

Anatomy and sites of compression
Origin from C5 & C6 from upper trunk of brachial plexus
| Suprascapular notch | Spinoglenoid notch |
|---|---|
|
SSN runs under superior transverse scapular ligament
Suprascapular artery and vein run over this ligament
|
SSN runs around spinous process
SSN runs under spinoglenoid ligament
|
|
Supplies supraspinatus after passing under ligament
|
Supplies infraspinatus |
|
Compression causes weakness of supraspinatus & infraspinatus
Usually secondary to trauma
|
Compression causes weakness of infraspinatus
Usually from spinoglenoid cyst secondary to labral tear |
 |
 |
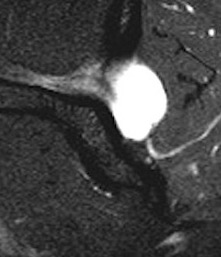
Spinoglenoid Cyst
Causes
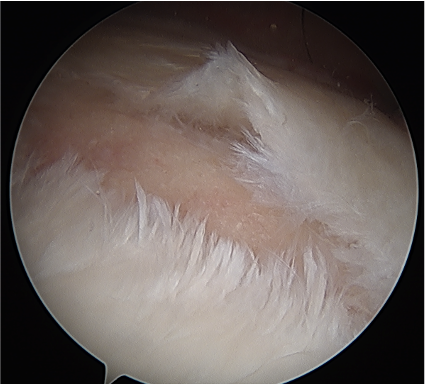
Posterosuperior labral tears & SLAP tears
- labral tear acts as a one way valve
- repairing the labral tear is usually sufficient to solve the problem
Presentation
Pain
- from SLAP tear or posterior labral tear
- from nerve root compression
Sometimes weakness
Rarely atrophy
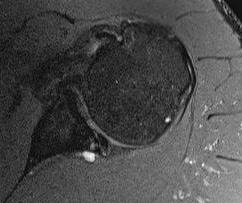
MRI
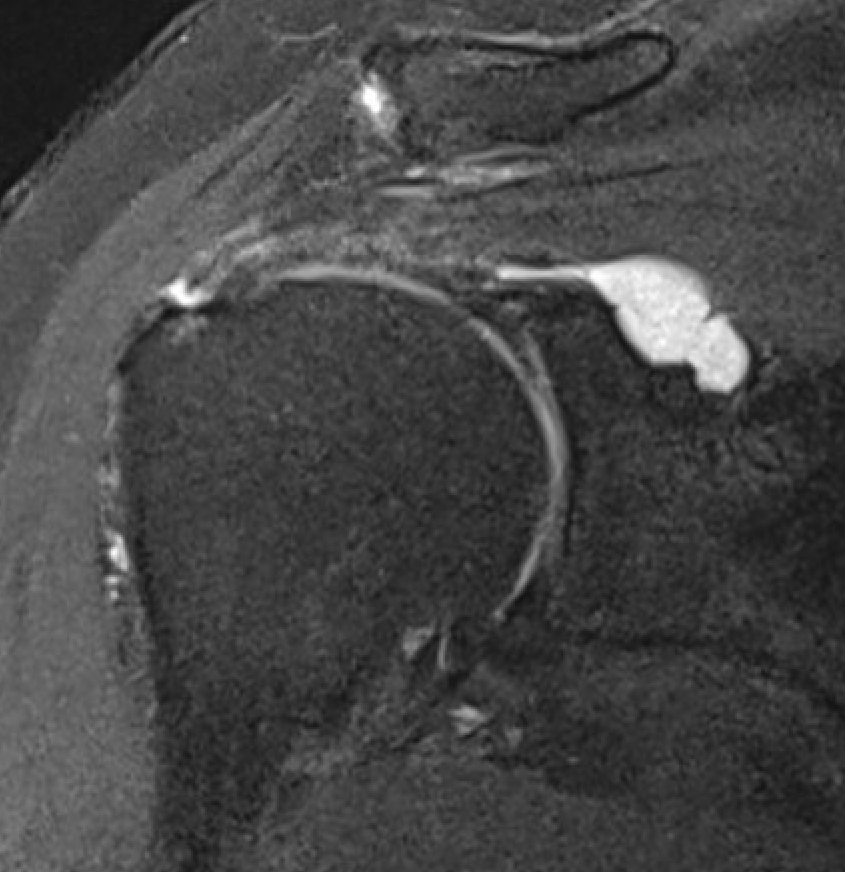
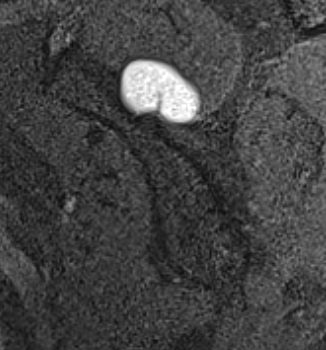
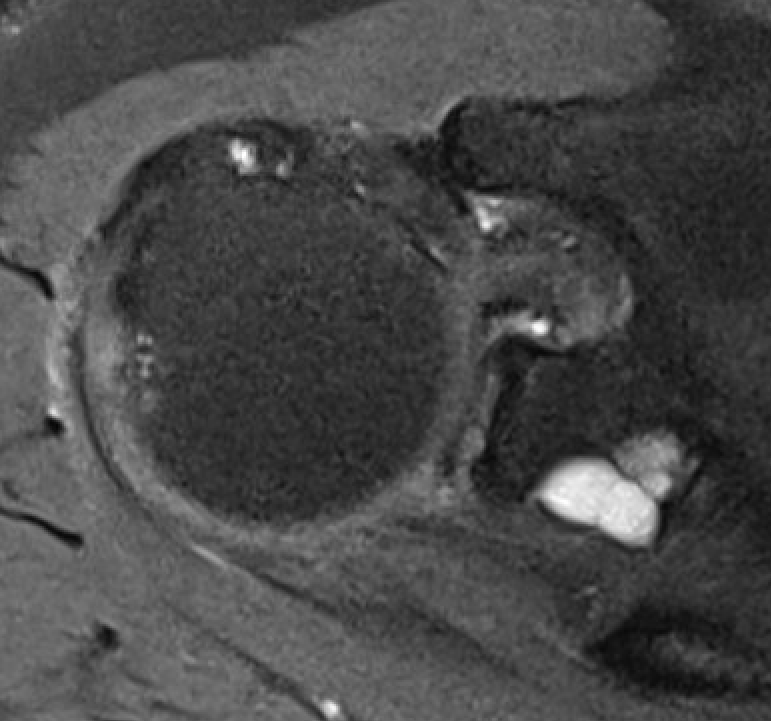
Spinoglenoid cyst


