Definition
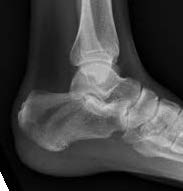
Essex-Lopresti classification intra-articular fractures
- joint depression
- tongue-type
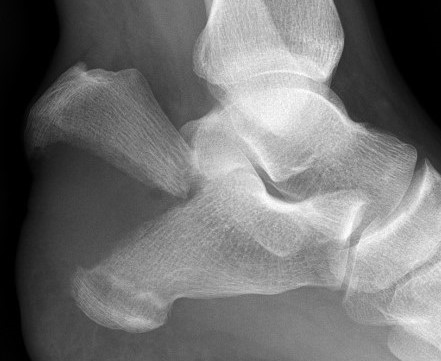
Tongue type
- involve posterior subtalar joint
- secondary fracture line extends posteriorly into calcaneal tuberosity
Differential diagnosis
Calcaneal tuberosity fractures
- extra-articular fractures
- also displaced by achilles tendon
- in older patients with osteoporosis
(see boneschool link)
Epidemiology
High energy in young patients
Pathology
Achilles tendon performs a deforming force
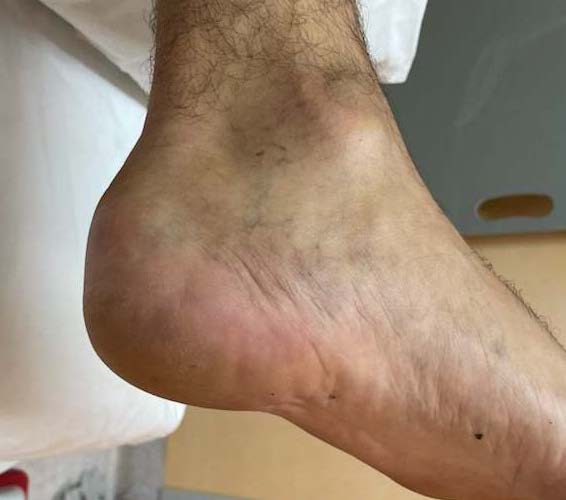
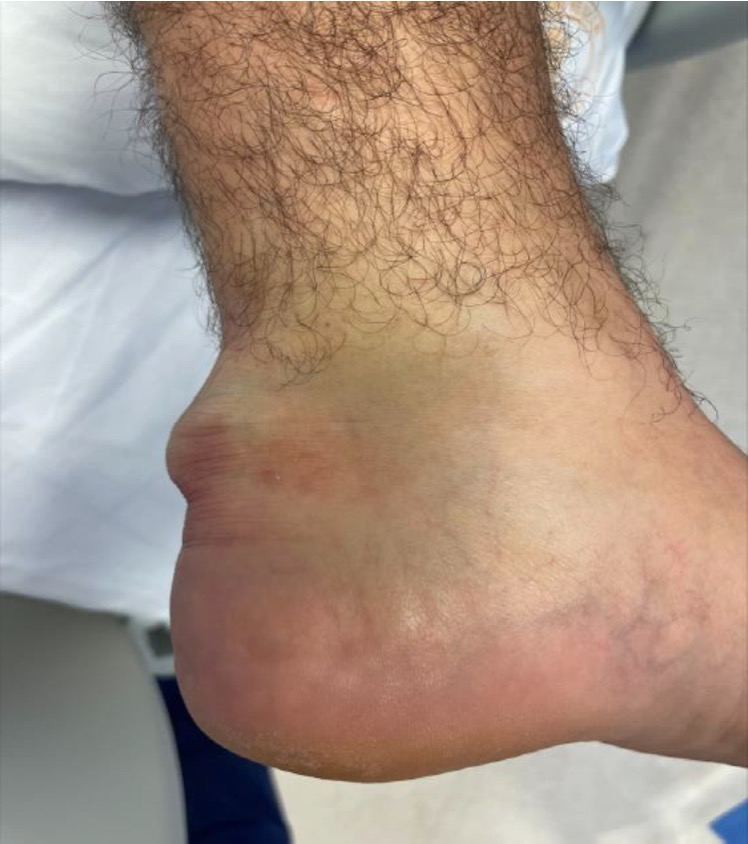
Posterior skin can be threatened and become ischemic / necrotic
Gardner et al J Orthop Trauma 2008
- 139 tongue type fractures
- 21% had posterior soft tissue compromise
- 6% required soft tissue coverage
- increased risk with increased fracture displacement / smoking / delayed referral
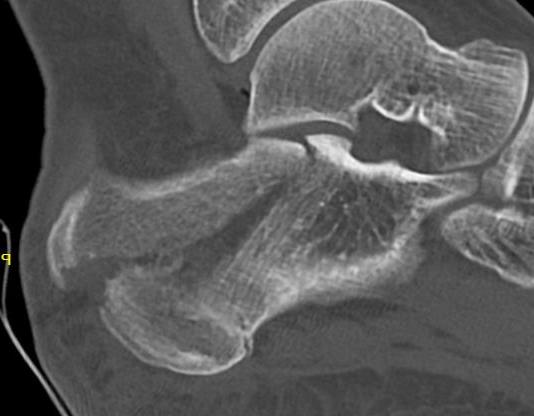
Imaging

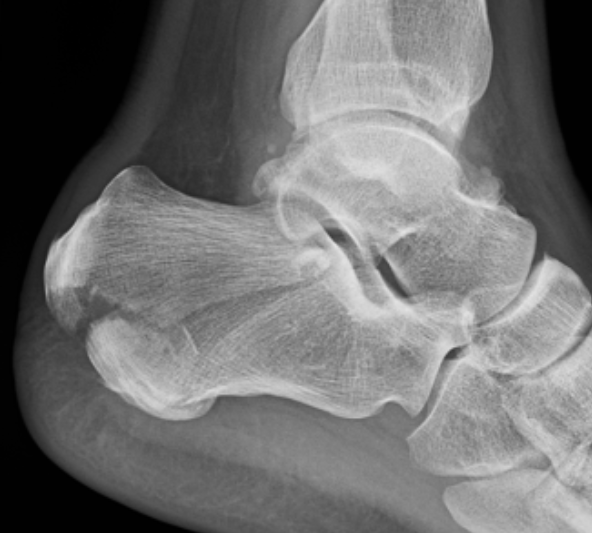
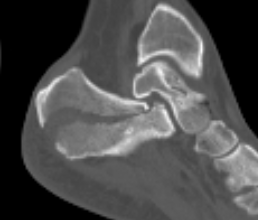
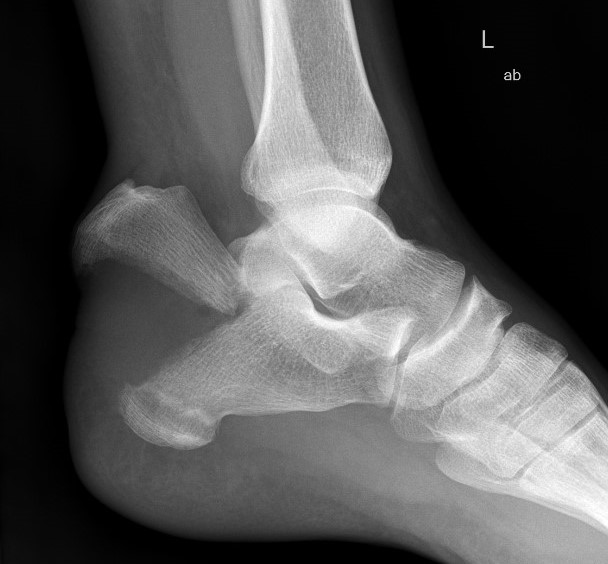
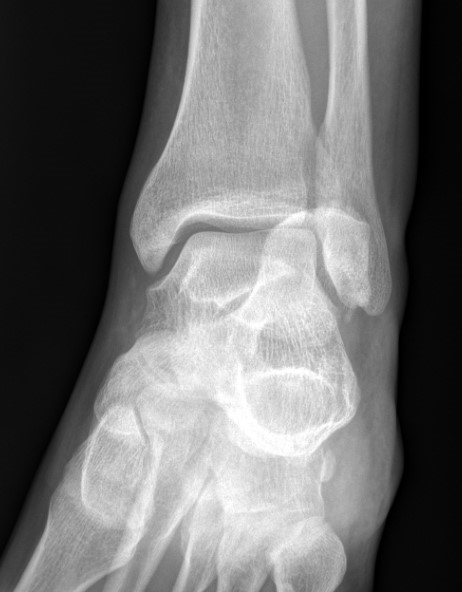
Operative Management
