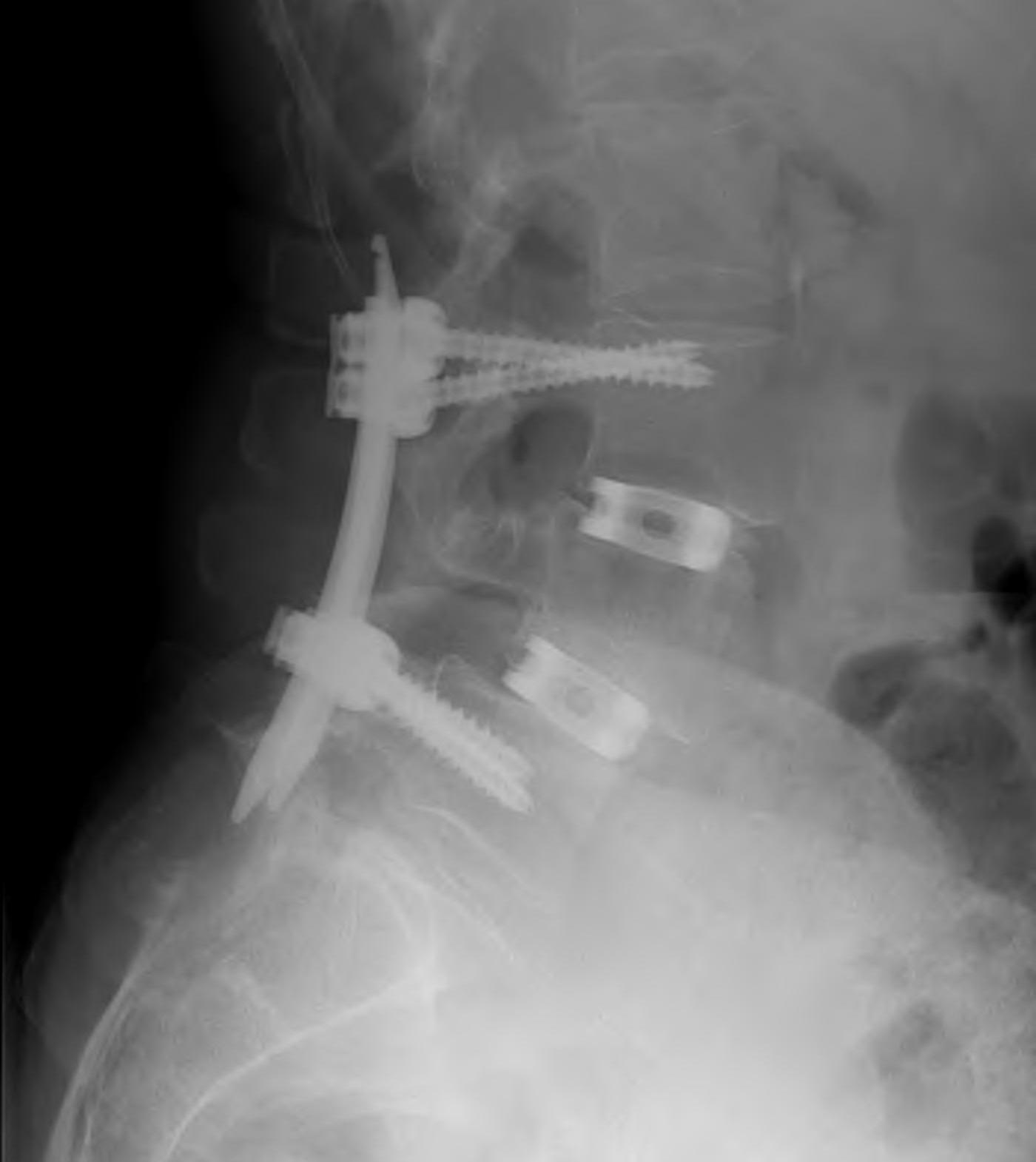
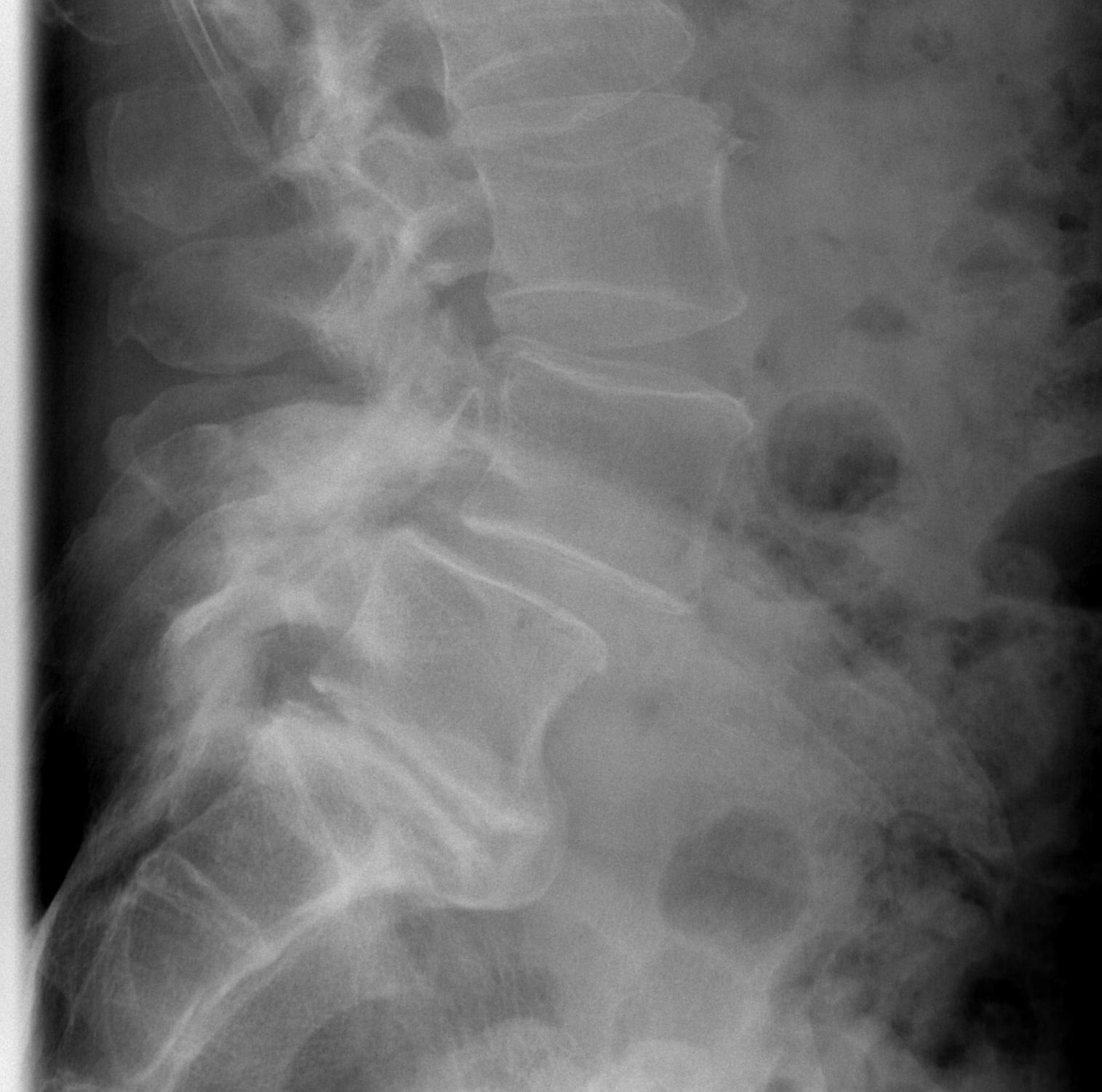
Definition
Spondylolithesis caused by
- facet joint degeneration
- no pars or dysplastic pathology
- disc space usually preserved
Most common at L4/5 level
Epidemiology
More common in elderly females
- F: M = 5:1
Diabetics
Pathogenesis
1. Facet degeneration
- body weight displaces lumbar vertebrae ventrally
- resisted by facet joints
2. Sagittal orientation of facet joints obviates restraining effect
Boden JBJS 1996
- facet joint angle L4 or L5 >45° to coronal plane
- 25x more likely to have degenerate spondylolisthesis
3. Segmental Instability
Pathology
Slip usually mild / rarely past Meyerding Grade II
- average 15%
- maximum 30%
- facet involvement may be asymmetrical & this causes rotatory component
Symptoms
1. Low Back Pain 80%
2. Radiculopathy
- sciatica 50%
- usually L5 in lateral recess
- can be L4 via narrowing foramen
3. Neurogenic Claudication 50%