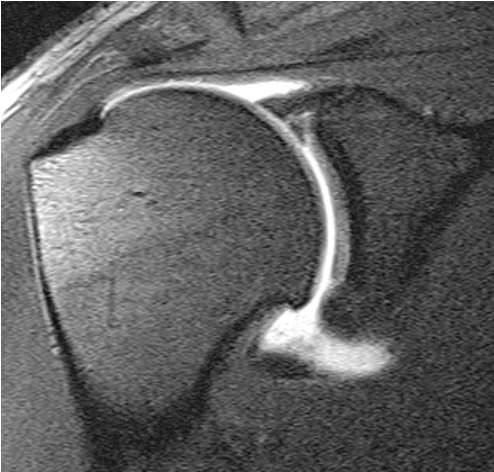
Spinoglenoid cyst with SLAP tear and posterosuperior labral tear
Differential diagnosis
Posterior labral cysts secondary to glenohumeral OA
EMG
May demonstrate denervation of infraspinatus
Options
Cyst decompression + labral repair
Labral repair alone
Results
Posterosuperior labral tears
- 42 patients with posterosuperior labral tear and spinoglenoid cyst
- posterior labral repair without cyst decompression
- cyst resolved in 88% on MRI and smaller in remainder
- all patients satisfied with outcome
SLAP tears
Schroeder et al Arthroscopy 2018
- systematic review of 160 SLAP tears with spinoglenoid cyst
- no difference in outcome between decompression + labral repair versus labral repair alone
Cyst decompression
Options
1. Through labral tear
2. Glenohumeral approach - posterior capsulotomy above IGHL
3. Subacromial approach - between supraspinatus and infraspinatus
Glenohumeral joint approach
Arthroscopy techniques spinoglenoid cyst decompression
Vumedi spinoglenoid cyst decompression video

