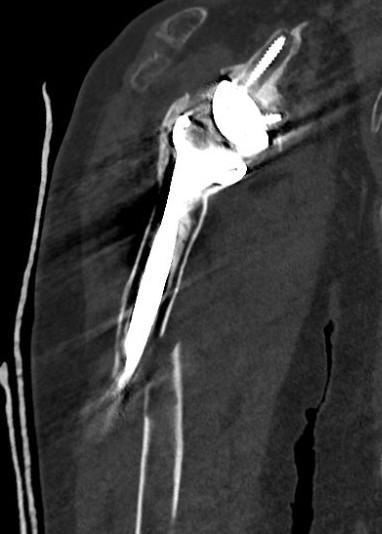
Lysis around humeral and glenoid component

Glenosphere loosening from metaglene