- worse with standing, relieved by flexion
- claudication distance is variable
- sensory changes
- normal pulses
4. Cauda Equina 5%
Signs
ROM
- normal lumbar forward flexion
- pain on extension
Minimal tenderness & spasm
Neurological deficit 50%
- sensory alteration 30%
- weakness 20%
Xray
AP
- facet hypertrophy / osteophyte formation
Lateral
- mild forward slip
Dynamic Views
- >10° or 4mm = objective instability
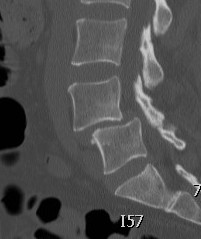
CT
Degeneration of facet

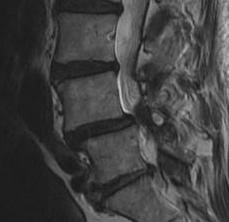
MRI
Demonstrate stenosis with spondylolithesis
NHx
Don't tend to progress past Grade II
Do well if have no neurological symptoms
Often need surgery for neurological claudication / stenosis
Management
Non-operative
Indications
Mild symptoms / short duration / unfit for surgery
Technique
Activity modification / analgesics / physio
Results
Weinstein et al N Eng J Med 2007
- RCT of operative v non operative, multicentred
- operative group had substantial improvement in pain and function at 2 years
Pearson et al Spine 2009
- SPORT
- RCT of operative v non operative
- operative group had significantly better outcomes
- grade 1 better outcome than grade 2 with surgery
- dynamic instability better outcome than static
Operative
Indications
- failure of non operative treatment
- radiculopathy / neurogenic claudication
- progressive neurological defect
- bladder or bowel symptoms
Principles / Issues
1. Decompress + fusion
- demonstrated superior results in degenerative spondylolithesis
Herkowitz et al Spine 1991
- fusion & decompression alone had better results at 3 years than decompression alone
- slip increased 95% vs 30%
2. Instrumentation
- instrumentation increases fusion rate
- ? solid fusion improves outcome
Fischgrund et al 1997
- RCT of PLF with and without instrumentation
- increased fusion rates with pedicle screws (82% v 45%)
- no evidence of superior outcome
Martin et al Spine 2007
- systematic review