Posterior glenohumeral capsulotomy and cyst decompression
Subacromial space approach
Ghodadra et al Arthroscopy 2009
- subacromial space
- identify spine of scapula and dissect between infraspinatous and supraspinatous
- accessory posterior portal, retract IS and nerve
- decompress with shaver


Subacromial space approach to cyst decompression
Suprascapular Notch Impingement / Entrapment
Etiology
Overhead athletes - volleyball / tennis / swimming
Overhead laborers
Cyst / masses in spinoglenoid notch
Enlarged suprascapular vein in spinoglenoid notch
Rotator cuff tears
- thought that pain from massive rotator cuff tears may be due to suprascapular nerve impingement
- systematic review of rotator cuff repair and SSN release
- no evidence for improved outcomes
Presentation
Pain
- posterolateral shoulder
- especially with overhead movement
Weakness atrophy of supraspinatus / infraspinatus in abscence of of rotator cuff tear
NCS / EMG
Diagnose suprascapular nerve entrapment and site of entrapment
MRI
Exclude rotator cuff tear
Look for cyst / mass / AV malformation at suprascapular notch
Local anesthetic to suprascapular nerve
Ultrasound guided
Can help confirm diagnosis
Operative management
Option
Superior transverse scapular ligament release - open / arthroscopic
Anatomical variations
1. Suprascapular nerve under superior transverse scapular ligament / suprascapular artery and vein above
2. Suprascapular nerve + vein under superior transverse scapular ligament / suprascapular artery above
3. Suprascapular nerve + vein + artery under superior transverse scapular ligament
Results
von Knoch et al Z Orthop Unfall 2021
- systematic review of suprascapular notch release
- good clinical results
- only 60% of patients had full motor recovery
Lafosse et al Arthroscopy 2007
- 10 patients with clinical and EMG evidence of suprascapular nerve compression
- no complications
- good / excellent clinical outcome in 9/10 patients
Arthroscopic Technique
Vumedi suprascapular nerve decompression video
Arthroscopy techniques suprascapular nerve decompression PDF
Beachchair
- camera in lateral subacromial portal
- shaver in anterolateral portal
- identify coracoacromial ligament and follow to base of coracoid
- medial to this is fatty area with transverse humeral ligament
- identify the conoid ligament attaching to the base of the coronoid


Coracoacromial ligagment (CAL), coracoid and fatty area medial to coracoid
Insert suprascapular portal / accessory Neviaser portal
- behind posterior edge of acromion and anterior to spine of scapular
- insert blunt instruments under clavicle, and use to dissect fatty area
- identify suprascapular artery passing over the top of the transverse scapular ligament
- divide transverse scapular ligament through Neviaser portal while retracting suprascapular nerve


Conoid liagment and suprascapular artery (SSA) traveling over the transverse scapular ligament (TSL)


Division of the transverse scapular ligament (TSL) above the suprascapular nerve (SSN)
Open Technique
Incision along spine of scapular
- sharply elevate trapezius off spine off scapula
- supraspinatus reflected inferiorly to expose notch
- preserve suprascapular nerve and artery
- divide superior transverse scapular ligament
