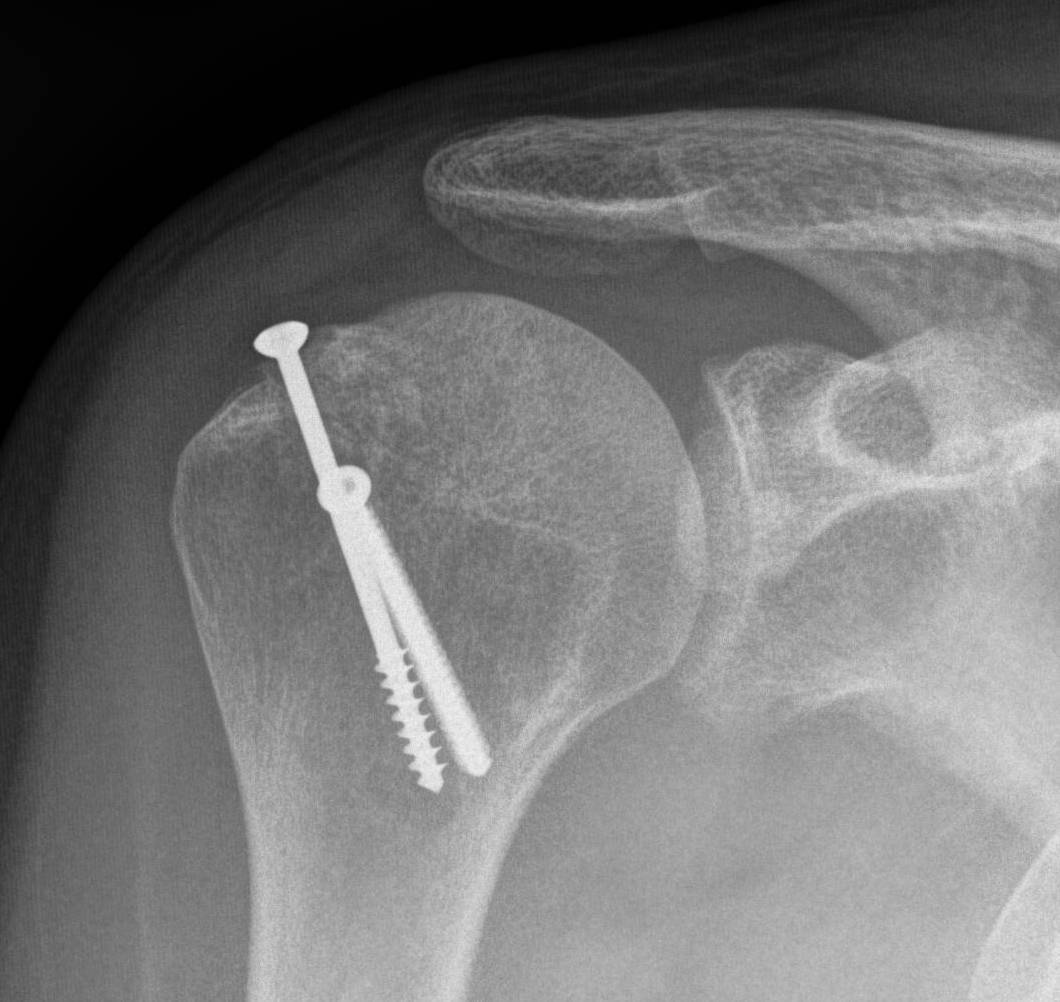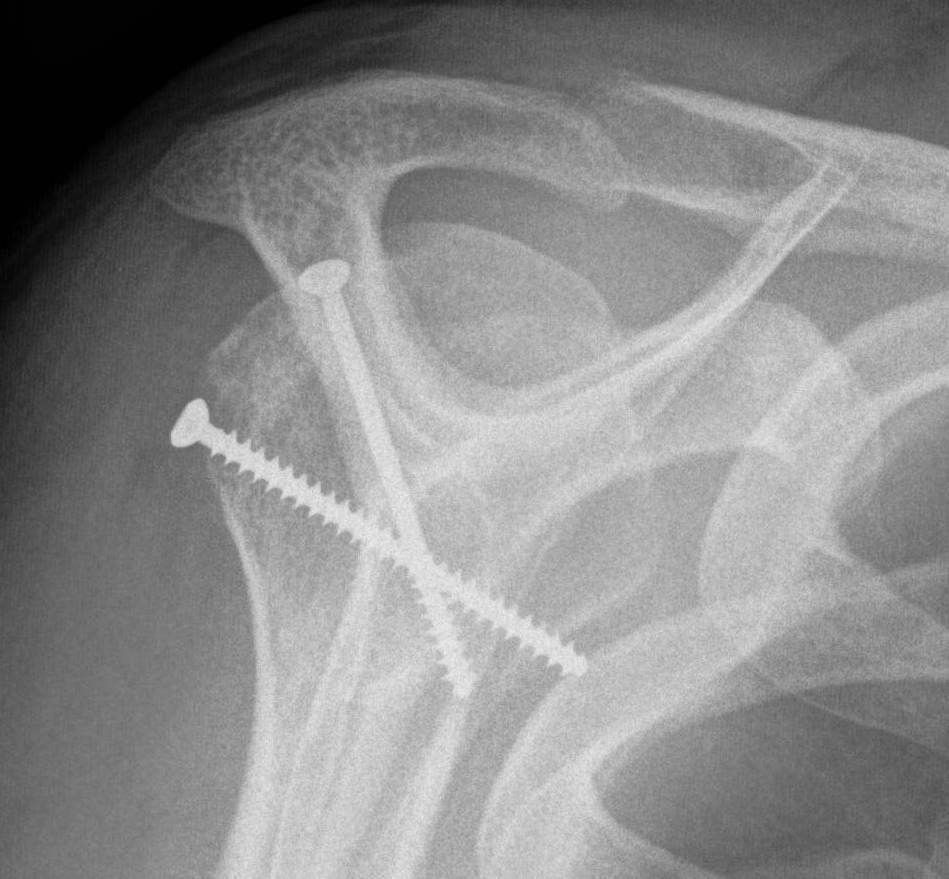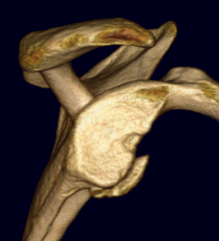
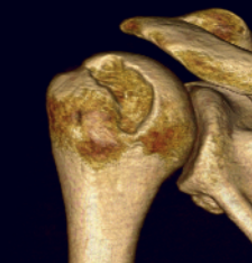
Operative management
Options
Arthroscopic labral repair +/- Remplissage
Glenoid bony block procedure
- Latarjet / Bristow
- free autograft / allograft
Hill Sachs allograft
Decision making factors
| Glenoid bone loss |
Humeral bone loss Hill Sachs |
Patient factors | Sports | Ligamentous laxity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Critical > 20 - 25%
|
> 30% articular surface | Age < 20 | Contact sports | |
|
Subcritical 10 - 20%
|
Engaging Hill Sachs - bipolar bone lesions - off track lesions |
Male | Competitive sports |
Zhang et al J Orthop Surg Res 2022
- systematic review of risk factors of recurrence after Bankart repair
- < 20 years, Hill-Sachs lesion, glenoid bone lesion, shoulder hyperlaxity, off-track lesion, male sex, contact sports