- fusion leads to better outcome than decompression alone
- evidence that instrumentation increases fusion rate
- no evidence that instrumentation improves outcome
3. Interbody cages
- increase foraminal height / important if radiculopathy
- improve fusion rates
Options
Decompression + PLF without instrumentation
Decompression + instrumented PLF
Decompression + PLF + interbody cage / PLIF / 360o fusion
Results
Abdu et al Spine 2009
- SPORT
- 360 patients comparing PLF / instrumented PLF / PLIF (360o fusion)
- no difference at 4 years in outcome
Decompression + Instrumented Posterolateral Fusion
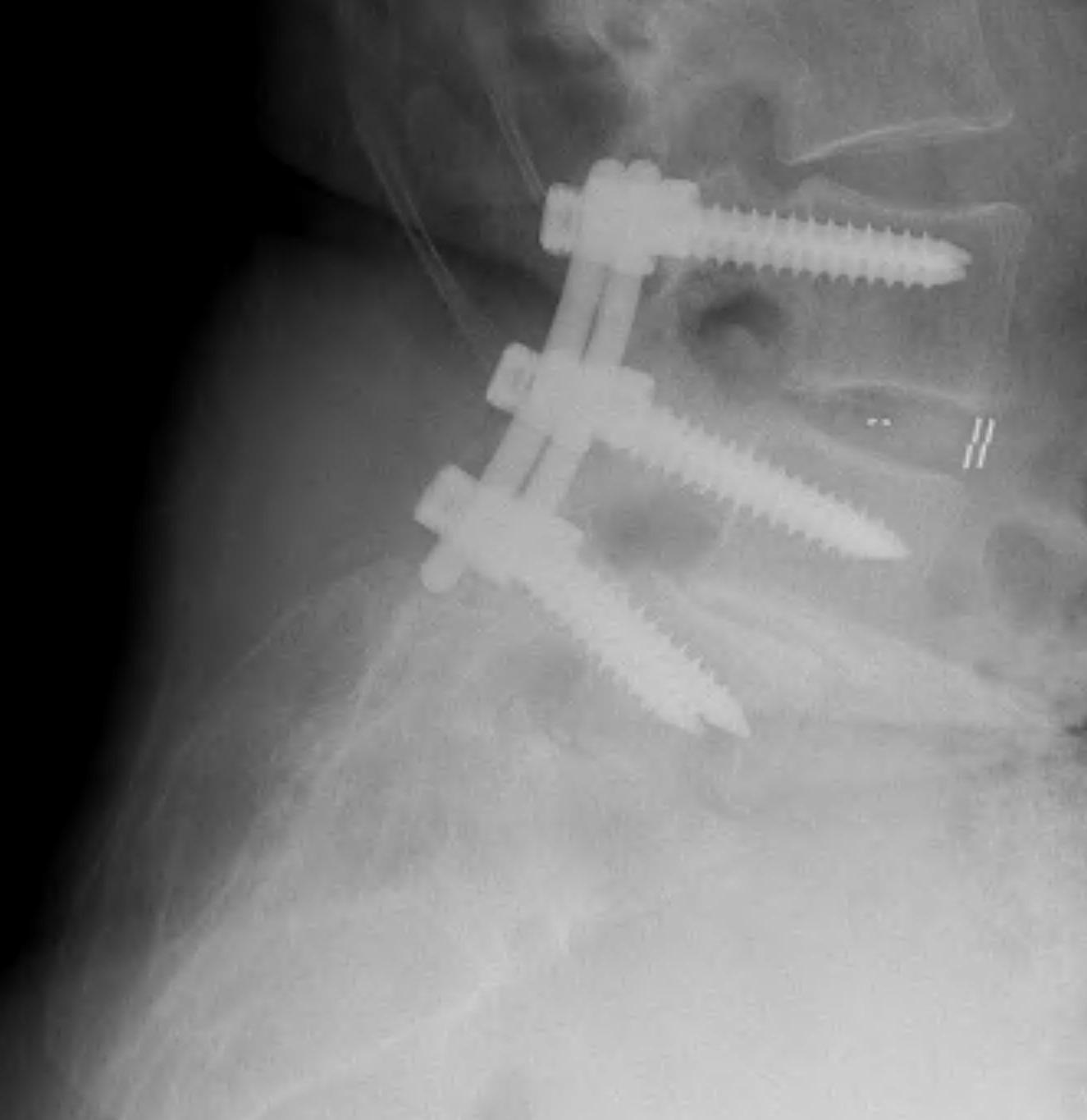
Technique
Midline incision
- elevate para-spinal muscles
- expose L4/5 facets and TP's
- laminectomy +/- foraminotomy
- pedicle screws + rods
- decorticate lamina, transverse processes, facet joints
- posterolateral fusion with BMP collagen and synthetic BG sushi rolls
Results
Decompression and PLIF / 360o fusion