Definition
Minimal trauma fracture
- secondary to osteoporosis
- wedge fractures
Epidemiology
F > M
More common in elderly patients
Uncommon in men < 75
- look for alternative diagnosis
DDx
Renal failure
Malignancy - metastasis
Infection
Clinically
Can present with pain
Can be asymptomatic
Issues
1. Pain
2. Deformity / kyphosis
Management
Non operative Management
Algorithm
1. Exclude other diagnosis
- metastasis
- primary malignancy
- infection
- CRF
2. Pain relief
- analgesics as required
3. Manage osteoporosis
- DEXA scan
- bisphosphonates
- vitamin D + calcium
4. Bracing
- indicated if kyphotic deformity > 20o
5. Early mobilisation
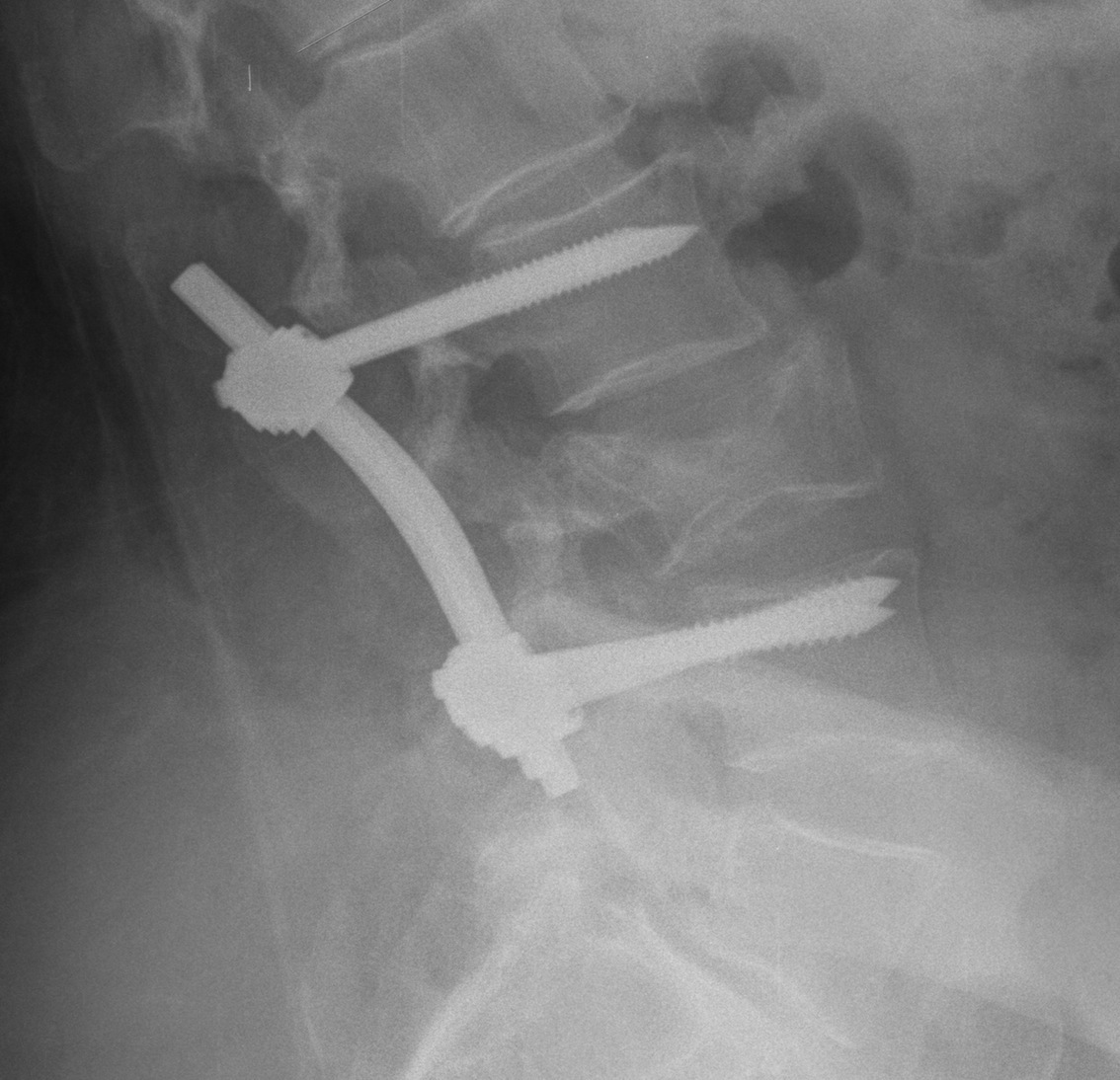
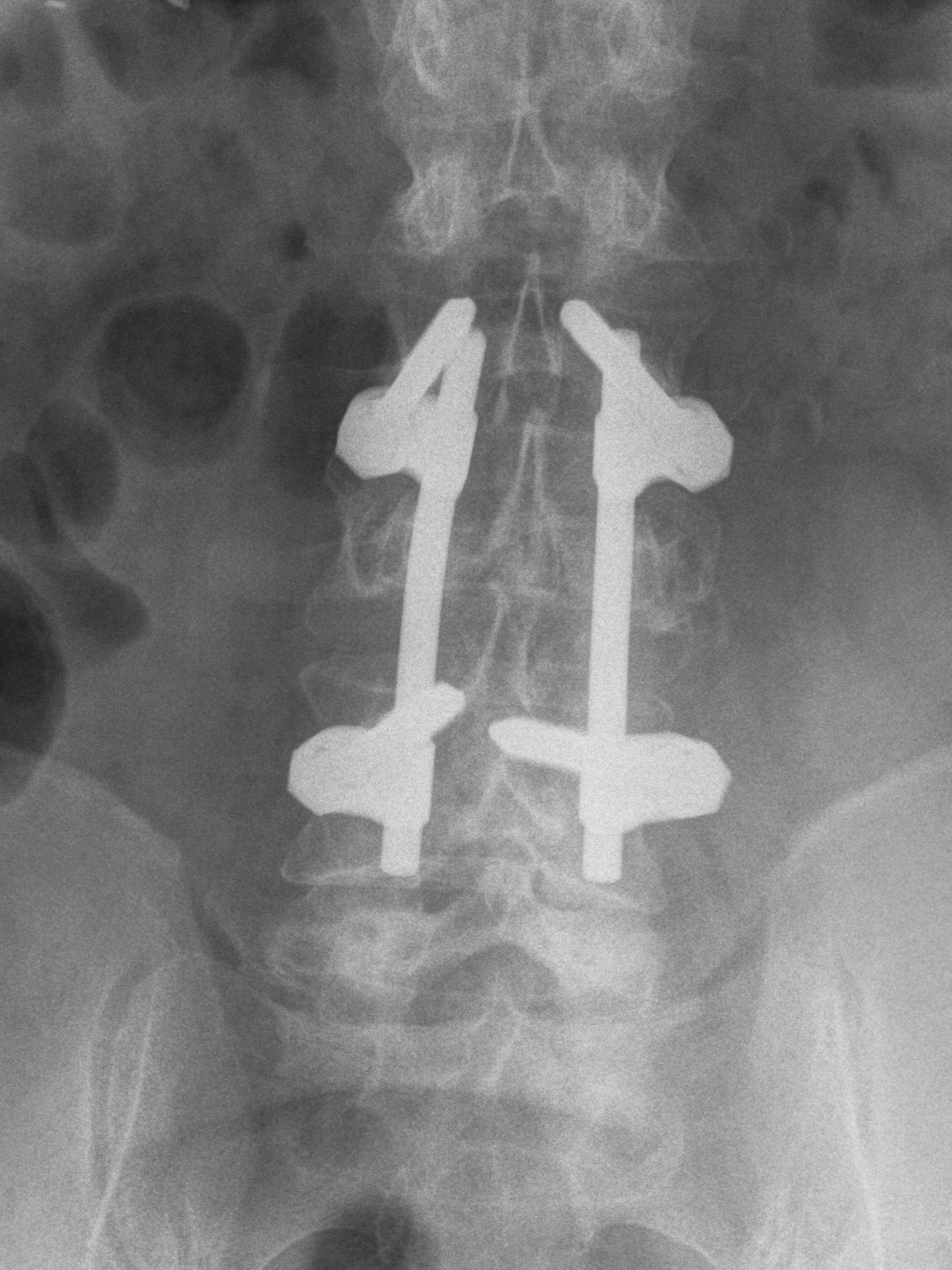
Operative Management
Options
Vertebroplasty
Kyphoplasty
Fusion
Vertebroplasty
Indications
Pain
- non responsive to non operative treatment
Technique
Percutaneous
- trochar into pedicle under fluoroscopy
- injection PMMA

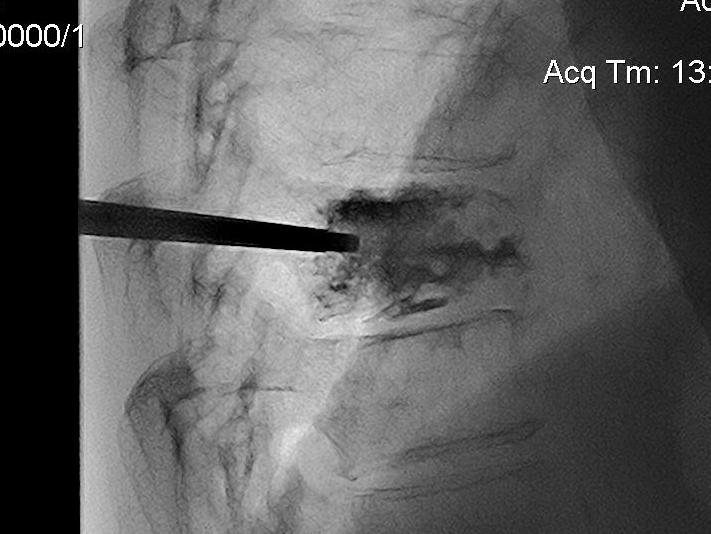
Results
Klazen et al Lancet 2010
- RCT of vertebroplasty v non operative treatment
- 431 patients over 50, all T5 or lower
- no complications
- immediate pain relief which was maintained at 1 year follow up
