Approaches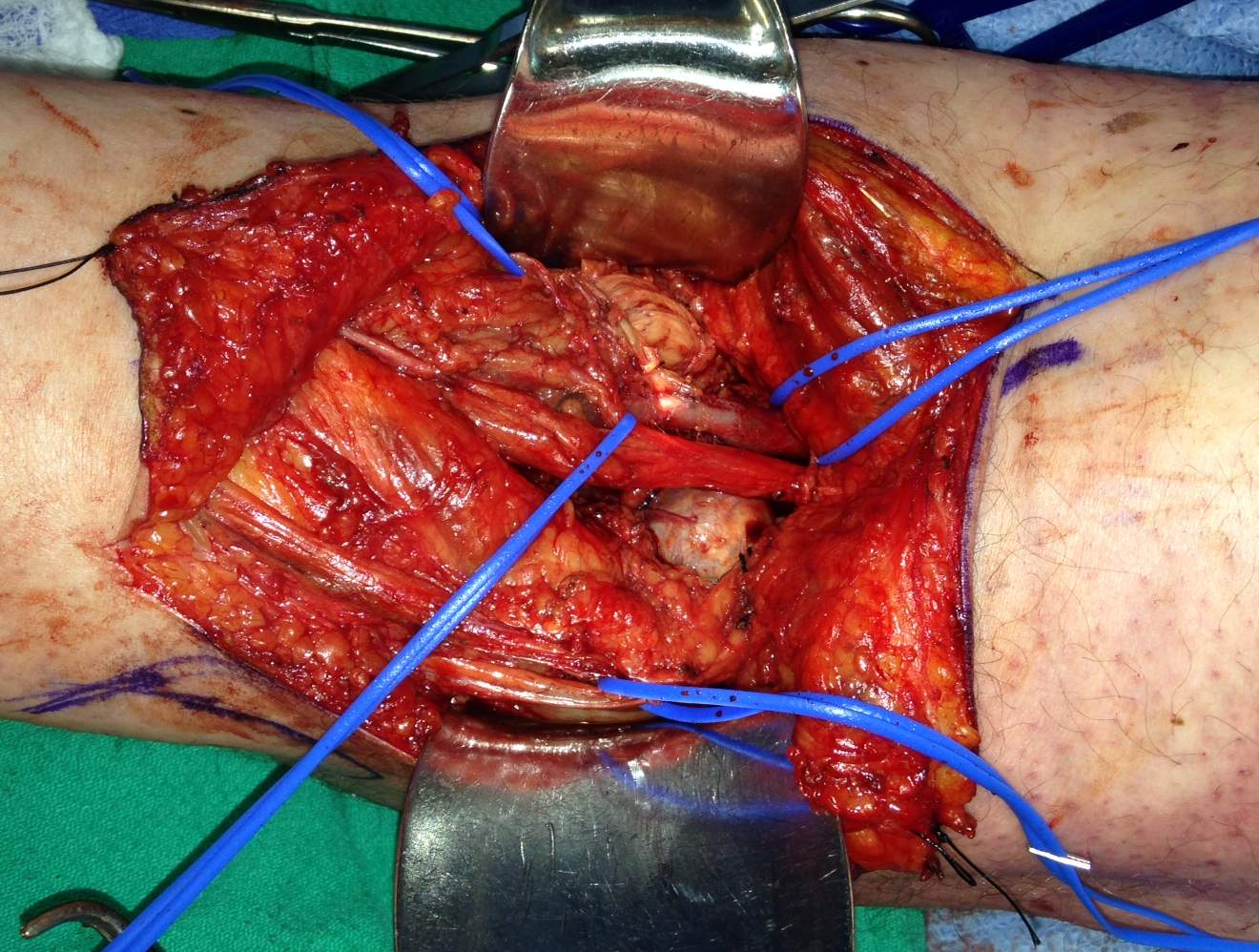
Medial Parapatellar
Medial
Lateral
Posterior
Modified Posterior
Medial Parapatellar Approach
Indications
Synovectomy
Patellectomy
TKR
Technique
Incision
- longitudinal straight midline incision
- point 5 cm above patella to below level of tibial tuberosity
No internervous plane
Superficial dissection
- between VM and RF through the quads tendon
- leaving thin tendinous cuff for repair to VM and along medial patella and patellar tendon
- synovium incised in line with the capsular incision
- dislocate patella laterally and flex knee to 90°
Dangers
- infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve cut often in this approach
- risk post operative neuroma formation
- patella tendon avulsion / reconstruction using semitendinosus tendon
Extensile measures
- can extend proximally as anteromedial approach to distal femur
- between rectus femoris & vastus medialis
Medial Approach
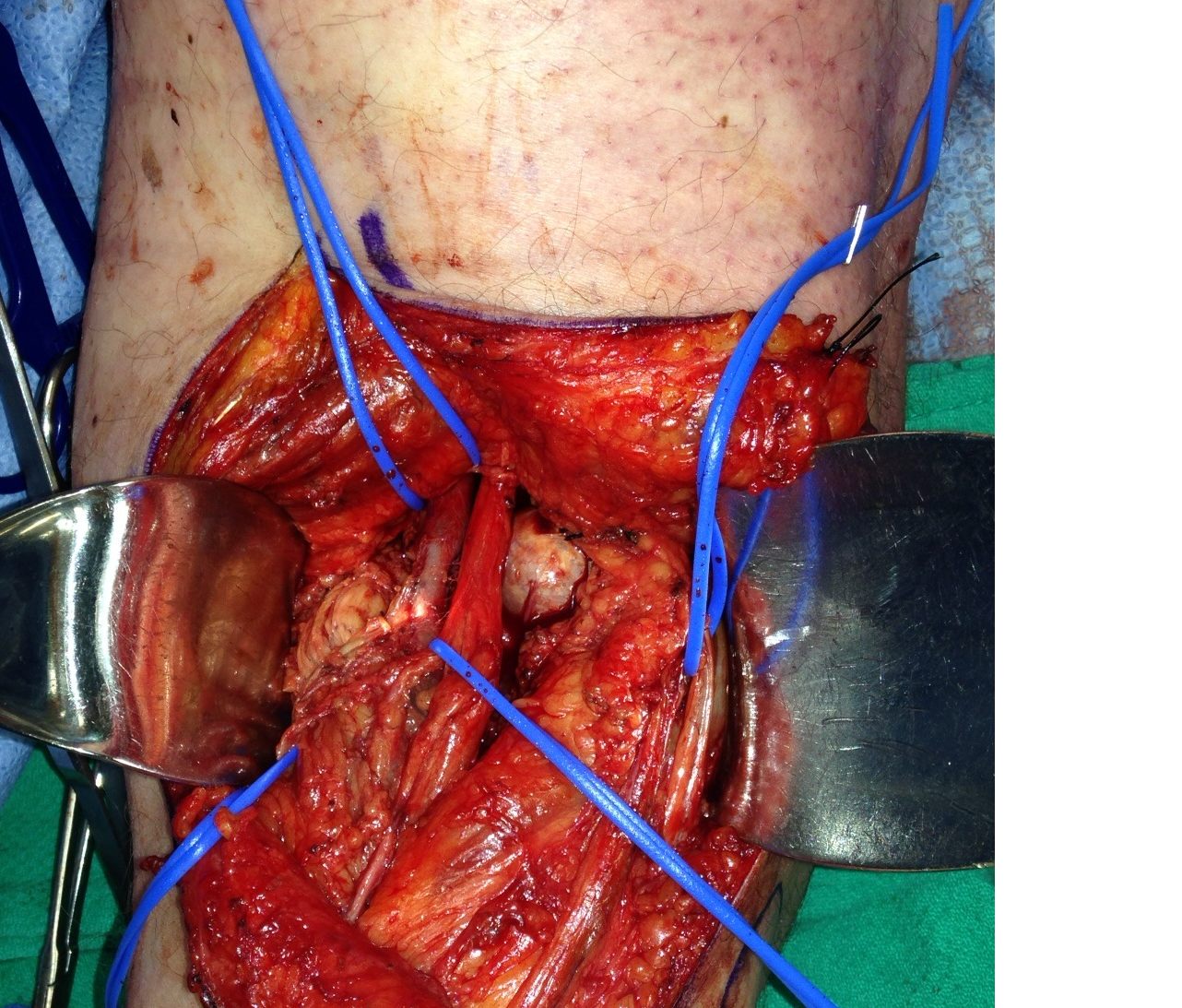
Indications
MCL repair
Inside out meniscal repair
Technique
Position
- patient supine with knee flexed and abducted over the other leg
- or knee flex 90°
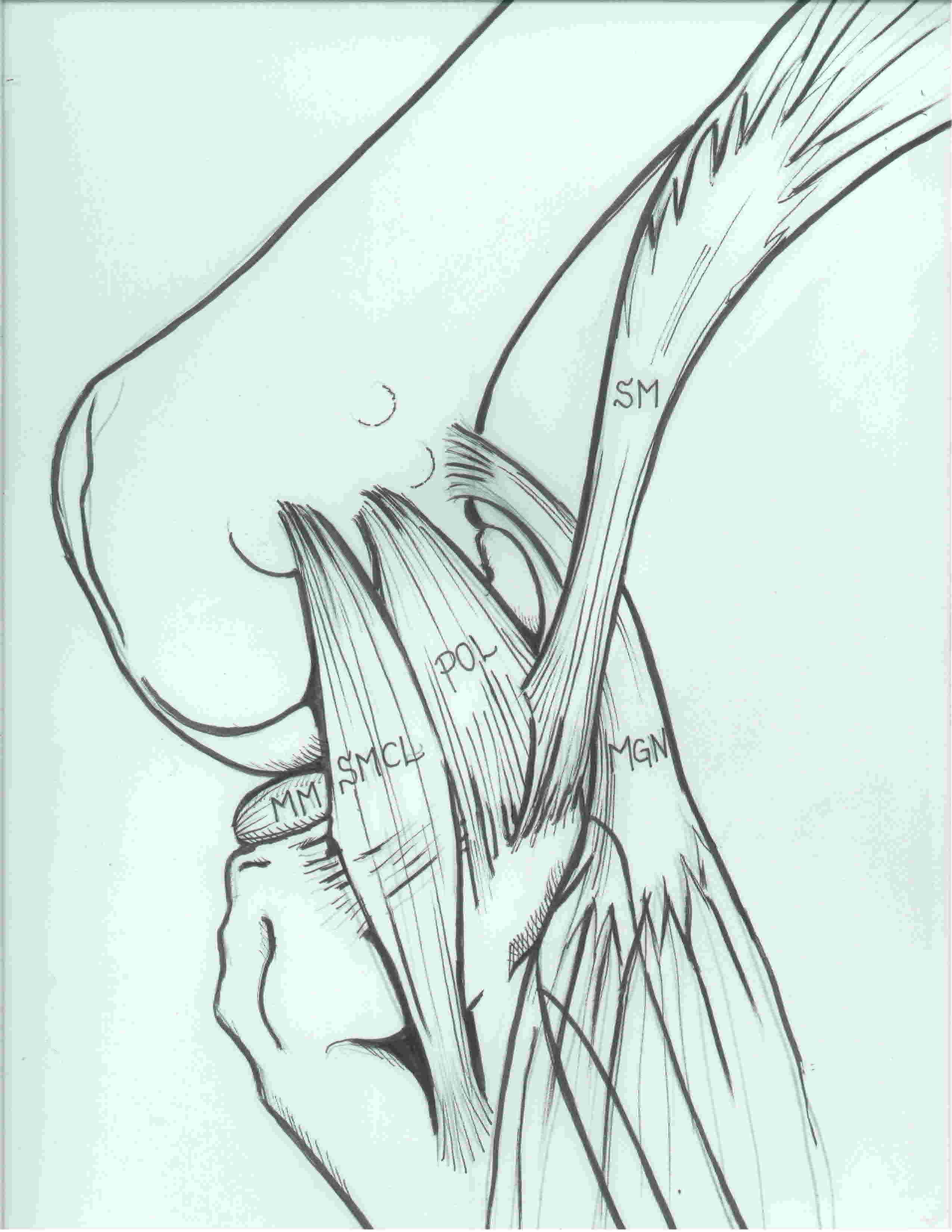
Landmarks
- locate infero-medial corner of patella and medial joint line
Incision
- curved incision centred on joint line