Instability Severity Index Score
6 preoperative factors to generate score out of 10
- attempts to predict success of arthroscopic stabilization procedure
Issues
- unclear why some factors worth more than others
- measurement of Hill Sachs / glenoid bone loss on xray
| Age | Degree of sport | Type of sport | Shoulder Hyperlaxity | Hill Sachs on xray | Loss of glenoid contour on xray |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 20 2 points | Competitive 2 | Contact 1 | Hyperlaxity 1 | Visible on ER 2 | Loss of contour 2 |
| > 20 0 points | Recreational 0 | Other 0 | Normal 0 | Not visible 0 | No loss 0 |
Loppini et al Arthroscopy 2019
- 670 arthroscopic Bankart repairs
- overall recurrence 17%
- ISIS < 3: 94% success
- ISIS 4 - 6: 86% success
- ISIS > 6: 55%
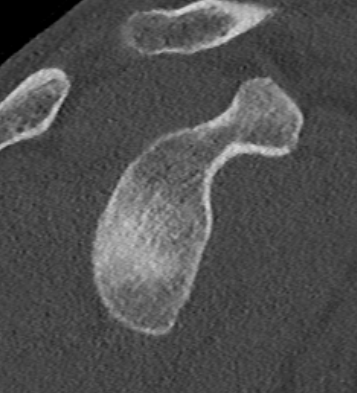
Glenoid bone loss
Incidence
- 3D CT of 100 consecutive shoulder instability
- 50% osseous Bankart lesion
- one large (25% glenoid)