Kyphoplasty
Indication
- pain relief
- restoration of deformity
Technique
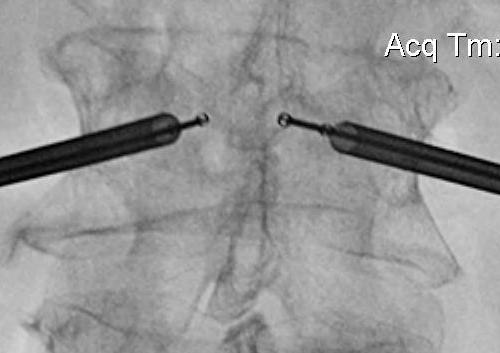


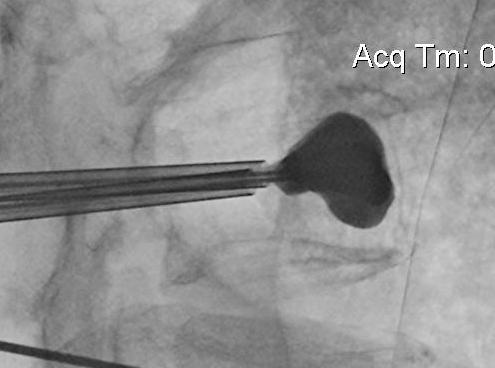
Insert a balloon first and inflate
- bilaterally into each pedicle
- will restore some anatomy
- then inject PMMA
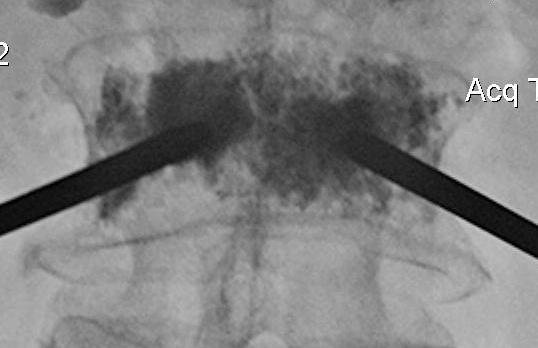

Results
Liu et al Osteoporosis Int 2010
- RCT of vertebroplasty v kyphoplasty
- improved vertebral height with increased injected PMMA in kyphoplasty
- no difference in outcome regards to pain relief
- 2/50 adjacent segment fractures in kyphoplasty group
- recommended vertebroplasty
Fusion