Indications
Displacement
Threatened skin
Timing
Semi urgent especially in setting of skin compromise
Options
Open reduction
Percutaneous reduction
van der Vliet et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2020
- 58 tongue type fractures
- 33 open reduction: 12% deep infection, revision 3% (1)
- 25 closed reduction: 0% deep infection, revision 16% (4)
Open reduction
Vertical limb of extensile lateral approach
- anterior to tendoachilles
- protect sural nerve
AO surgery reference tongue type calcaneum
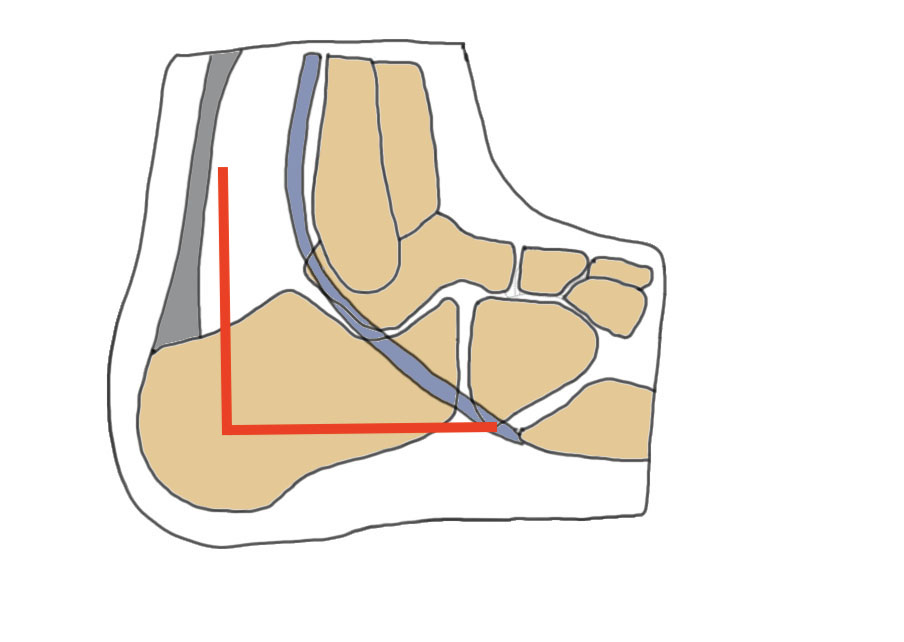
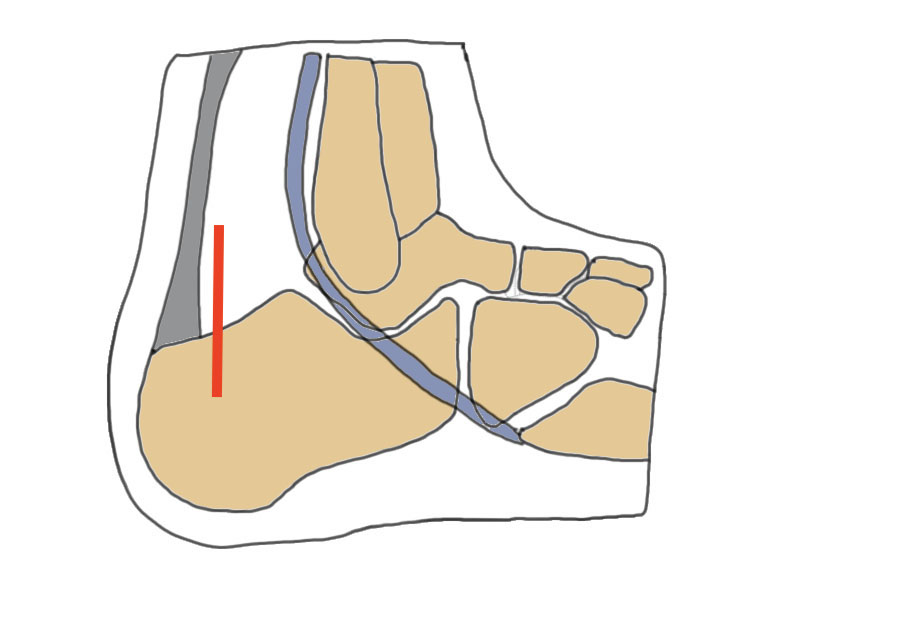