- middle of incision runs parallel to medial border of patella and 3 cm medial from it
- preserve long saphenous vein and saphenous nerve
No internervous plane
Superficial dissection
- incise deep fascia along anterior part of sartorius
- flex knee to allow sartorius to move posteriorly
- semitendinosis and gracilis exposed
- retract pes posteriorly to expose the tibial insertion of the superficial MCL 6-7 cm below the joint line
Deep dissection
Anterior to Superficial MCL
- use to expose the superficial MCL , ACL and anterior medial meniscus
- medial parapatellar incision to enter the joint above medial meniscus
Posterior to Superficial MCL
- access to posterior 1/3 of the medial meniscus and posteromedial corner of knee
- retract the pes posteriorly
- back of the medial femoral condyle seen
- expose the posteromedial capsule by retracting the medial head of gastrocnemius
- postero-medial capsulotomy possible
Femoral insertion MCL
- elevate vastus medialis superiorly
Dangers
- infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve
- long saphenous vein
- medial inferior geniculate artery - lies beneath medial head of gastrocnemius & can be damaged when lifted off capsule
- popliteal artery lies against posterior joint capsule adjacent to medial head of gastrocnemius
- knee flex at 90° allows artery fall posteriorly
- can develop haematoma beneath skin flap with subsequent necrosis
Lateral Approach
Indication
Access to all structures on lateral aspect of the knee
Posterolateral corner repair / reconstruction
Technique
Position
- sandbag under buttock on affected side with knee flexed 90o on foot rest
Incision
- along lateral aspect of the thigh and 3cm lateral to patella curving down to the Gerdys Tubercle
Superficial dissection
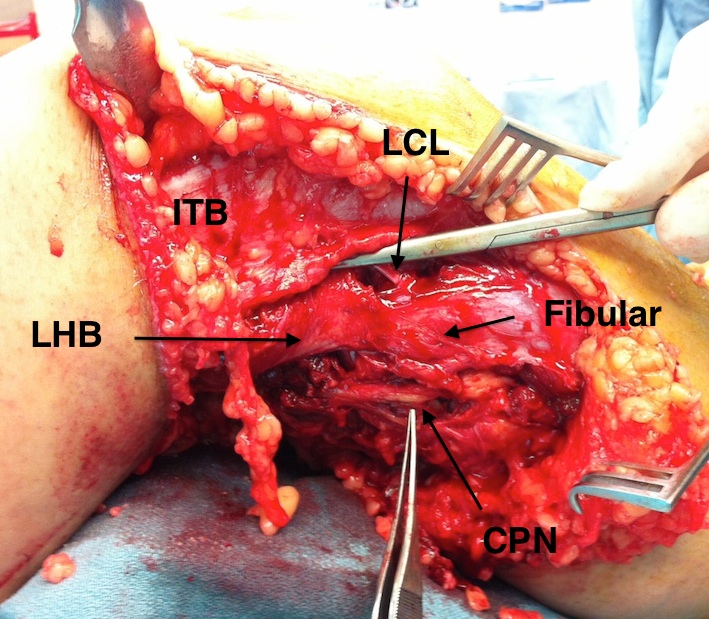
- internervous Plane between ITB and the Biceps femoris
- identify and protect CPN at posterior border of the biceps tendon
- in acute injuries identify outside zone of injury and trace back to abnormal area
- LCL origin on fibula identified between ITB and BF
- LCL insertion on femur identified in split of ITB
- posterolateral corner of the knee exposed
- enter joint anterior or posterior to the LCL
Anterior to LCL
- create lateral parapatellar approach
- incise the lateral patellar retinacular fibres
- begin arthrotomy 2cm above the joint line to avoid the lateral meniscus
Posterior to the LCL
- dissect between the lateral head of gastrocneumius and posterolateral capsule
- control LSGA in this plane
- peel lateral gastrocnemius off capuslte
- popliteus tendon can lie over the lateral capsule
- capsulotomy 2cm above joint to protect posterior horn of lateral meniscus
- protect the intracapsular popliteus
Posterior Approach
Indications
Repair of the neurovascular structures of the knee
Repair of avulsion fractures of PCL attachment
Excision of popliteal cysts
Access to posterior capsule of knee
Technique
Position
- patient prone on table with tourniquet except for vascular repairs
Incision
- start incision over biceps tendon superiorly
- curve across the popliteal fossa
- extend distally medial to the medial head of gastrocnemius
No internervous plane
Superficial dissection
- reflect skin flaps with the underlying fat
- find short saphenous vein and then sural nerve
- sural nerve is deep to deep fascia
- follow back to the popliteal fossa to its origin from tibial nerve
- find origin of CPN from sciatic nerve at apex of fossa
Deep dissection
- popliteal artery and vein located deep & medial to tibial nerve
- artery / vein / tibial nerve: medial to lateral
- MGA may need to be ligated to mobilise the popliteal artery
- access joint via postermedial joint capsule
- medial head of gastroc tendinous head reflected from the femur laterally and inferiorly to protect N-V bundle
Modified Posterior Approach
Concept
- between semitendinosus and medial head gastrocneumius
- medial head of gastrocnemius mobilised laterally to protect NV structures