- 54% medium size (10% glenoid)
- 44% small (3% glenoid)
Critical / subcritical bone loss
- consecutive series of arthroscopic Bankart repair
- worsened outcomes with increasing glenoid bone loss
- 3% v 10% v 16% v 25%
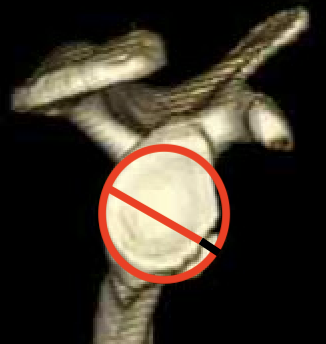
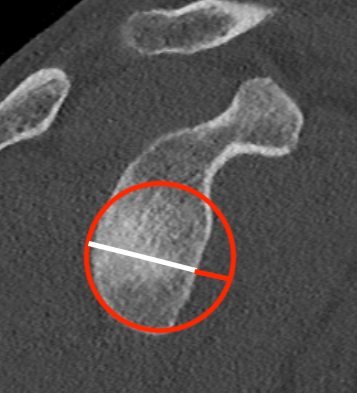
Best fit circle measurement
Best fit circle over inferior glenoid
- perpendicular line through center of circle
- measure percentage bone loss

10 - 15% defect
20 - 25% defect
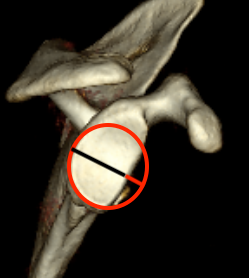
20 - 25% defect
Engaging Hill Sachs
Incidence
Yiannakopoulos et al Arthroscopy 2007
- 127 shoulder dislocations
- 88% Hill Sachs
Measurement Hill Sachs
Best fit circle of the articular surface of humeral head
Measure percentage involvement of articular surface
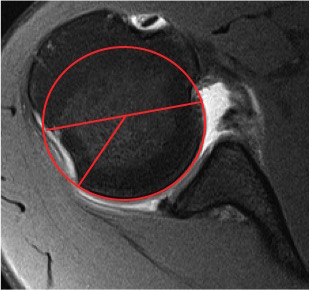
Hill Sachs 30% of the articular surface
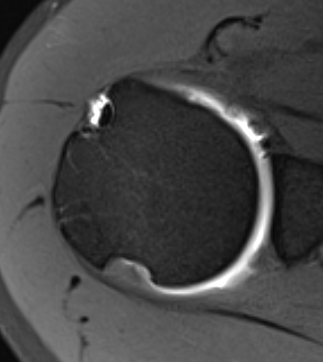
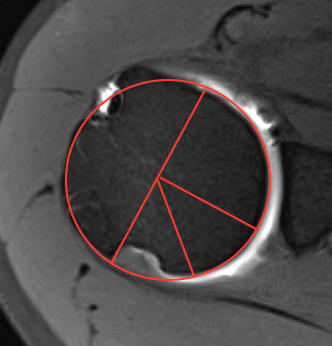
