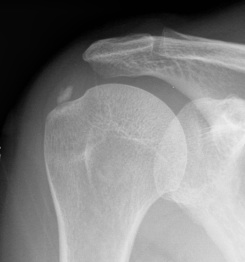

Definition
Characterized by calcium deposits in the rotator cuff tendon or subacromial bursa
Will spontaneously regress in majority of cases
Epidemiology
40 - 60 years of age
Female > Male
Supraspinatus > infraspinatus > subscapularis
Etiology
Local ischemia / degeneration / calcification
Associated with diabetes and hypothyrodism
Classification of calcific stage
| Formative Stage | Resting Stage | Reabsorptive Stage |
|---|---|---|
| Minimal pain | Acute pain | |
| Chalk appearance | Toothpaste / fluffy appearance |
Symptoms
Acute pain
- may present to emergency with severe pain
- DDx infection
X-ray


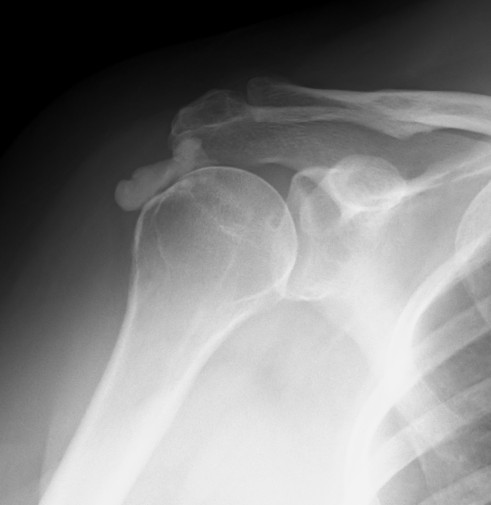
Supraspinatus calcification



Subscapularis calcification
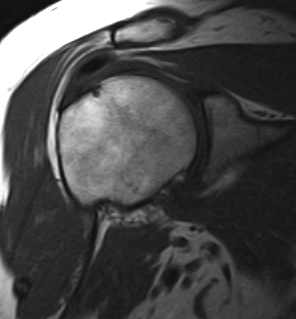
MRI
Calcium has low signal intensity on all sequences





Ultrasound


Management
Non operative Management
Options
Corticosteroid injection
Shock wave therapy
Ultrasound guided needling
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ECSW)

Bannuru et al Ann Intern Med 2014
- systematic review of 20 RCTs
- ECSW for calcific tendonitis
- high energy ECSW superior to placebo
- systematic review of 5 RCT
- comparing high energy to low energy ECSW
- better results with high energy ECSW
Ultrasound guided needle aspiration and irrigation / lavage / Barbotage
Technique
Vumedi ultrasound guided needling video
Ultrasound guided procedure under LA
- one needle into deposit, inject saline
- one needle into deposit, aspirate
- create inflow outflow
- want minimal punctures for this to work
- usually supplement with cortisone injection to reduce pain
Results
- systematic review of 700 patients and 22 studies
- comparing ECSW to ultrasound guided needling
- over long term follow up, needling more effective at decreasing pain and calcium size
Operative Management
Options
Debridement of calcium deposit +/- rotator cuff repair
Open / mini open / arthroscopic
Results
- systematic review of operative versus nonoperative management
- operative management: 85% complete resolution of calcium
- ultrasound guided needling: 67% complete resolution of calcium
Arthroscopic Technique
Technique
Vumedi arthroscopic treatment of calcific tendonitis video
Locate calcium lump
- remove bursa with shaver
- deposit may be obvious
- however may have to use needle: get cloud of calcium when find deposit
- longitudinally split tendon and currette calcium
- repair rotator cuff


Location of calcium deposit under vision and with needle



Longitudinal incision of rotator cuff / debridement of calcium / rotator cuff repair