Extended lateral approach Vertical limb for tongue type
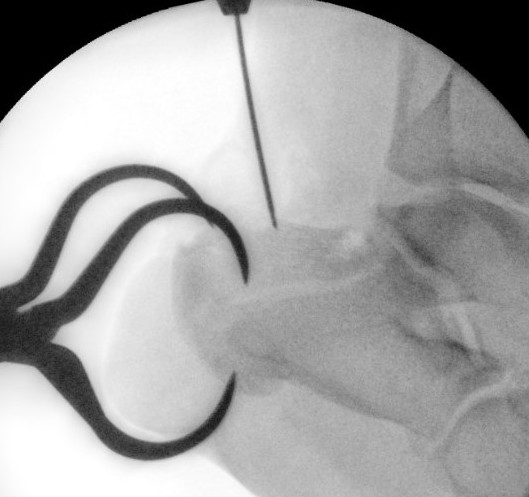
Percutaneous technique
Percutaneous incisions
- lateral and anterior to achilles tendon
- at inferior edge of calcaneum
- allows insertion of clamp to reduce fracture
Vumedi tongue-type percutaneous fixation
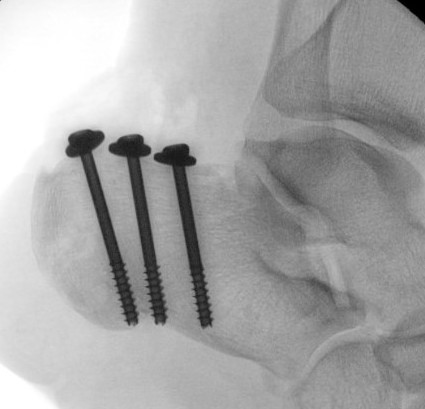
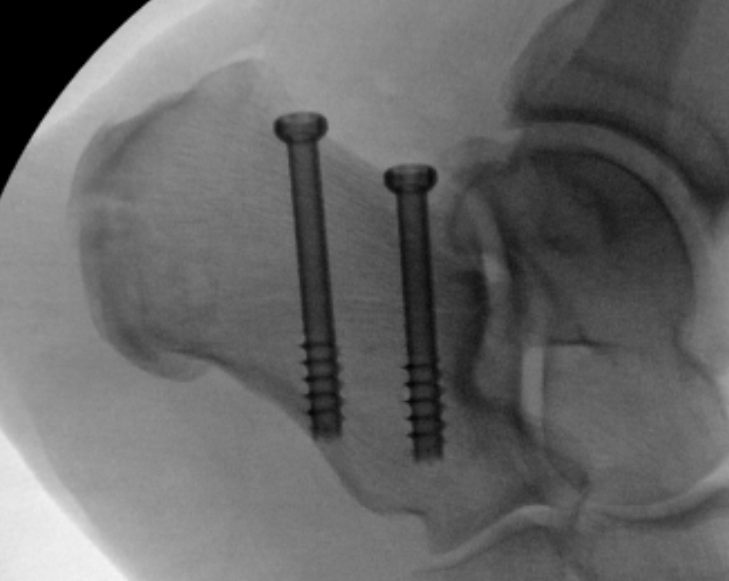
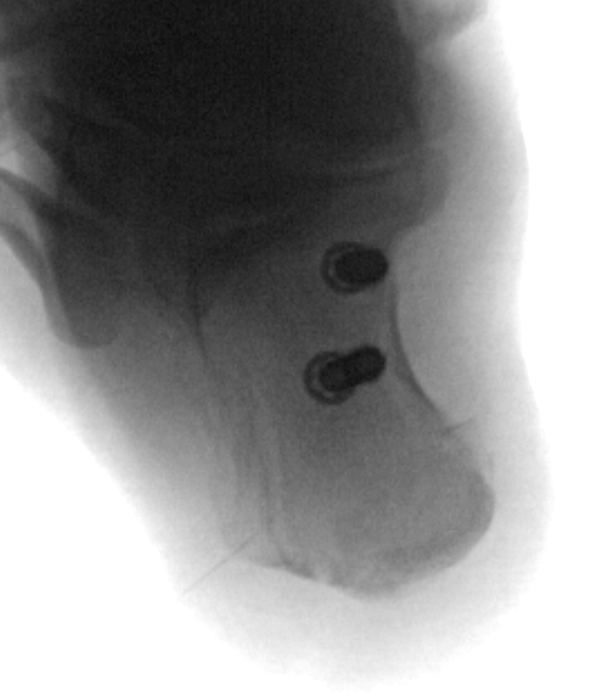
ORIF
Reduce fracture with clamps
Insert 2 - 3 screws
- bicortical fixation
- anterior to weight bearing posterior tuberosity
- cast with foot plantar flexed