Hill Sachs 25% of the articular surface
Engaging Hill Sachs
Concept
- Hill Sachs lesion engages with anterior glenoid in abduction / external rotation
- complex interplay between glenoid bone loss and humeral bone loss / bipolar bone loss
Glenoid track is 83% of glenoid width of intact glenoid
- subtract any glenoid bone loss
- 83%D - d
- this distance from medial rotator cuff foot print on humeral head
- engaging or off track lesion: Hill Sachs medial to medial border of this line
- non engaging or on track lesion: Hill Sachs medial border lateral to medial border of this line


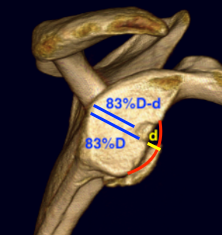
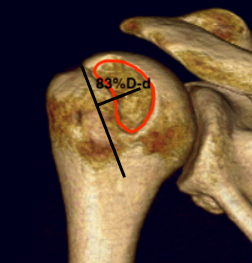
Engaging Hill Sachs in setting of bipolar bone lesion
- systematic review of modalities for glenoid track / bipolar bone lesions
- 3D CT most accurate
- reliability of 2D MRI unclear
Arthroscopic labral repair +/- Remplissage
Indications
Minimal glenoid bone loss
Non contact athlete
Remplissage
Tenodesis of infraspinatus / posterior capsule into Hill Sachs defect
Makes defect extra-articular / non engaging
Results
Remplissage
Villareal-Espinosa et al KSSTA 2024
- systematic review of Bankart repair v Bankart + Remplissage
- reduced recurrent instability with Bankart + Remplissage with no difference in ROM
Arthroscopic Bankart v Glenoid bone block procedure
Gouveia et al Arthroscopy 2019
- systematic review of 10 - 15% mean glenoid bone loss
- recurrence arthroscopic bankart: 6 - 13%
- recurrence bone block: 0 - 8%
- complication arthroscopic bankart: 0 - 2%
- complication bone block: 0 - 67%
- systematic review of arthroscopic bankart v Latarjet
- high recurrence with arthroscopic bankart
- higher infection with Latarjet
Glenoid bone block procedures
Indications
Critical glenoid bone loss 20 - 25%
Subcritical bone loss / bipolar bone lesions / engaging Hill Sachs
Contact athlete
Results
Latarjet versus free bone block procedures
- systematic review of 3900 Latarjet versus 600 free bone block procedures
- recurrent instability: Latarjet 5%, FBB 3%
- complications: Latarjet 4%, FBB 5%
- OA: Latarjet 12%, FBB 4%
- return to sport: Latarjet 73%, FBB 88%
Distal tibial allograft (DTA)
- systematic review of DTA for shoulder instability with bone loss
- 8 studies and 329 patients
- recurrent instability 1.5%
- complication rate 7%
- hardware complications 4%
- graft resorption 37%
Free autograft versus free allograft
- systematic review
- free autograft (iliac crest / free coracoid) versus free allograft (DTA / iliac crest / femoral head)
- recurrent instability 3% with no difference between groups
- autograft: 11% OA
- allograft: 1% OA
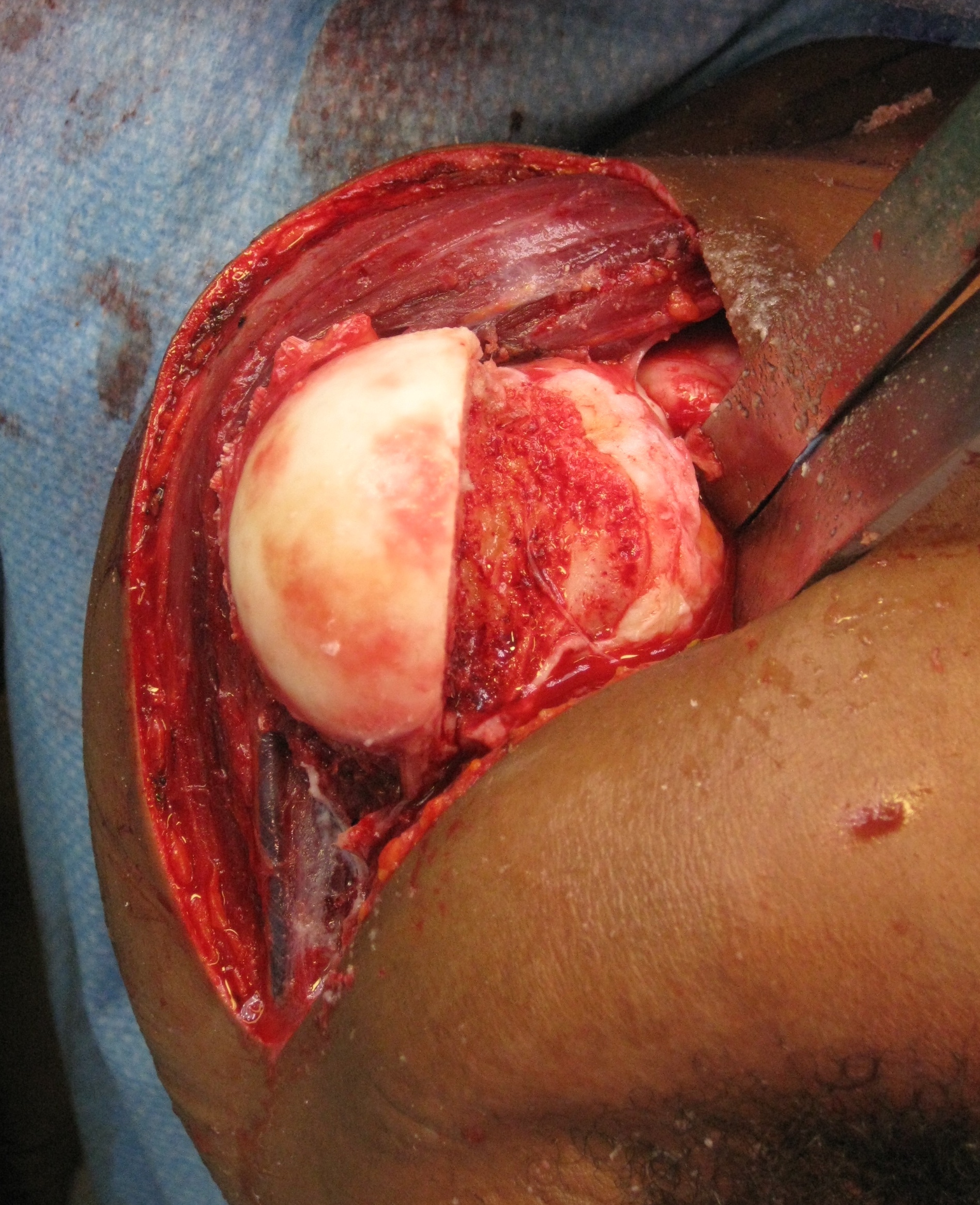
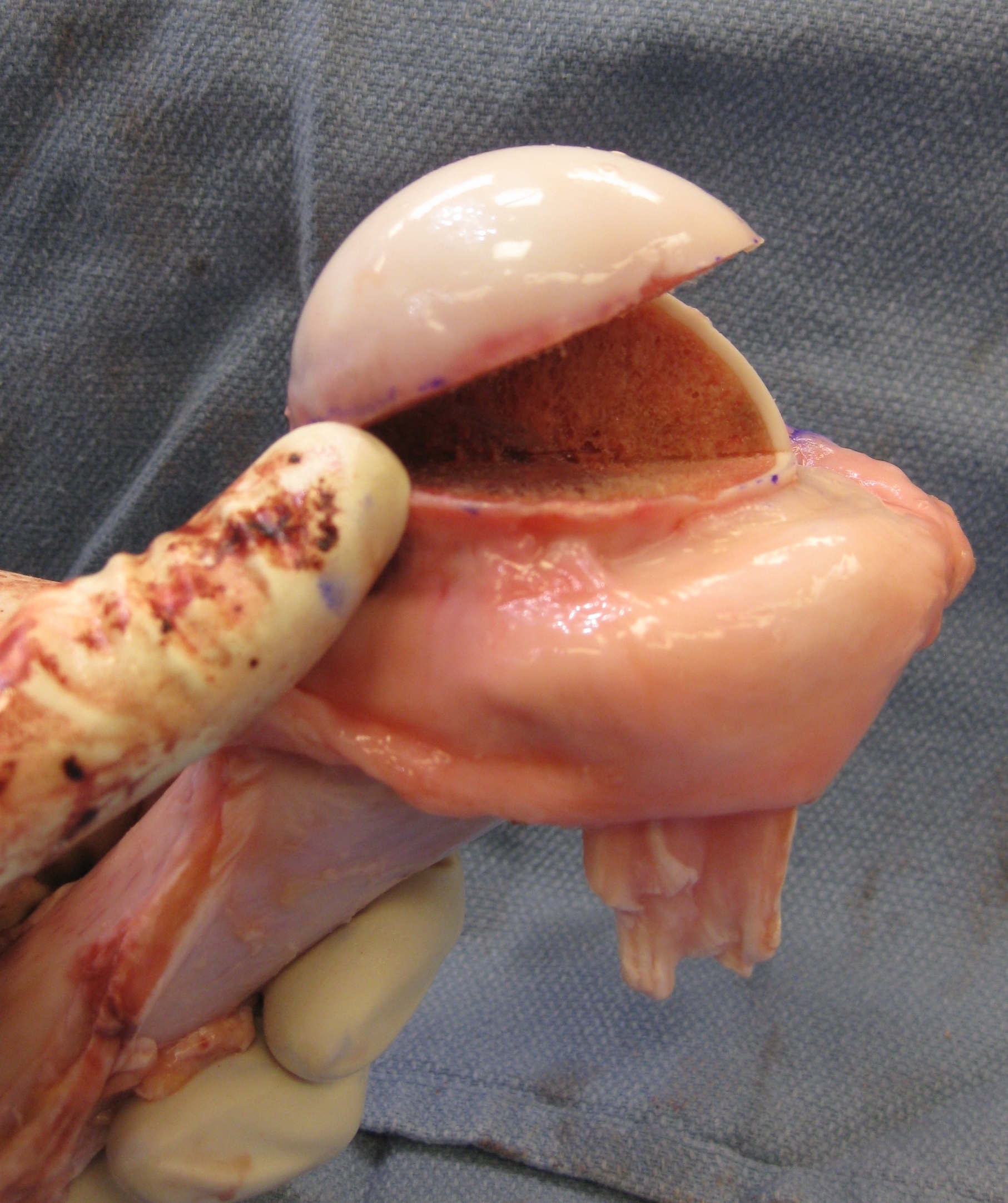
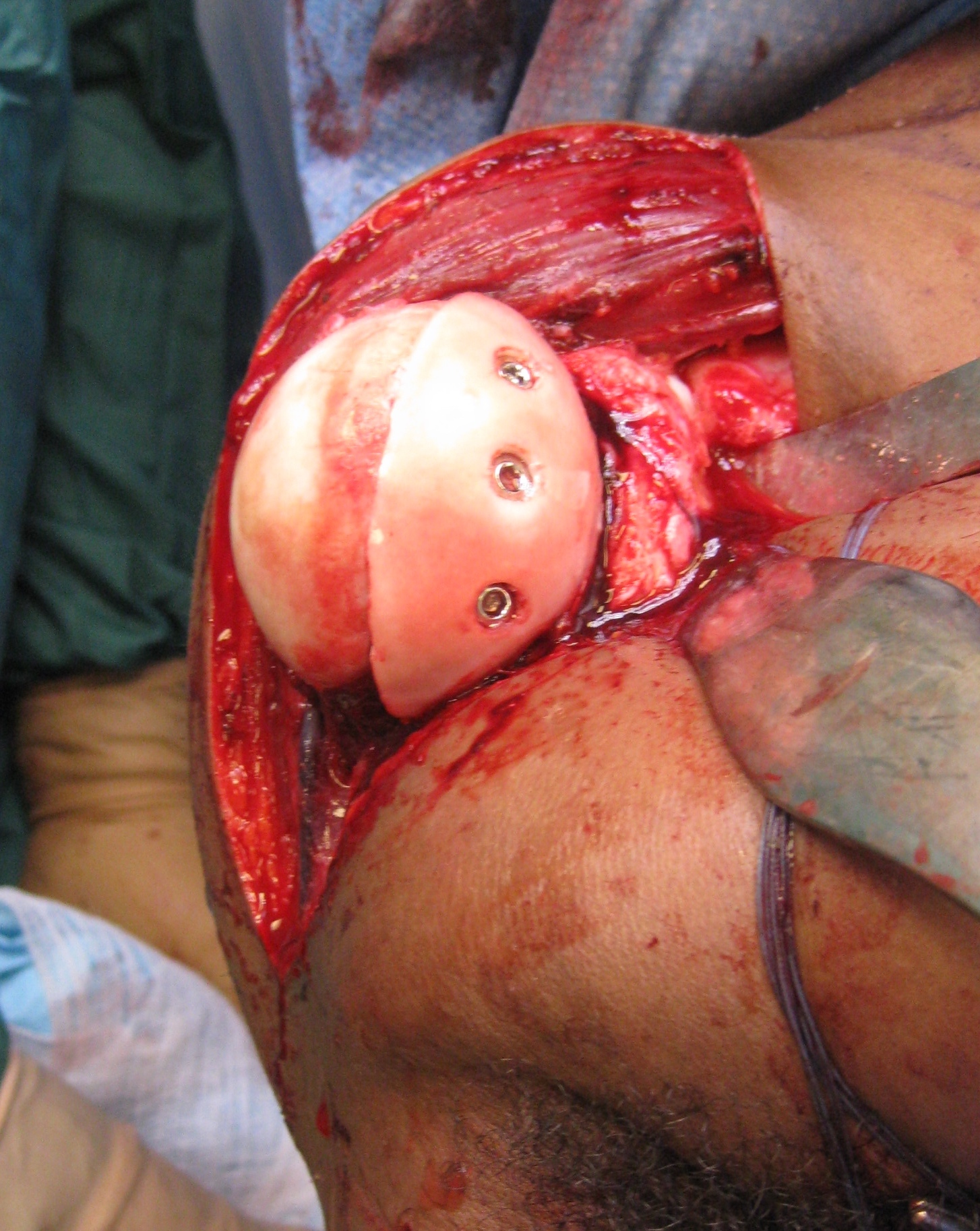
Humeral head allograft
Indications
Large Hill Sachs defect
Technique